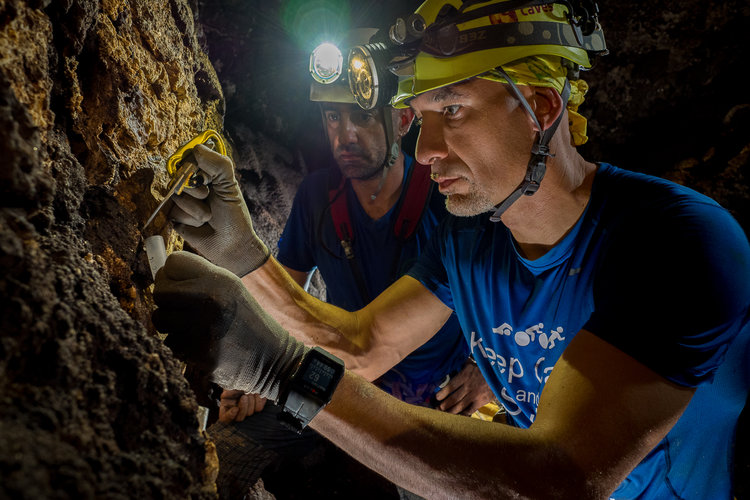
Searching for life in strange places
Last year schoolchildren were invited to dig up some earth in search of creepy-crawlies and underground life. Astronauts taking part in ESA’s underground training course CAVES joined the worldwide experiment from deep under Sardinia, Italy, and the results from their survey have revealed new habitats and rare species.
The ‘Catch that bug!’ experiment taught procedures for sampling and recognising species and calculating biodiversity in soil. The results are stored in an online database, creating an overview of ecosystems from wherever students have taken part.
During CAVES 2013, ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli worked with cave biologist and experiment designer Paolo Marcia from the University of Sassari to survey an area close to the entrance of the Sos Jocos cave.


Access the video
In a square just 20 cm across , the two Paolos found and catalogued 25 species earning the patch of Earth a biodiversity factor of 0.85 out of 1, despite these bugs living completely without sunlight. A total of 124 creepy-crawlies were found, implying a population density of over 3 billion per sq. km.
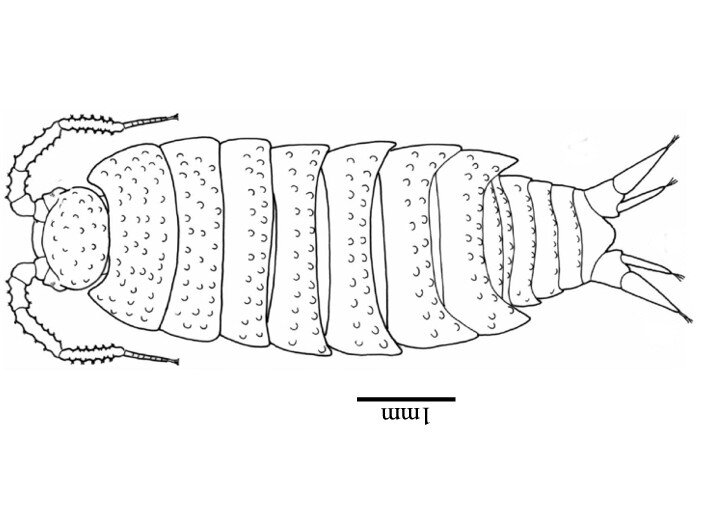
One of the 25 species identified is a rare Alpioniscus thanit that has never been seen before in this cave. Only discovered in 2009 and thought to be exclusive to the island of Sardinia, this crustacean seems to be a better traveller than previously thought. Alpioniscus thanit are the only creepy-crawlies of the species that can live in caves and above ground, seemingly able to travel from caves to the soil or vice-versa. The woodlice-like animal is only about 6 mm long and is so rare it has not been included in field books.
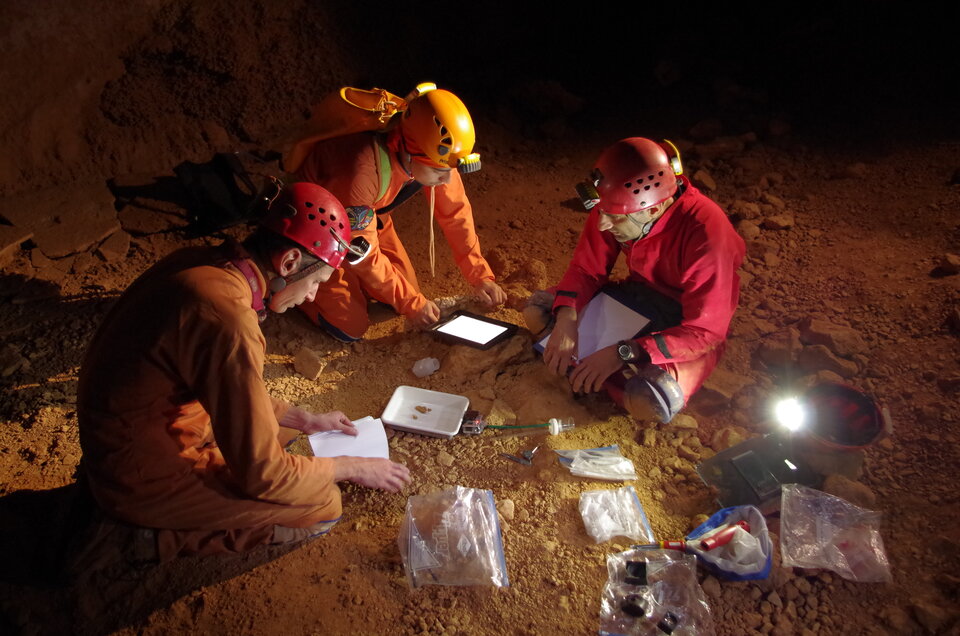

During CAVES 2013, the astronauts in training found yet more rare species. One of which, the beetle Actenipus pipiai, is found only in Sardinian caves. Now that biologists have three samples of the same beetle they can perform a DNA analysis to understand where the beetle fits in the evolutionary tree, solving a decade-long debate among biologists.
Another 4 mm isopod was found that belongs to a new species discovered by Paolo Marcia three years ago. Thanks to the work of the astronauts, this species can now be described and soon will be given a scientific name.
Do you want to join in the fun searching for life and learn about Earth biology while getting your hands dirty? Watch Paolo and Paolo run through the experiment and download the experiment details for your classroom. Who knows what you may find.


















