CDF Studies Implications of Advanced Manufacturing
Wikipedia defines Advanced Manufacturing (AM) as the use of innovative technology to improve products or processes.
ESA have already carried out a number of studies under the General Studies Program looking specifically at the “System Impact of Additive Manufacturing Technology Design Features.” The main findings of these studies was that design for AM requires a holistic functional view of the system and potential savings (mass, lead-time, cost) and performance increase were highlighted.
It was identified that, to take full advantage of the advanced manufacturing opportunities, a new design methodology needs to be developed, with an emphasis on a multidisciplinary approach to promote combinations of elements from different functional domains.
The CDF Space Hardware Advanced Manufacturing Engineering (SHAME) study and consecutive industrial activity were proposed and approved in the frame of GSP CFI 2015, with the CDF study being carried out between April and May 2016.
The goal of the study was to formalise a new design approach for the engineering of units (or assemblies) to be built with advanced manufacturing technologies.
The study had the following objectives:
- Assess the re-definition of interface requirements potentially amended by the multi-functionality enabled by AM technologies
- Trade-off new materials and related processes
- Address Product Assurance issues
- Perform Life Cycle Analysis
- Investigate and propose verification strategies
- Identify technologies, models and tools, potentially requiring development
- Perform a programmatic analysis (cost, risk and schedule) and highlight advantages and disadvantages derived by the usage of AM.

To allow some quantitative analysis to be carried out, the study used two existing design cases as models and then developed options based on these examples. This allowed various scenarios to be analysed to determine under which circumstances AM proved beneficial.
Advanced Manufacturing brings innovative materials and processes to the table, which become additional design parameters populating the systems design trade-spaces. Suddenly multifunctional solutions, previously inconceivable, are enabled by the new manufacturing techniques, with a re-definition of interfaces and related requirements, shifted from “discipline” boundaries to “units” or “assembly” boundaries.
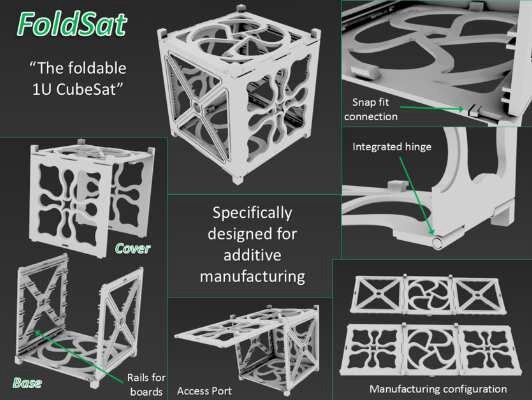
This redefinition of boundaries was one of the major discussion points during the study and the CDF has helped identify many of the processes and interfaces that need to be addressed. One clear example is that the early involvement of Material & Process Engineers in the design proved to be an essential ingredient of the “Design for AM” recipe.
The design freedom brought by AM calls for unconventional design solutions, creativity becomes a need, and infusion from non-space is invaluable. Biomimicry and architecture principles enriched the concurrent design environment, which proved to be particularly well suited with the needs and objectives of the new design methodology.
The study conclusions were clear in that there is a potential role for AM in space engineering. In addition, the study proposed recommendations for injecting AM into the project life cycle, from early design up to the procurement phases and ultimately to the assembly, integration and verification phases, indicating required modelling tools, technologies and redefined engineering roles and expertises.
There is a lot of reasonable skepticism about the adoption of AM solutions in space, but results of studies and activities conducted so far indicates advantages and potentials. It therefore seems to be advantageous to convert the skepticism into a cautious commitment to investigate what is feasible and reasonable.


