The dark side of the Universe
AMS embarked on a mission to explore distant and uncharted realms of our Universe, where answers to some longstanding questions in particle physics and cosmology may be revealed and unexpected phenomena may be discovered.
“Never in the history of science were we so aware of our ignorance: we know that we do not know anything about what makes 95% of our Universe.” - Prof. Roberto Battiston, Deputy Spokeperson of AMS-02
Capturing the cosmic rays

Over the past decades there have been many fundamental discoveries in astrophysics, such as pulsars, microwave background radiation and gamma-ray bursts.
However, cosmic rays come up against a thin but effective wall – Earth’s atmosphere absorbs and changes the charged particles, so they cannot be easily measured on the ground. In addition, their electric charge can only be identified by their trajectory in a magnetic field. Now with a magnetic detector in space, astronomers and particle physicists are eagerly awaiting the data.
Antimatter

The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer studies high-energy cosmic rays, helping scientists to understand why there is a conspicuous preponderance of matter over antimatter in the visible Universe. AMS will search for antimatter to the edge of the observable universe.
Normal visible matter, like stars, planets and galaxies, accounts for less than 5% of the Universe. According to theories and indirect observations, the other 95% is ‘dark matter’ and ‘dark energy’, but little is known of them.
Dark matter
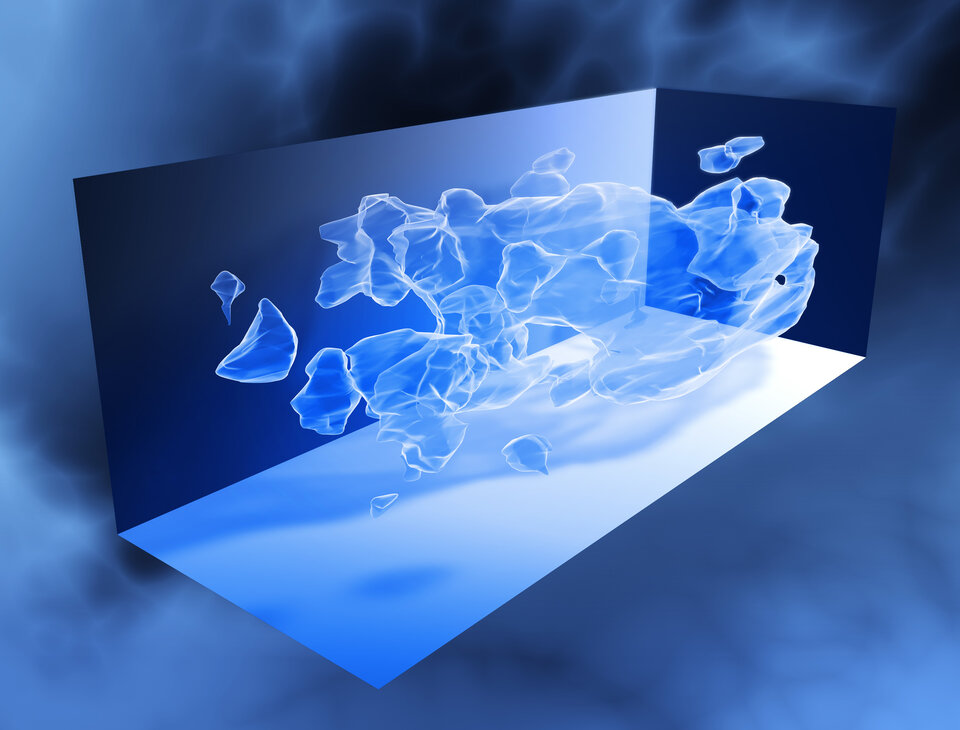
Dark matter is believed to account for up to 23% of the mass of the Universe. It has not been directly detected, but it has been discerned through its gravitational effect on other objects. Its origin and structure remain a mystery. It might consist of ‘neutralinos’, hypothetical particles that may be detected indirectly by AMS-02.
Prof. Ting’s experiment will increase the sensitivity of the search by between a thousand and a million times, revealing a totally different domain by finding the neutralino or something else. AMS-02 might also detect a new, exotic form of matter predicted by scientists: a very heavy elementary particle dubbed the ‘strangelet’.
Dark energy

Repulsive dark energy, believed to be accelerating the expansion of the cosmos, makes up the balance, and even less is known about it. Although AMS-02 is not expected to tell us much more about dark energy, the observations will affect the wider view of the composition of the Universe and thus shed light on the mysterious dark energy.
In addition, AMS-02’s possible observation of antimatter nuclei would be a major step in revolutionising our knowledge of the Universe. At the beginning of time and space, the fate of the Universe balanced on the almost-identical amounts of matter and antimatter. The cosmos, as we know it now, is made of matter, but there is no compelling reason why antimatter, antistars and antigalaxies do not exist.