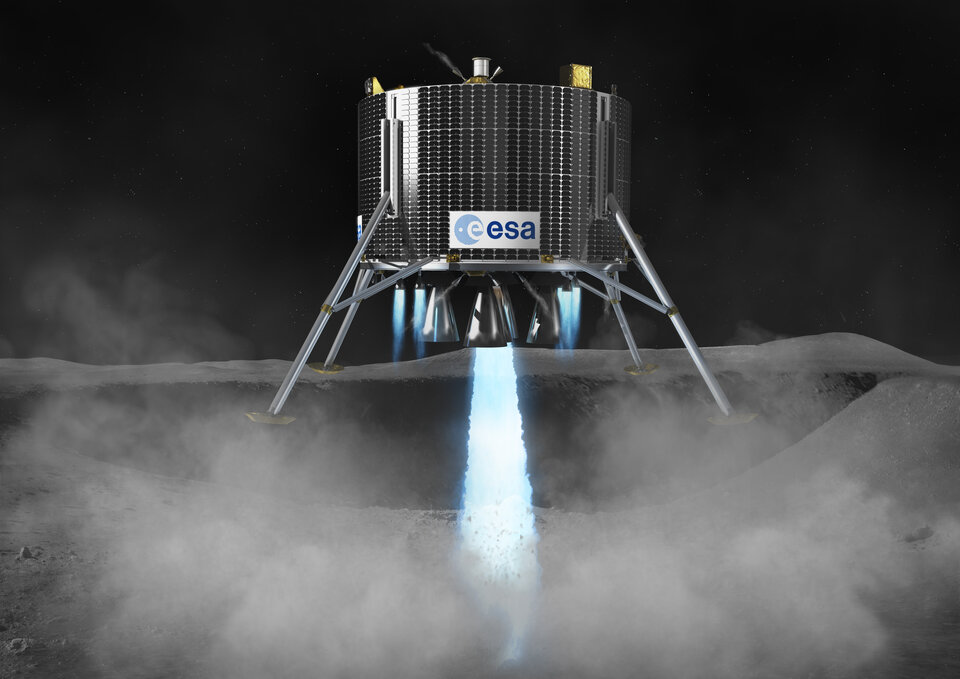
Lunar Lander flight phases
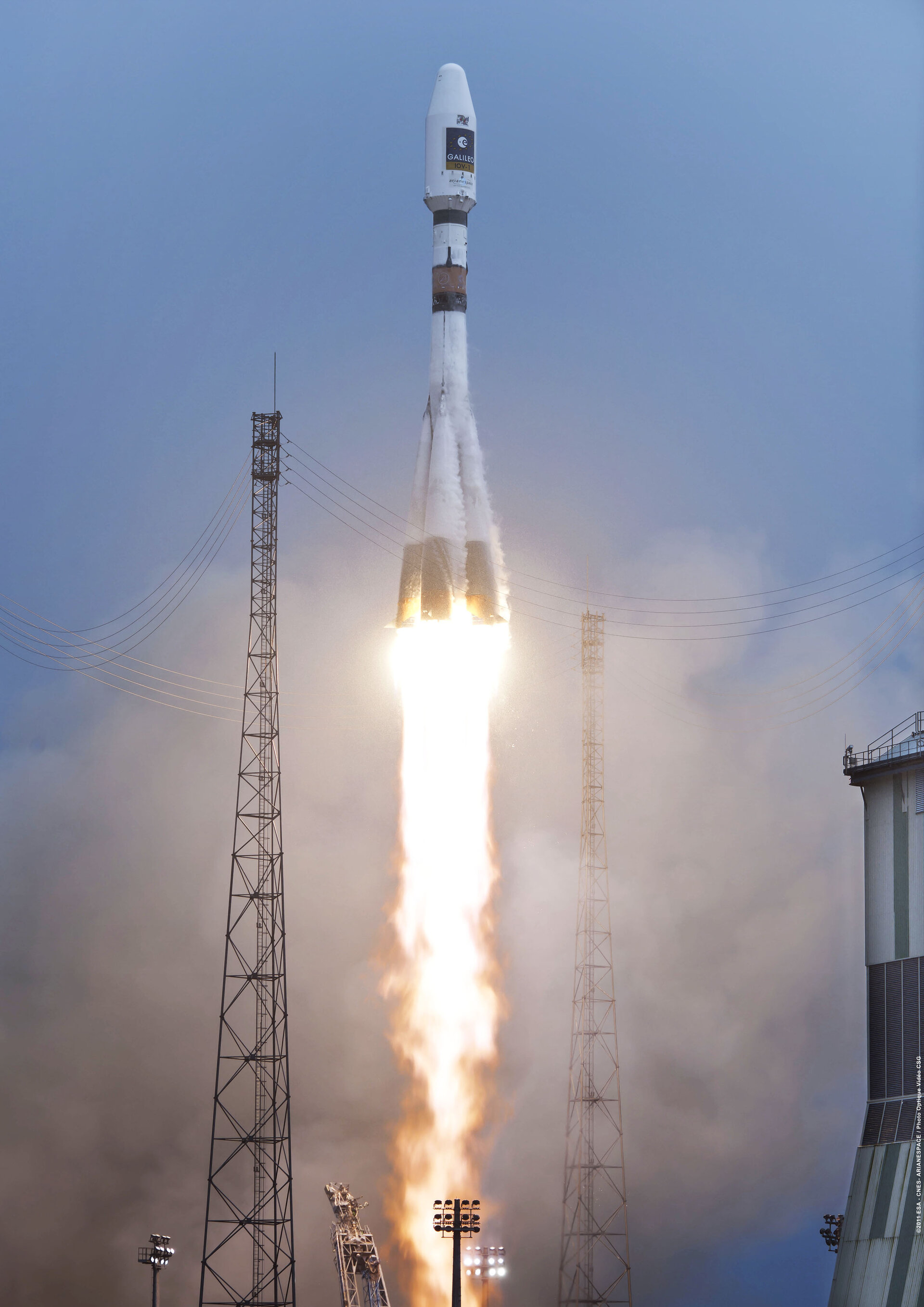
Lunar Lander will be launched in 2018 from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana on a Soyuz rocket. The launcher’s Fregat upper stage will inject it into a highly elliptical orbit before the Lander uses its own propulsion system to reach the Moon.
After insertion into a polar orbit, the Lander establishes a circular orbit 100 km up and waits for the correct phasing with respect to the Sun, Earth and Moon for the descent. In this low orbit, ground tracking accurately determines the craft’s position and velocity.
Once given the ‘go’ command, Lunar Lander begins the descent sequence and uses its sensors, image processing, guidance, navigation and control software to land.
Firing its engines once over the North Pole, the vehicle coasts for half an orbit towards the opposite polar region. During this phase, the lander matches landmarks from its realtime camera images with landmarks in its memory to estimate its position.
Closing in on the polar region, it begins its main braking phase by firing its main engines at maximum thrust. During this period, it calculates velocity by tracking images features.
Approaching its destination, the Lander adjusts the thrust level, progressively shutting down the main engines and fine-tuning by pulsing its smaller engines.
Once the landing site comes into view, it scans the surface with a laser for hazards such as slopes, boulders, craters and shadows. If the site seems too dangerous, it can decide to target a safer zone.

The final descent demands a high degree of autonomy – critical decisions need to be taken immediately, including selecting a safe target, while continuously monitoring the vehicle’s status and available resources.
Status information is transmitted directly to Earth during the most critical phases. There is no time for any ground intervention, placing severe requirements on Lunar Lander’s intelligence and autonomy.
During the last few seconds, the craft descends vertically and comes to rest on its four legs. The moment of touchdown is the end of Lunar Lander’s journey to the Moon but only the beginning of its exploration of the South Pole region.





