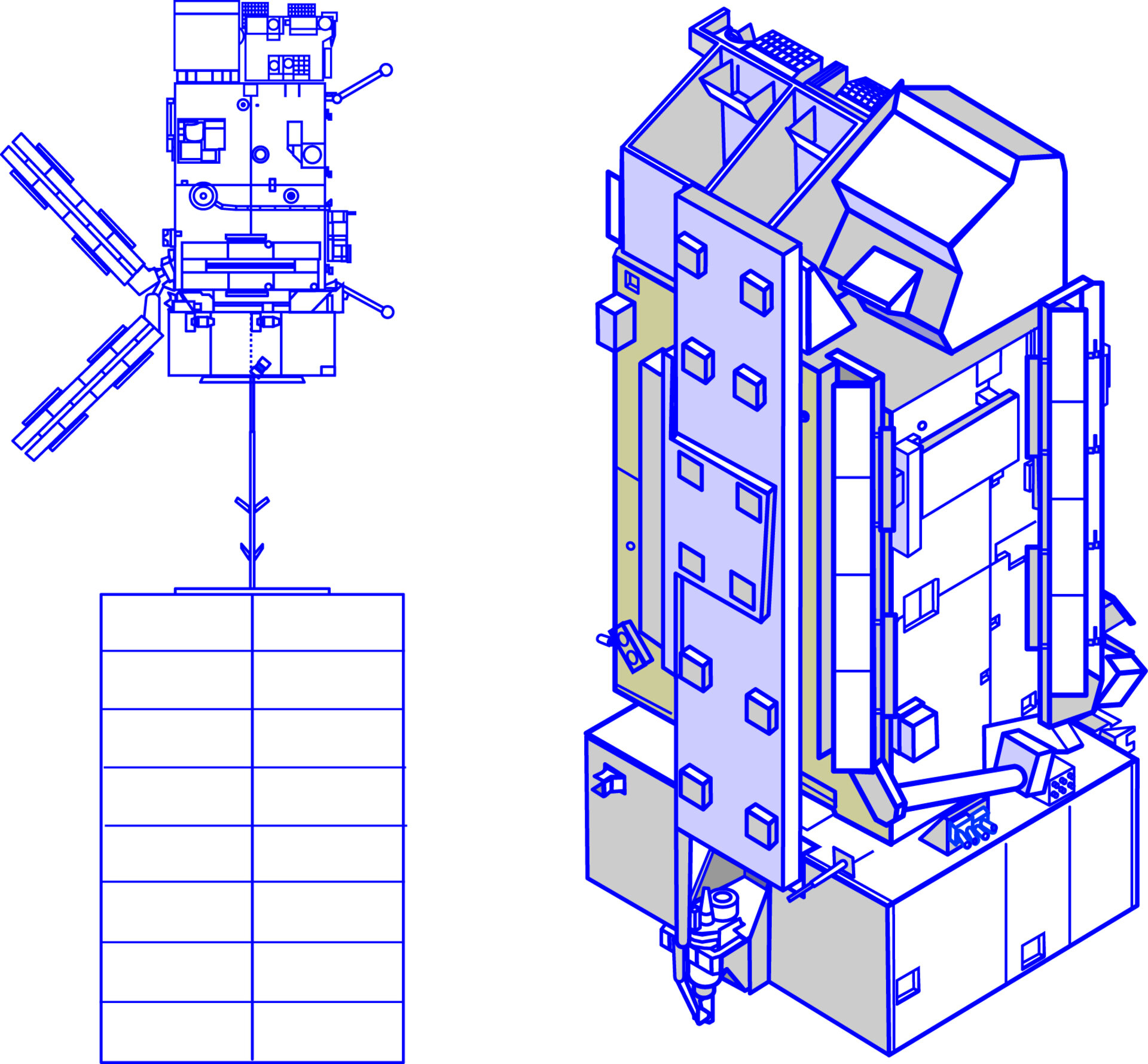
Service Module electrical power
Power generation, storage, distribution and control
Electrical power is generated by an eight-panel solar array.
Five batteries store energy, allowing power supply during:
- Launch and Early Orbit Phase (LEOP)
- eclipse and contingency mode
- temporary power peak demand above the solar array capability during sunlight
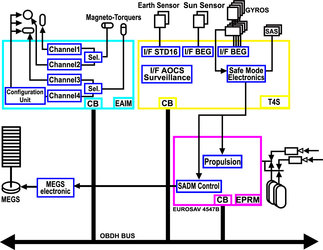
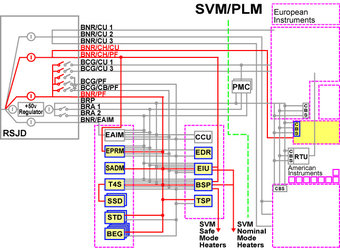
The primary power bus is unregulated and distributes power to the Service Module (SVM) and Payload Module (PLM) units.
The 28 V power regulation needed by the American instruments is provided by a dedicated Power Control Unit (PCU) located in the PLM.
Power is controlled by a dedicated unit (RSJD) that is in charge of the:
- balance among the power provided by the solar array
- spacecraft power demand and the batteries recharge
- distribution of several power buses
- managing the batteries' thermal control
- provides switch-off lines for the satellite management in case of failure conditions
Solar array
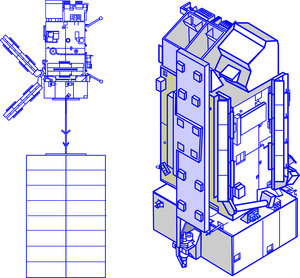
The solar array is derived from the Environment Satellite (ENVISAT). It has a single wing, flat pack design solar array. It consists of eight hinged rigid solar cell panels (each 1 m x 5 m), equipped with BSR type solar cells. The solar array cant angle is 20° and the generated power capability is 3828 W end of life.
Deployment
The satellite commands and monitors solar array deployment keeping track of:
- deployment progress
- position indicators
- temperature of the deployment motors and panels
The array electrical power is transferred through a cable harness along the primary deployment arm up to the Solar Array Drive Mechanism (SADM), mounted on the spacecraft side of the interface. The SADM rotates to hold the solar array correctly orientated towards the Sun.