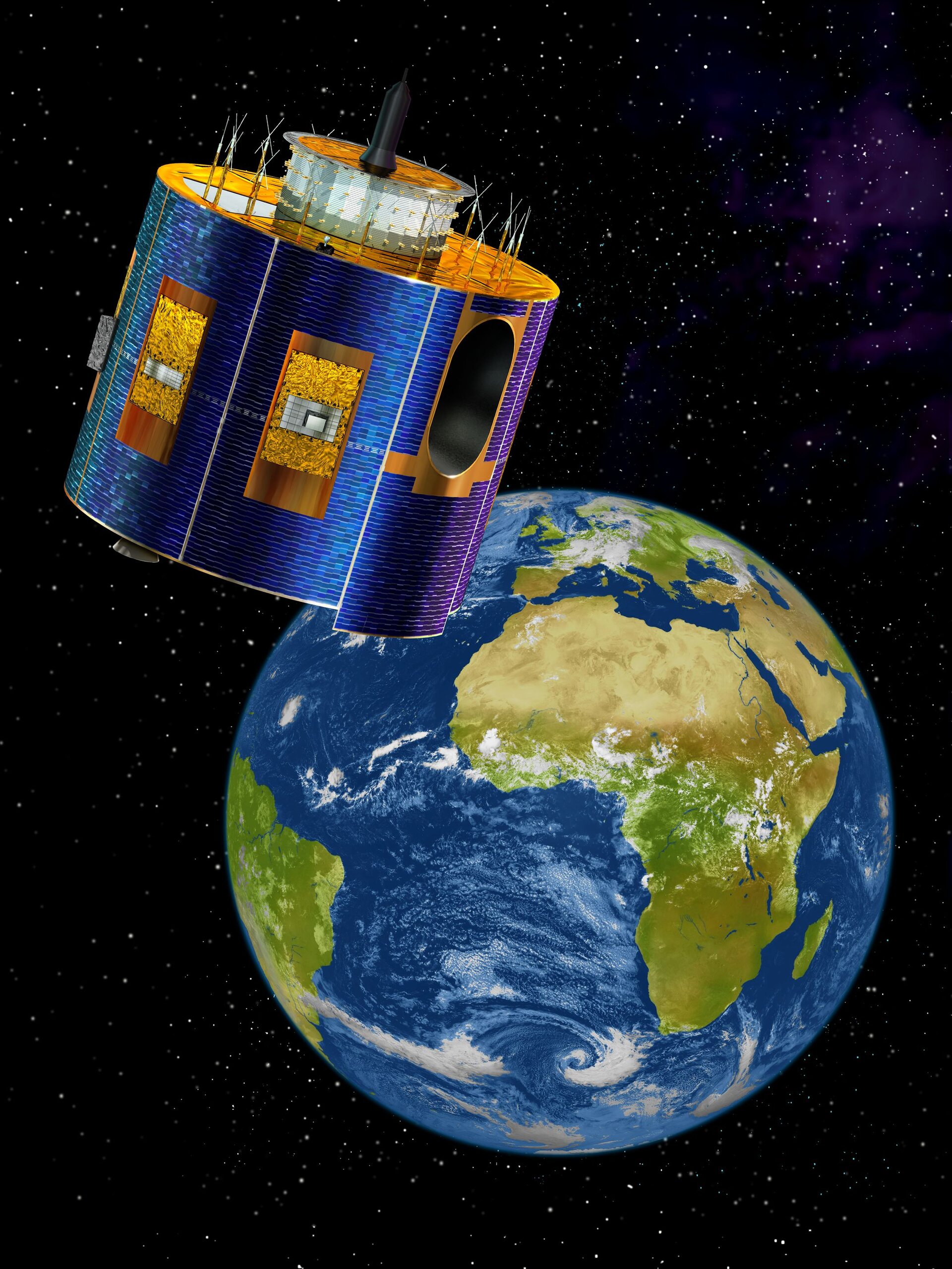
MSG-2 commissioning begins
Control of the second Meteosat Second Generation (MSG-2) satellite has been passed from ESA's European Space Operations Centre to the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) so that commissioning operations can begin.
ESOC, located in Darmstadt, Germany, was responsible for the Lower Earth Operations Phase (LEOP) after the launch of the satellite on 21 December. The satellite arrived safely on station at 6.5° West longitude in geostationary orbit at 36,000 km above the Earth.
Working from its Control Centre, also in Darmstadt, on Tuesday EUMETSAT will activate the onboard instruments, SEVIRI and GERB, and will verifiy that all electronic components are performing well. The first MSG-2 signal was already received by the EUMETSAT commissioning team on 28 December 2005 from the MSG ground station in Usingen.

During the commissioning period, which will last until Summer 2006, the satellite and ground systems will be carefully tested and tuned to prepare it for routine operations.
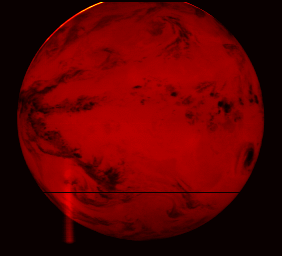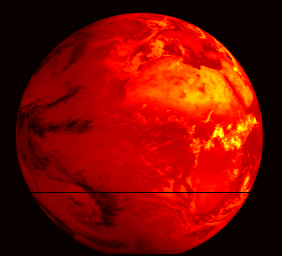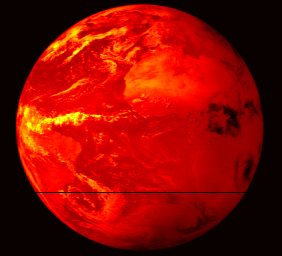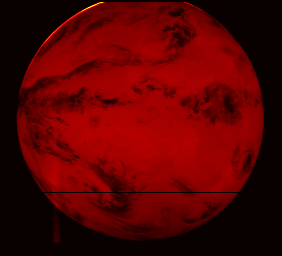
The first image from MSG-2 is foreseen for end of January 2006 and dissemination of imagery to the meteorological user communities for evaluation purposes is expected for spring.
About MSG
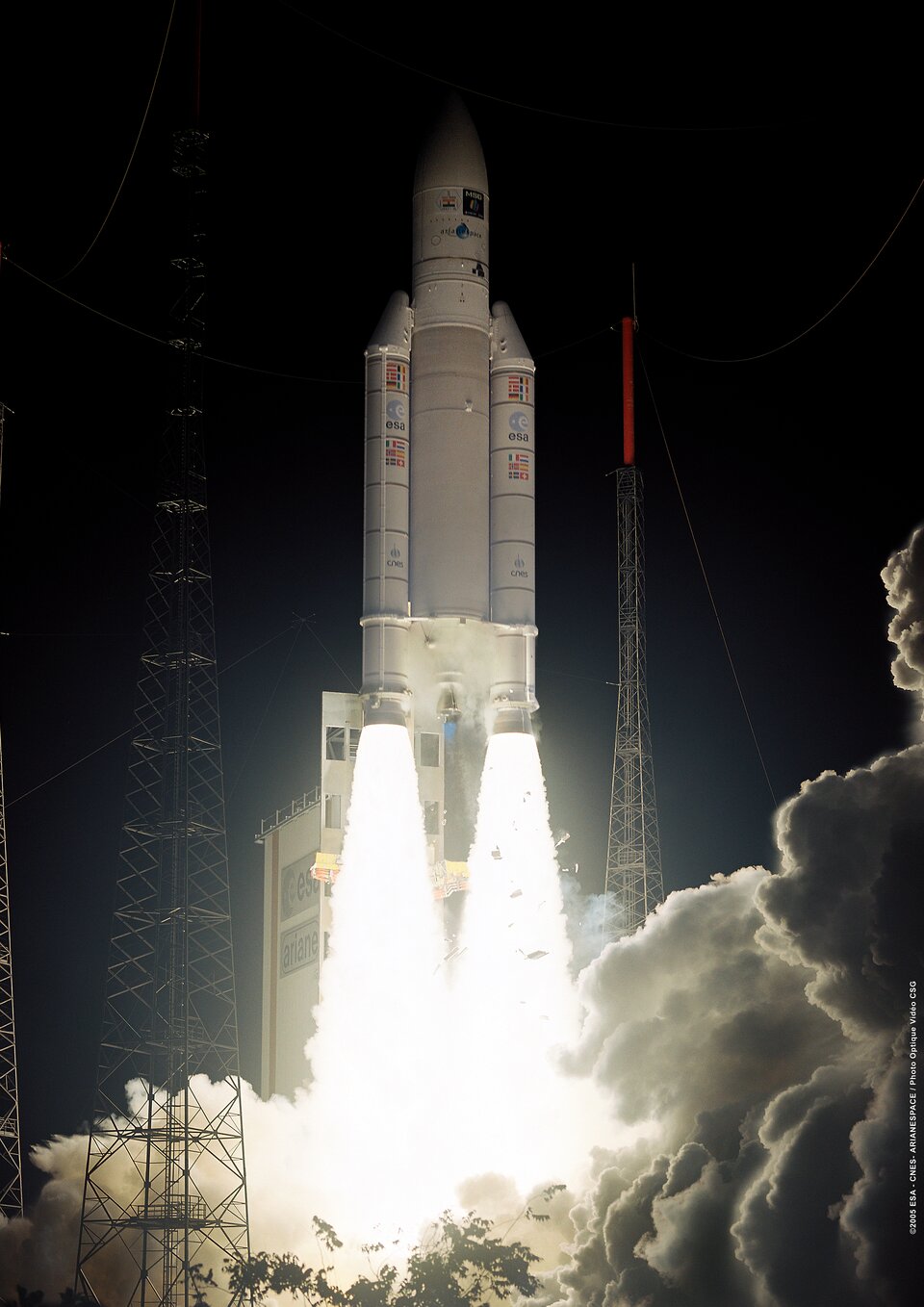

Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) is a joint project between ESA and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) and follows up the success of the first generation Meteosat weather satellite series with a larger design boasting higher performance. The first in a planned series of MSG satellites was launched in 2002, entering into service with EUMETSAT in early 2004 and now renamed Meteosat-8. MSG-2 was launched in turn on 21 December 2005, in order to guarantee continuity of service well into the future.
The MSG satellites provide improved information and imagery for weather forecasting as well as other applications such as hydrology, agriculture and environmental studies. The data collected are routinely used for the study of weather and climate change and have proven to be vital in the context of severe weather situations where they help to reduce losses of human life and property.