About IASI
The Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI) is probably the most advanced instrument carried on the MetOp satellite. Marking a significant technological step forward, it will provide meteorologists with data of unprecedented accuracy and resolution on atmospheric temperature and humidity with which to improve weather prediction. This European instrument is also destined to provide a wealth of data on various components of the atmosphere to further our understanding of atmospheric processes and the interactions between atmospheric chemistry, climate and pollution. In addition, the IASI will deliver data on land-surface emissivity and sea-surface temperature (in cloud free conditions).
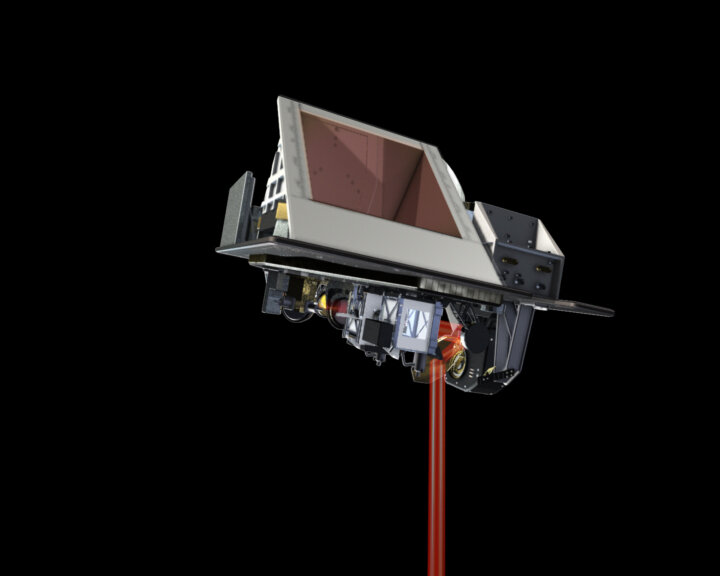

The sophisticated ISAI instrument is a Fourier Transform Spectrometer based on a Michelson Interferometer coupled to an integrated imaging system that observes and measures infrared radiation emitted from the Earth. The optical interferometry process offers fine spectral samplings of the atmosphere in the infrared band between wavelengths of 3.4 and 15.5 microns. This enables the instrument to establish temperature and water vapour profiles in the troposphere and the lower stratosphere, as well as measure quantities of ozone, carbon monoxide, methane and other compounds, all of which play major roles in atmospheric processes such as the greenhouse effect.

The IASI instrument will deliver profiles on temperature with an accuracy of 1° Kelvin and a vertical resolution of 1 kilometre and profiles of humidity with an accuracy of 10% and a vertical resolution of 1 kilometre. This degree of resolution also allows chemical components in small concentrations to be detected. With a swath width on the Earth's surface of about 2,000 kilometres, global coverage will be achieved in 12 hours. For optimum operation, the IASI measurement cycle is synchronised with that of the AMSU instruments.
The Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES) is leading the IASI development in association with EUMETSAT. ALCATEL is the instrument Prime Contractor. The IASI will fly on MetOp-A, -B and -C.
IASI measurements
The IASI system aims at observing and measuring the infrared spectrum emitted by the earth. These measurements are compatible in terms of sampling, resolution, accuracy and overall performances with the mission objectives of providing information on:
The profile of temperature in the troposphere and lower stratosphere with an accuracy of 1K, a vertical resolution of 1 km in the low troposphere and an horizontal sampling of 25 km.
The profiles of water vapour in the troposphere with an accuracy of 10% on relative humidity, a vertical resolution of 1 km in the lower troposphere and an horizontal sampling of 25 km.
The total amount of ozone with an accuracy of 5% and an horizontal sampling of typically 25 km, possibly also ozone vertical distribution with an accuracy of 10% and a vertical resolution providing two or three pieces of independent information.
Fractional cloud cover and cloud top temperature/pressure.
- Sea and land surface temperatures.
In addition, IASI has the ability to measure the total column content of the main greenhouse gas. It will supply valuable data for scientific studies to achieve a closer understanding of climate processes and to represent them better in global models.
| Geophysical variables | Vertical resolution | Horizontal resolution | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature profile |
1 Km (low Troposphere) |
25 Km (cloud free) |
1K (cloud free) |
| Humidity profile |
1-2 Km (low Troposphere) |
25 Km (cloud free) |
10% (cloud free) |
| Ozone total amount | Integrated content |
25 Km (cloud free) |
5% (cloud free) |
| CO, CH4, N2O | Integrated content | 100 Km |
10% (cloud free) |
IASI fields of View
Interferometer
The IASI interferometer field of view is square, seen under an angle of 3.33 x 3.33°. Information matrix of 2 x 2 circular pixels seen under an angle of 1.25°. The overall swath is ± 48.3° with respect to the nadir direction, corresponding to 30 mirror positions.
Imager
The IASI imager field of view is based on an array matrix, analysing a square field that is slightly larger than the interferometer one.