Concurrent Engineering methodologies applied to Anomaly Treatment
Concurrent Engineering (CE) has widely proven its efficiency and advantages, especially for the preliminary phases of a project, by maximising the number of activities running in parallel. This minimises the associated costs while improving the quality of the results. A study was carried out as part of the ESA General Studies Program (GSP) to investigate whether CE methodologies could be applied to improve the treatment of anomalies during a project life-cycle.
Anomalies may occur at any stage of a project and they cause impacts on time and cost. The term Anomaly Treatment (AT) refers to the process that starts after the detection of an anomaly.
An industrial consortium lead by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, along with EADS Astrium Satellites in Friedrichshafen and Università del Piemonte Orientale (UNIPMN) as subcontractors and supported by the Computer Science Department of Universita degli Studi di Torino and by the Aeronautics and Space Engineering Department of Politecnico di Torino, carried out the study whose objectives were as follows:
The basis of the study was that the application of CE technologies on an anomaly may be particularly useful especially when a large number of disciplines are involved.
The study started with the collection of data on the state of the art in the application of CE to AT with the use of a questionnaire sent to 55 companies worldwide. Responses to the questionnaire were integrated with information found in publications. Recommendations and requirements for a prototype tool (CAT – Collaborative Anomaly Tool) were derived.
The tool is intended to act as a centralised resource manager and to allow the integration of different tools. It allows multiple actors to connect simultaneously, to share resources, to request further analysis, to inspect results from those analyses, to provide feedback on the analysis and to better cooperate towards the common goal of solving the anomaly. The CAT based process is shown in the figure.
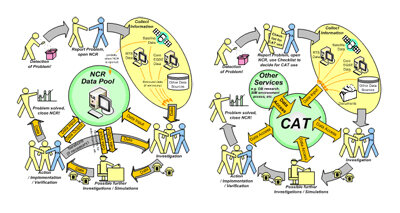
The study ended with a practical demonstration of the CAT prototype through test cases chosen from real anomalies on the GOCE satellite involving 3 locations in different countries and 2 Primes. The test cases demonstrated a large time saving for the retrieval of information related to previous investigations on similar anomalies (e.g. link to the MATED database), project data and anomaly analysis request and result.
The study showed that there is the potential for CE methodologies to be of benefit in the investigation and treatment of anomalies and made several recommendations to be studied in the future.


