Contactless Electromagnetic Device for Even Distribution of Nanoparticles in Alloy Matrices
| 630 - Abstract: |
| Space applications often require lightweight structural parts with high strength and stiffness. Up to now, nano-composites with these features are produced using ultrasound probes, for instance. The prior art involves a contact between the probe and the composites, which can lead to contamination. In the following, a technique will be introduced that refrains from any contact of the production device and the product. Licence agreements are sought. |
Description:
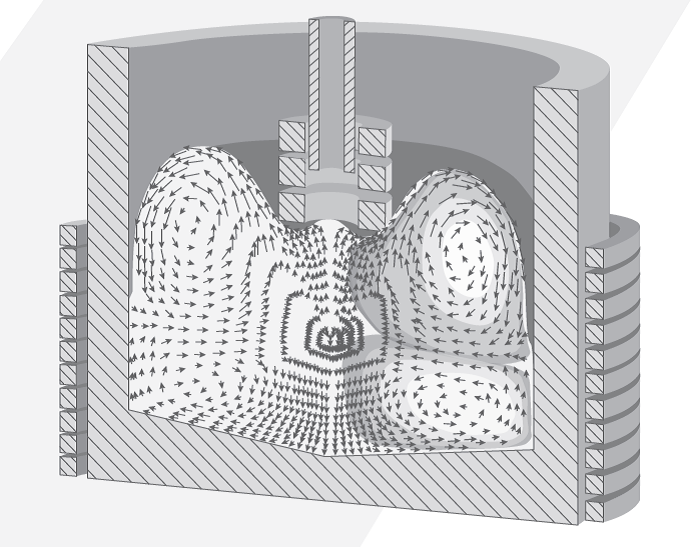
The invention comprises a system for the production of metal components and metal matrix nano composites. The process makes use of a contactless electromagnetic device. Basing on an adjustable electromagnetic coil, the system is an efficient alternative in comparison to normally used ultrasound probes. The problem of prior art associated with the probe and metal contact is solved by the invention using this coil.
The method allows for nanoparticle dispersion in liquid molten metal. The even distribution of added nanoparticles in an alloy matrix is especially important for the manufacturing of large components.
Innovations and advantages:
- Contactless approach reduces the risk of contamination, extends the probe time utility and achieves higher temperatures.
- Stronger stirring of nanoparticles which extends capacity and reduces timing.
- Expels large size impurities on to the surface of the melt through the induced current.
- Influences the microstructure formation during additive manufacturing for scaling down the technology.
Domain of application:
The main applications of this technology relate to its capacity to manufacture alloys/composites with specific electromagnetic or mechanical characteristics such as electromagnets, superconductors, shape memory components etc. These types of materials are of particular interest for:
- aeronautic and automotive (engines, turbines, structural parts)
- thermo-electric power plants (electricity transportation, thermal isolation)
- biomedicine (prosthesis)