ESA BIC SPiN: Revolutionizing satellite manufacturing by plug and play concepts
ESA Business Incubation Centre Bavaria start-up company SPiN proposes a plug and play solution to standardise and simplify satellite production. Their universal adapter allows to assemble satellites like Lego. Meet SPIN at ESA's Start-ups Zone powered by ESA space solutions at IAC 2018.
Long lead times and high costs are barriers for new projects and innovation. Thales Alenia Space CEO, Jean-LoIc Galle described this pain by saying at the World Satellite Business Week last year, "The (satellites) lead times used to be 36 months. Now customers are asking between 12 and 18 months of lead time of production. We all know it is extremely difficult to build a satellite in 12 months.”
According to Galle, meeting such requirements is only possible by using standardized buses and payloads that could be just taken off the shelf.
SPiN's solution is the plug and play universal adapter MAGIC (Multipurpose Adapter Genetic Interface Connector) that allows to assemble satellites like if they were a Lego construction. The company are introducing adapters to decentralize the satellite to common building blocks.
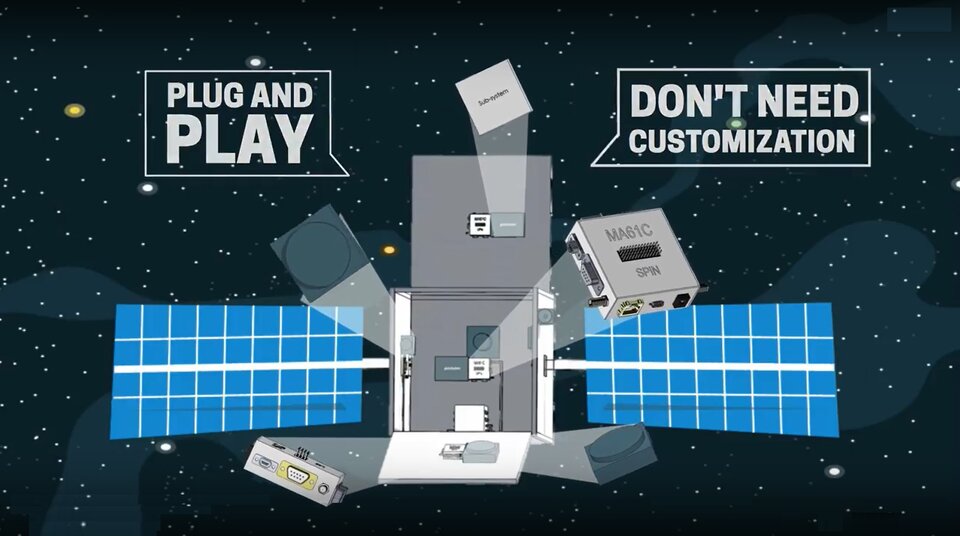
MA61C connects any satellite’s electronics without user intervention or hardware customization. It is a universal adapter that sits next to the subsystem and automatically connects it to the satellite on-board computer, without user intervention. Its driver recognizes and integrates subsystems software.
This technology allows using off the shelf hardware components for space missions. Units such as star tracker, power distribution and transceiver can be reused from previous mission without the need to customize their interface or software.
SPiN`s MAGIC Multipurpose Generic Interface Connector

EGSE plug and play tool
Easy and quick connectivity tool to any digital subsystem through commonly used space interfaces. It connects to a laptop via USB connection to monitor and command through a friendly graphic user interface.
Intelligent data node
Plug and play remote data node that connects between the satellite onboard computer and subsystem through existing interface. The data nodes allow fast and smart integration, including diagnostic and monitoring functions.
Wireless router
Connects the spacecraft onboard computer to different subsystems through wireless communication. The adapter is equipped with smart sensors for local monitoring.

"Our MA61C adapter addresses the needs to reuse hardware design from previous projects and plug and play integration, removing costs by up to 60% without changing the supply chain," said Ran Qedar, SPiN co-founder and CEO.
"And it is immediately implementable."
Their innovation focus on spinning in technology from other industries into space to make it more affordable. SPiN`s goal is to reduce satellite manufacturing time and costs, simplify the design process and introduce smart technologies into the integration process.
ESA BIC Bavaria boosts the SPiN start-up

SPiN was founded by Ran Qedar, now CEO, Giulia Federico, now COO, and Saish Sridharan, now CTO. Together theu have over 15 years of experience from work in the space industry.
Following the demonstration of their concept in 2016, with the following official presentation at a dedicated event with satellite manufacturers and the University of Bremen ZARM, the thre entrepreneurs were accepted at ESA Business Incubation Centre Bavaria to turn their idea into a viable business.
In 2018, at the Toulouse Space Show SPiN demonstrated the first prototype of their universal adapter MAGIC (Multipurpose Adapter Genetic Interface Connector), version MA61C. The prototype was connected with a camera subsystem that was automatically identifies and commanded through MAGIC’s Graphical User Interface.

World's largest ecosystem for space-related entrepreneurship
ESA’s Technology Transfer and Business Incubation Programme Office (TTPO) operates the ‘ESA space solutions’ network of Business Incubation Centres (ESA BICs) and Technology Transfer Brokers offering complete access to all aspects of space-related innovation, technology and intellectual properties and is a gateway to ESA and European space research and developments.
Today, there are 20 ESA BICs in 17 European countries – Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, the Netherlands and UK – forming the largest ecosystem in the world for space-related entrepreneurship.
Over 650 start-ups have been fostered and another 150 new start-ups are taken in yearly at ESA BICs to be supported under the two-years business development boosting programme.
Visit “Start-ups Zone powered by ESA space solutions”
Meet all the start-ups from 1 October until 5 October at the dedicated Start-ups Zone powered by ESA space solutions at IAC 2018 area at IAC 2018.
The SPiN entrepreneurs will be at the Start-ups Zone at IAC 2018 from 3 October noon until 5 October, and be pitching their business 4 October.



