Time Synchronization and Positioning in indoor GNSS receivers
| 716 - Abstract: |
| Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals are broadly used for time synchronization purposes, for instance for applications in the telecommunication, finance and energy sectors. To avoid coverage problems, the GNSS signals are mainly used for outdoor applications. Due to limited availability and degraded performance, the usage of GNSS signals in indoor conditions is challenging. Nevertheless, indoor time synchronization and positioning are expected to be important, i.e. for 5G telecommunication networks. The present invention has been developed to overcome the challenges previously mentioned. ESA is looking for partners who would be interested in licensing and implementing this patent. |
Description:
The European Space Agency proposes a method to estimate the joint composite channel and to synchronize time in indoor propagation conditions based on satellite navigation signals.
The method provided considers as baseline a static receiver in a known position featuring an array of N antennas (with N ≥ 1), and targets the fine time synchronization in deep fading and strong multipath conditions typical of indoor scenarios. For this purpose, the received navigation signals are exploited in order to:
a) achieve time synchronization even when only non-line-of-sight (NLOS) multipath signal components are received by the receiver, and
b) mitigate the degradation introduced by the NLOS indoor channel by estimating a composite channel vector via monte-carlo methods.
The method has been assessed via software simulations considering a realistic indoor propagation channel, showing a clear improvement of the resulting time synchronization performance with respect to a conventional time estimation approach.
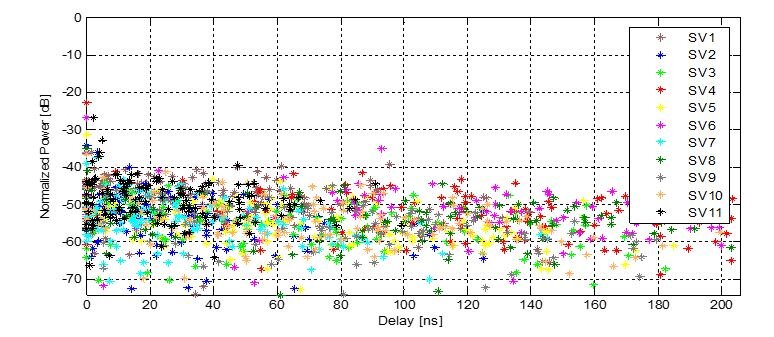
With the present invention, satellite navigation signals can be exploited for achieving timing accuracies below 100 ns in indoor conditions. Figure 1 shows some results of the simulations. An analysis of the results reveals that the proposed method has improved characteristics compared to the state-of-the-art.
Innovations and advantages:
The invention proposed by the European Space Agency:
- Allows a robust and accurate time synchronization in indoor conditions, while being independent of wired setups.
- Enables the direct usage of GNSS signals in indoor conditions, which is of particular interest for a diverse set of applications.
- Is of interest for manufacturers and service providers exploiting timing and positioning in challenging propagation conditions.
Domain of application:
This improvement can be beneficial for domains of applications in space and non-space areas:
- Ground GNSS-based timing applications (i.e. application at user level)
- Telecommunication applications (e.g. indoor 5G small cells)
- Finance sector (i.e. mobile applications as personal banking)
- Energy sector
The technology is among others of interest for GNSS receiver manufacturers, indoor small cells manufacturers and telecommunication service providers.