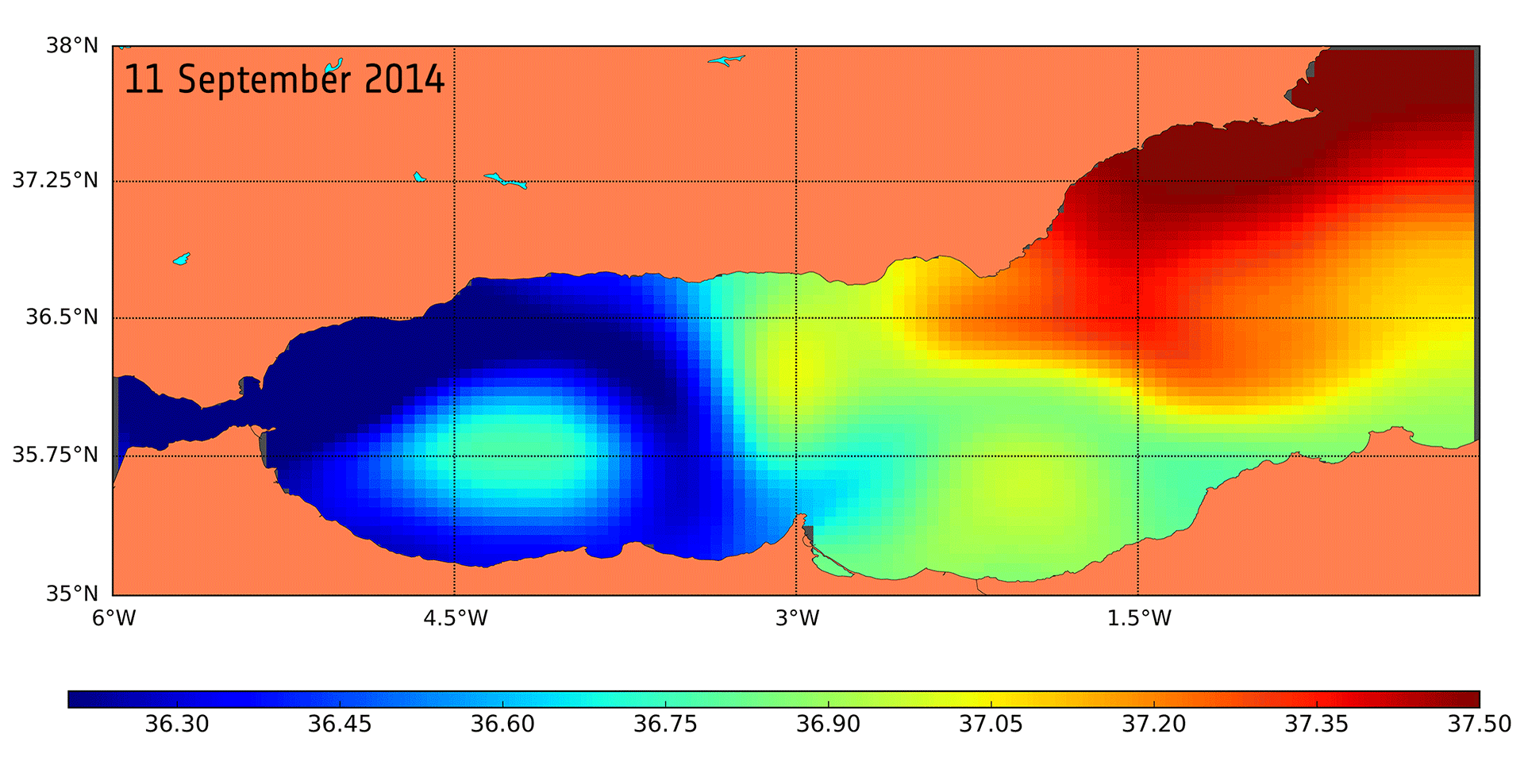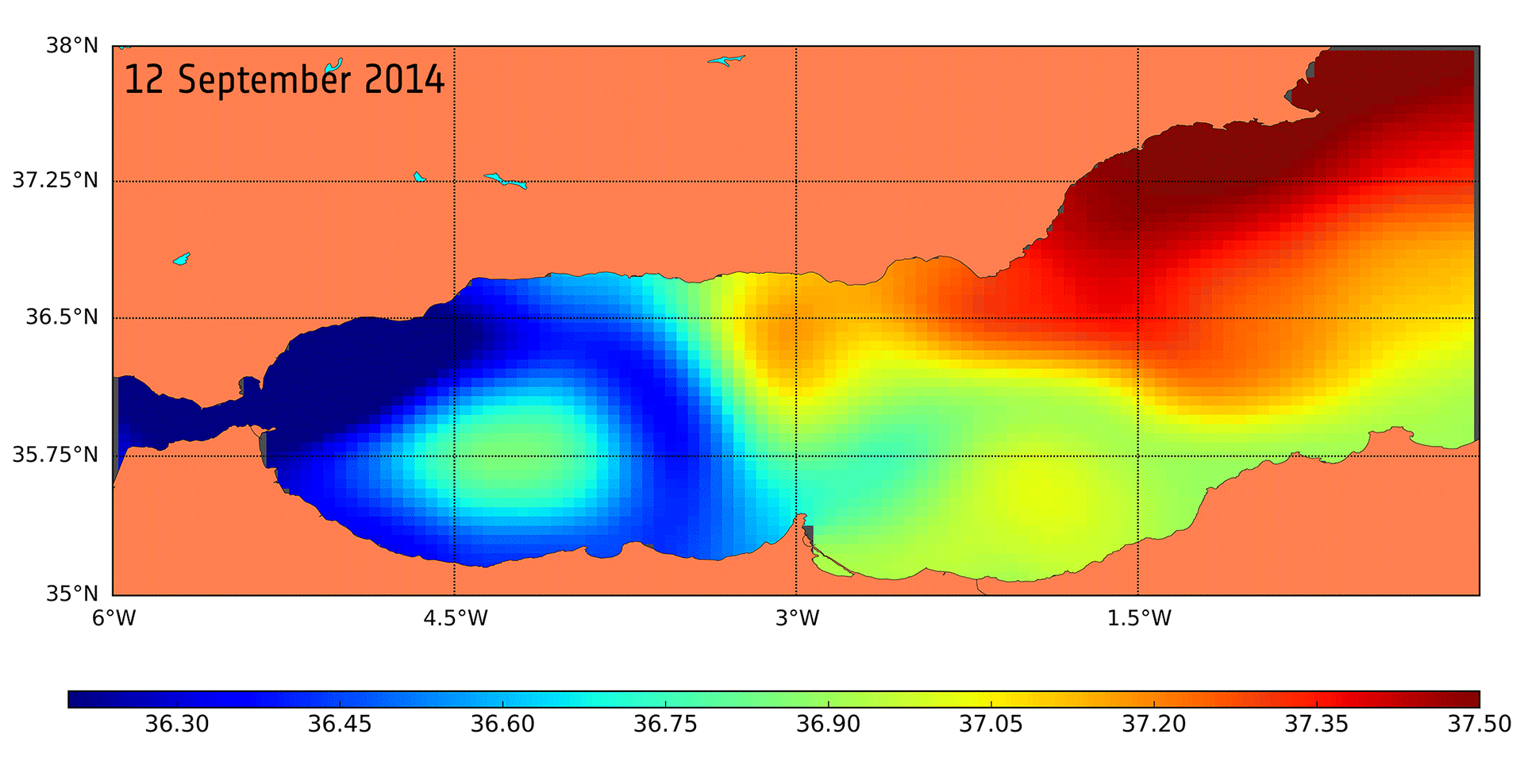
Water cycle wrapped
As our climate changes, the availability of freshwater is a growing issue for many people around the world. Understanding the water cycle and how the climate and human usage is causing shifts in natural cycling processes is vital to safeguarding supplies. While numerous satellites measure individual components of the water cycle, it has never been described as a whole over a particular region – until now.
Cycling through the oceans, land, ice and the atmosphere, the principles of the way water moves around our planet have remained the same for billions of years.
Climate change and our ever-increasing demand for freshwater is affecting the natural balance of this cycle. However, to understand exactly what is going on, scientists need to study the cycle as a whole.
This is extremely difficult because different satellites offer different types of data, which need to be merged in a coherent way to realise a true picture.
The subject of a recent paper and discussed as a significant scientific result at this week’s Living Planet Symposium in Italy, scientists have been able to do this for the Mediterranean region.
This is a complex region, and one that is particularly susceptible to climate change.
Most of the freshwater that enters the Mediterranean Sea comes from precipitation and from rivers to the north. The sea evaporates more water than it receives from precipitation and river discharge. However, in terms of quantity, this is balanced by the water it gets from the Atlantic Ocean flowing in through the Strait of Gibraltar.
The Mediterranean region only has 3% of the world's freshwater resources, while it is home to over 7% of the world’s population. Nearly 60% of the world's water-poor people – those that survive on less than an average of 1000 cubic metres per person per year – live in southern Mediterranean countries and in the Middle East alone.
Filipe Aires, from Estellus in France, said, “Water in the Mediterranean is under pressure, so better understanding how the water cycle works could help manage this precious resource.
“However, it is a complicated region with respect to its climate, weather and varying landscapes, all of which affect the way water is cycled.
“Thanks to a project funded by ESA that allowed us to merge satellite data from various partner space agencies, we have now been able to characterise the full water cycle over the Mediterranean.”
The US–German GRACE mission, for example, measured how gravity changes over time and allowed scientists to effectively weigh water and, therefore, estimate how much is held in different parts of the water cycle every month.
Dr Aires and team were able to use a multitude of satellite data along with a water conservation rule for the terrestrial–ocean–atmosphere parts of the cycle, as visualised in the animation above.
Victor Pellet, from the Laboratory for Studies of Radiation and Matter in Astrophysics and Atmospheres, added, “Our methodology has improved estimates of the Mediterranean water components. Through this new technique, we can also offer an alternative means to estimate the net flows across the Bosporus and Strait of Gibraltar, which are very difficult quantities to measure.”
“The output of this study will be used to calibrate models that are used to forecast climate change. This new technique now paves the way for other regions to be studied in the same way, and will hopefully be extended to cover the full globe in the future.”
ESA’s Diego Fernandez Prieto, noted, “The water cycle is one of the most fundamental systems on our planet. A better understanding of the intricacies of this delicate system is not only a step forward for the scientific community, but also one that will, in turn, benefit society at large.
“Water is clearly one of our most precious resources and under increasing pressure. Having a better understanding of the cycle and how it is being affected by change will certainly help those managing essential supplies of freshwater.”
We are changing our natural world faster than at any other time in history. Understanding the intricacies of how Earth works as a system and the impact that human activity is having on natural processes are huge environmental challenges. Satellites are vital for taking the pulse of our planet, delivering the information we need to understand and monitor our precious world, and for making decisions to safeguard our future. Earth observation data is also key to a myriad of practical applications to improve everyday life and to boost economies. This week we focus on the world’s biggest conference on Earth observation where thousands of scientists and data users discuss the latest results and look to the future of Earth observation.