Europe to support Artemis CubeSats in return to Moon
In brief
Half a century since Apollo, the Artemis I mission is set to launch on 16 November with a test flight that prepares humankind for our next adventure at the Moon, and Europe is playing a crucial role.
Joining NASA’s Orion spacecraft on the powerful Space Launch System rocket are ten CubeSats that will help prepare for the return of astronauts to our lunar companion. ESA’s deep space antennas, along with the Goonhilly Earth Station in the UK, will be tracking six of the small satellites, ensuring they arrive where they need to be, and their data gets back home.
In-depth


Access the video
Each about the size of a large shoe box, their mission objectives vary as much as their final destinations – the Moon, Earth orbit, deep space, even an asteroid. What unites them is the promise of enhancing our understanding of the space environment from asteroids to space radiation, while demonstrating new technologies for use on future missions getting humans to the Moon, to stay.
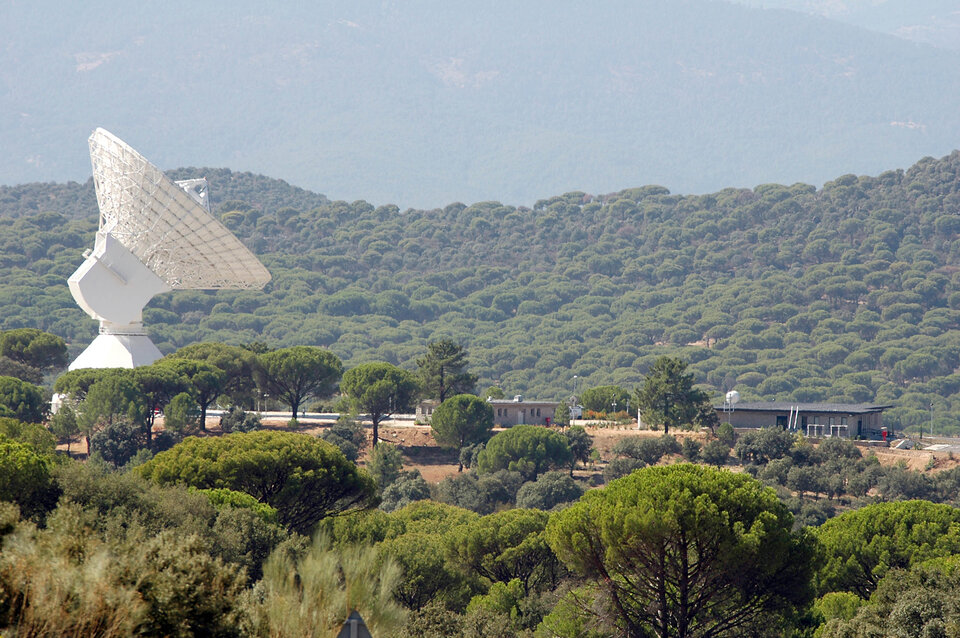

“Our Estrack stations will be critical in determining the CubeSat trajectories, returning their data home and supporting the commanding of the six spacecraft,” explains Lucy Santana, responsible for ESA ground facility services for deep space missions.
“We’re very proud to do our bit in returning humankind to the Moon”.
CubeSats disperse

About an hour and a half after launch, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) will perform a ‘trans-lunar injection burn’ to nudge Orion and the fleet of CubeSats in the direction of the Moon. The CubeSats will then be deployed, dispersing like dandelion seeds spread in the wind.
In the hours after liftoff, CubeSats will be deployed at specific times based on the requirements of each mission. ArgoMoon from the Italian Space Agency (ASI) will be the first that ESA tracks just a few hours after launch with the Cebreros station in Spain.
Very soon after separation, as the rest of the CubeSats are deployed, more eyes on the sky will be needed as they move into their own trajectories. For this, ESA in cooperation with Goonhilly will provide about 75 hours of tracking support across its deep space stations in the two weeks after launch.
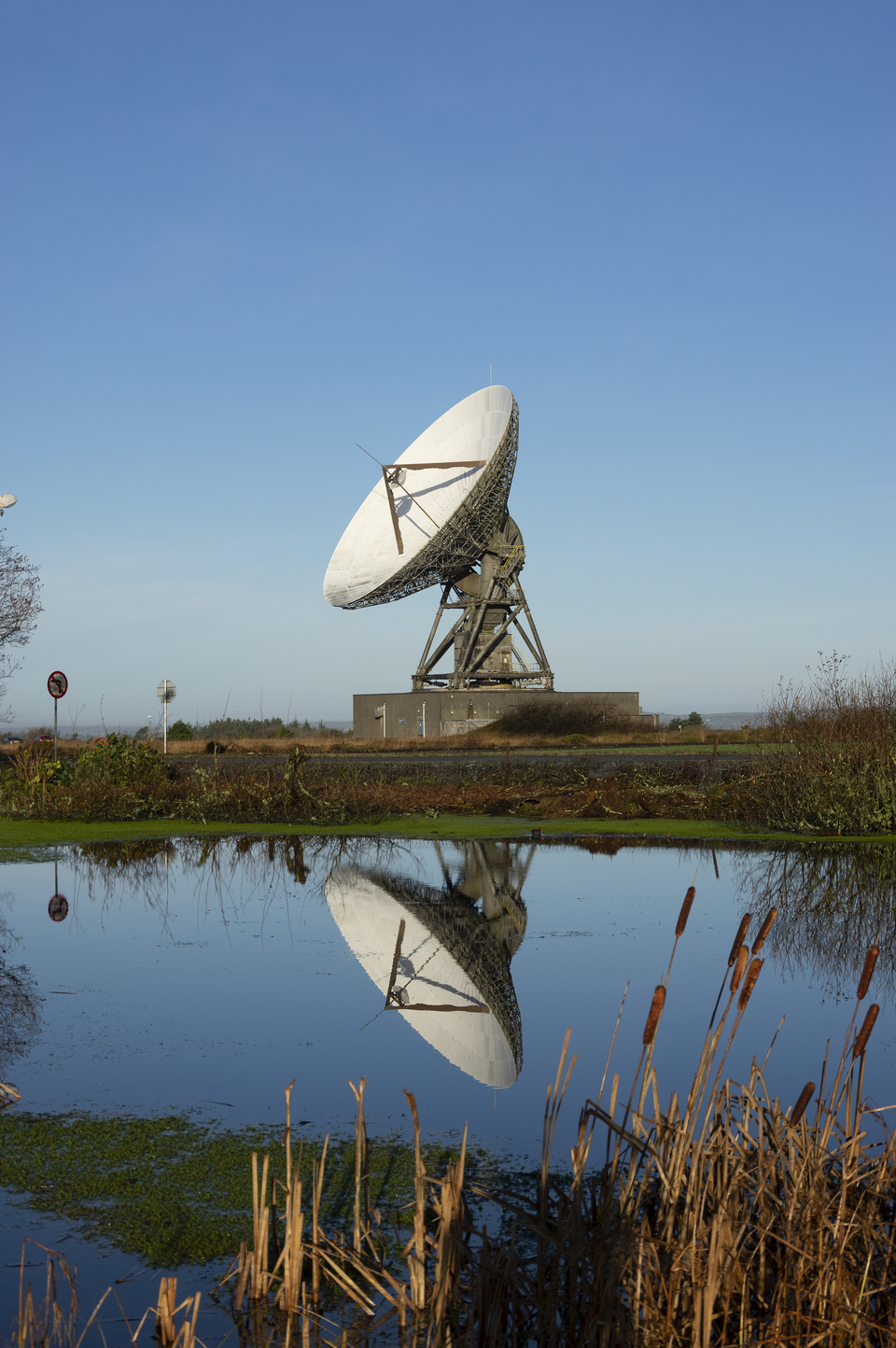

“We look forward to contributing to this iconic mission from here in the UK. Goonhilly played a role in distributing the Apollo Moon landing footage back in 1969: we’re now taking one step further and supporting humanity’s return to the Moon”, explains Matthew Cosby, Chief Technology Officer at Goonhilly.
“Our 32m deep space antenna has been used to communicate with ESA spacecraft since 2021. Supporting the Artemis I CubeSats is a fantastic way to further showcase our capabilities as we continue to expand this commercial service.”
Making waves
One of the main ways Estrack will support the Artemis CubeSats is by pinning down their location and trajectory using an effect called ‘the Doppler shift’. Each satellite is transmitting information at a frequency of around 8 GHz, which stations on Earth will acquire and track.
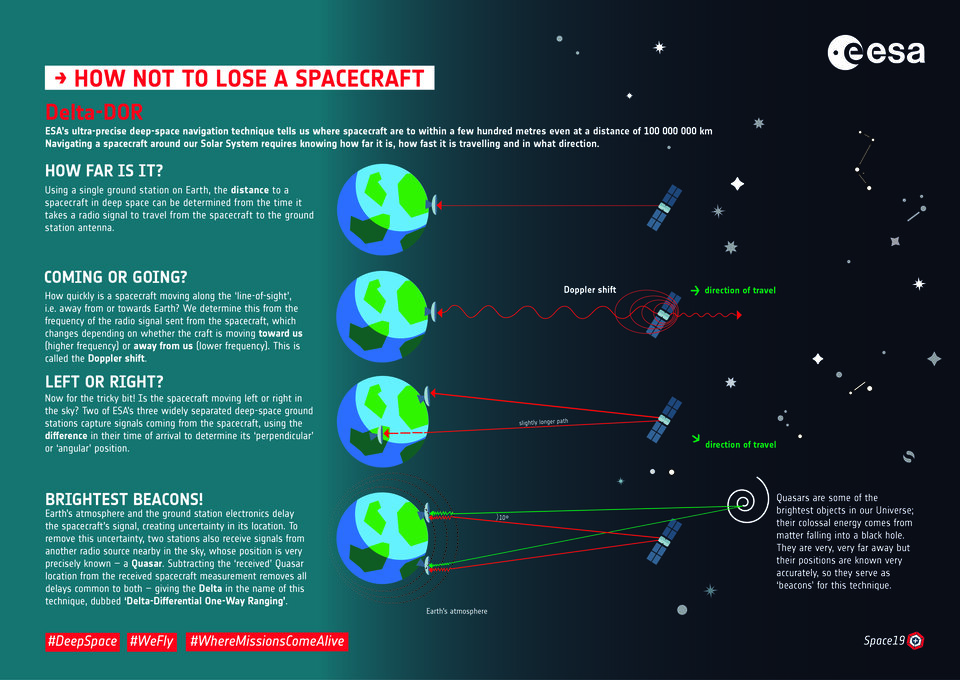
If the spacecraft is moving towards Earth while emitting its message, the light wave gets slightly squashed, shortening the wavelength and increasing its frequency. Conversely, if the CubeSat is moving away from Earth, its message is stretched, and its frequency lengthened. With this information, mission control will be able to have an accurate estimation of where the spacecraft are and where they are headed.
Forward to the Moon - small satellites offering a big return
The CubeSats being connected to Earth by Goonhilly and ESA’s deep space antennas illustrate the potential of small spacecraft in providing great insights.
Lunar IceCube and LunaH-map are designed to search the Moon for water – the discovery of which would be crucial for long-term missions as it is needed for explorers to harvest breathable air and create rocket fuel from ice.
Biosentinel and CuSP will add to our understanding of space radiation, filling critical gaps in knowledge about the health risks to explorers in deep space from solar radiation and high-energy galactic cosmic rays.
Finally, ArgoMoon and NEA Scout will demonstrate new operations technologies that will shape the way we fly future missions to the Moon.
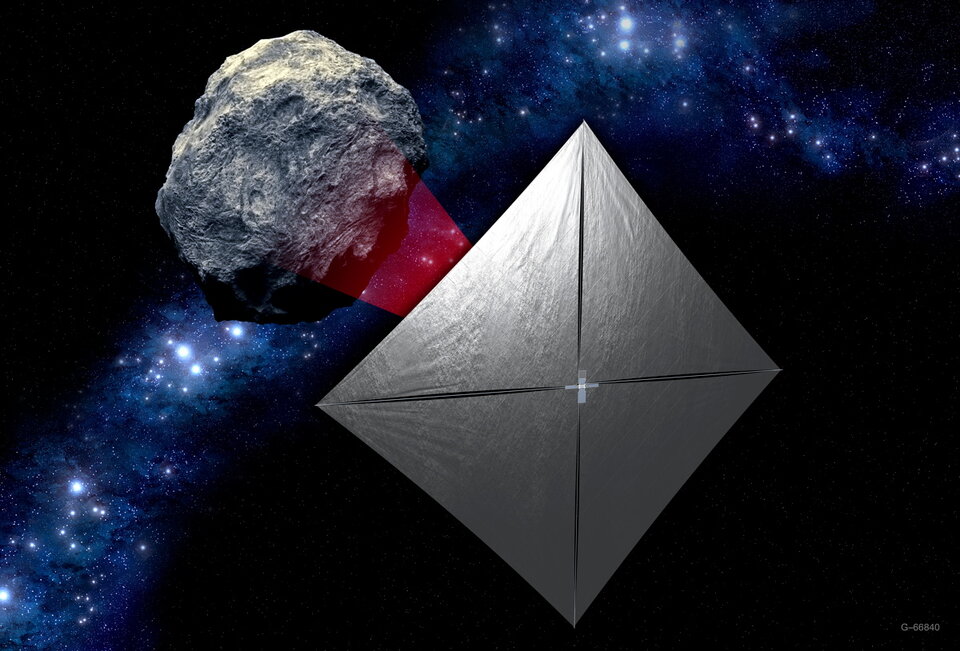
NEA Scout will visit the smallest ever asteroid to be studied by a spacecraft – 2020 GE is thought to be a little smaller than a school bus. While exploring the asteroid, it will use an 86-square-metre solar sail to harness solar radiation for propulsion.
The data from these first-of-a-kind missions will stream in through European antennas on Earth, where teams will get it where it needs to be and ensure we keep track of the dispersing satellites.
Landing on the Moon was hard. Returning for a longer stay will require even more planning, imagination and ingenuity, and ESA’s Estrack network of antennas dotted across the globe will be vital. With decades of experience in ground operations and a global network of eyes on the sky, ESA is playing a leading role in connecting Earth to space as we go forward to the Moon.
Follow @esaoperations live from 12:00 CEST on 29 Aug to get insights straight from the heart of ESA mission control, as the Artemis CubeSats are deployed, found, and spread their wings and Europe helps bring humankind to the Moon, and catch the live stream on ESA Web TV, Channel 1 from 12:30 CEST.









