International day for the eradication of poverty
Goal 1 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) calls for an eradication of poverty in all its forms. The achievements of these goals by 2030 is a global matter and of major importance for the most vulnerable populations on earth. The fulfilment of the SDGs will require the full commitment of decision-makers, international organizations and stakeholders.
The European Space Agency, as an international organization, is determined to use its scientific, technological and innovative research for the benefits of humankind. The commitment to ending poverty is present across all ESA directorates.
“Eradicating poverty in all its forms”: Empowering Rural Women, Men and Children
According to the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), 75% of the world's poorest people - 1.4 billion women, children and men - live in rural areas and depend on agriculture and related activities for their livelihoods.
ESA continually develops innovative methods for Earth Observation in combination with field observations for improved crop mapping and monitoring, crop health monitoring, forecasting and management of agricultural irrigation, precision farming, precision fertilization, crop anomaly detection and yield forecasting.

Satellite derived information products are also deployed in order to boost the resilience of the rural economy to naturally occurring hazards, such as flooding, volcanic eruptions and drought, and to help the development of a sustainable agriculture in the poorest countries.
Food security in developing countries lies at the heart of ESA activities through use of EO data for, for instance, rice crop estimation and monitoring. Rice is the primary staple for two thirds of the world’s poor (IFAD). Developing enhanced EO methods for disaster-resilient rice crop management in Asia aims at increasing productivity and securing farmer's incomes.
Access to education

Providing decent education to all is of key importance for the eradication of poverty and wealth creation. At ESA, efforts to provide decent educational opportunities for the poorest children were made through clusters of satcom-enabled schools in rural areas (e.g., SWAY4edu2).
Moreover, education in developing countries is the core of ESA projects focused on the provision of educational content and Internet access to African primary and professional high schools (e.g., ISIDE 4 Africa).
Reduced inequalities between rural and urban areas
Ensuring that all women and men, and particularly those living in poor conditions, have equal rights to economic resources and appropriate new technology, contributes to eradicating poverty.
Anti-poverty measures can also be found through efforts to reduce rural-urban disparities which account for a large share of income inequality. In addition, access to financial services in underserved developing areas is another step to reducing inequalities (e.g., Satfin Africa).
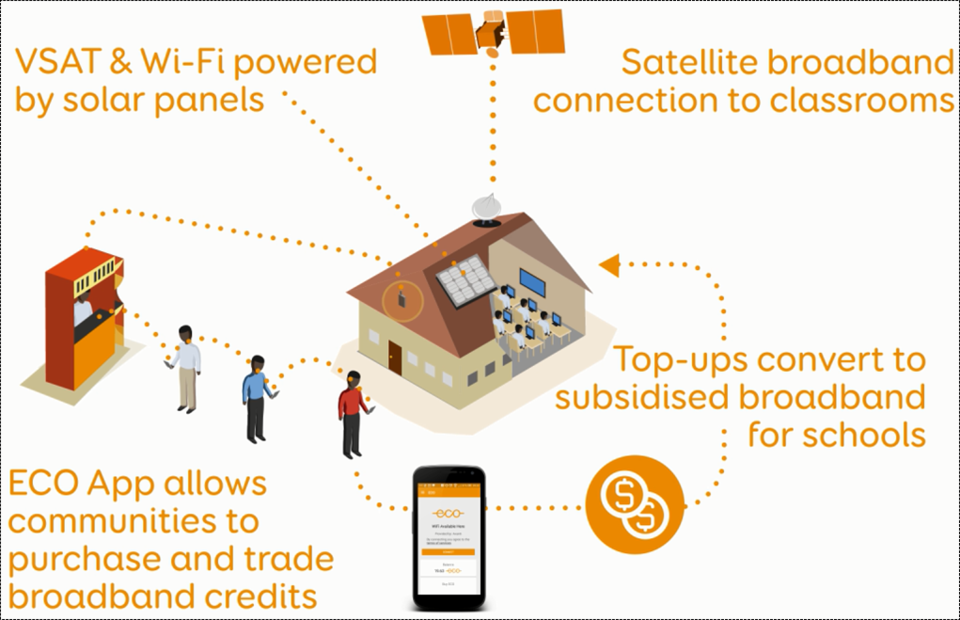
The Internet has become a crucial tool for education, economic growth, strong institutions and free access to information among many things. A lack of access to broadband in rural communities can enhance the rural-urban gap.
ESA, in partnership with the private sector, has made increased efforts to overcome the “digital divide” barrier (BARRD - Broadband Access for Rural Regeneration with DVB-RCS, ECO - Every Community Online).
Access to decent healthcare

Poverty pushes people to live in tough environments, with no decent shelter, clean water or adequate sanitation. These circumstances intensify poor health and well-being conditions for the poorest.
Satellite-based telemedicine is present within numerous ESA activities. It ensures equal access to medical expertise independently of geographical location (Sahel, KosmoMed, T@HIS, SatNetCode, Euromednet, TelAny.
EO-derived information is also used within ESA projects for epidemiology studies and climate-related health risk analysis in developing countries, among other applications.




