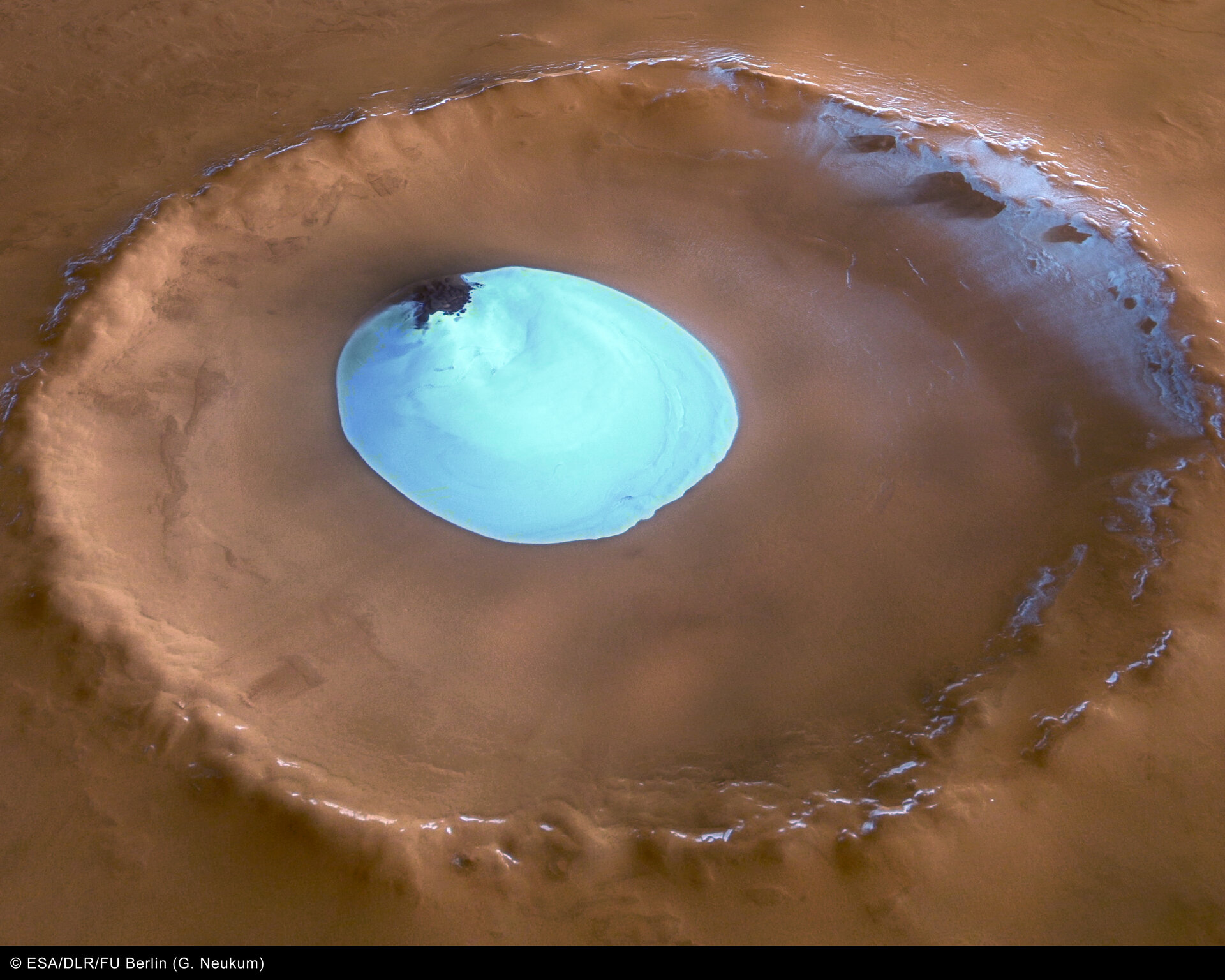
Water ice in crater at Martian north pole
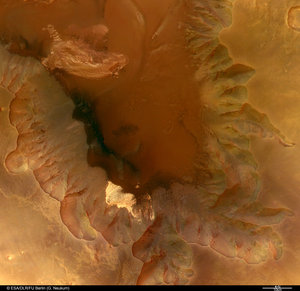
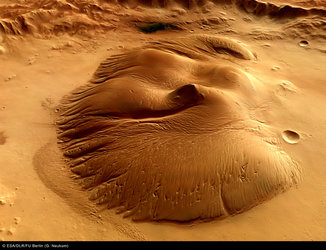
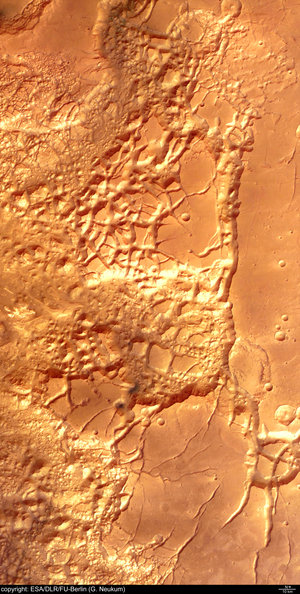
These images, taken by the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) on board ESA’s Mars Express spacecraft, show a patch of water ice sitting on the floor of an unnamed crater near the Martian north pole.
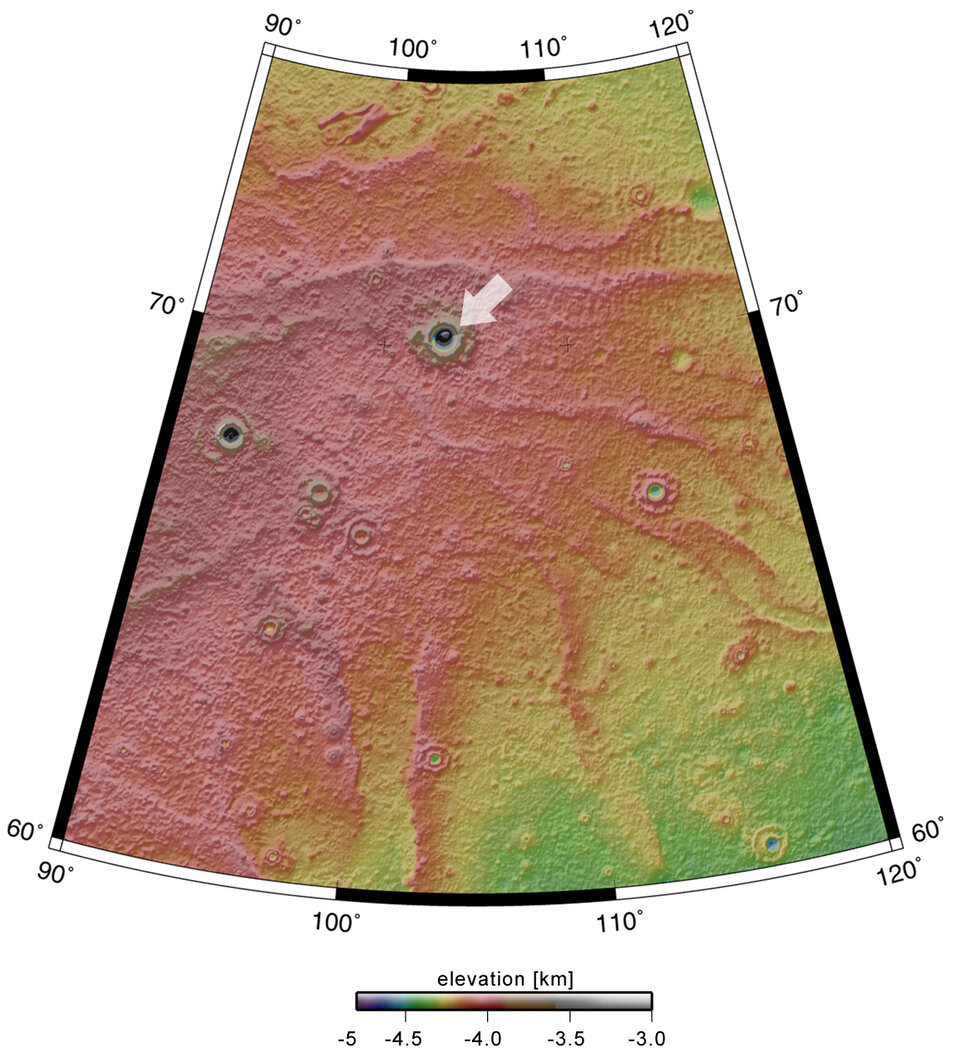
The HRSC obtained these images during orbit 1343 with a ground resolution of approximately 15 metres per pixel. The unnamed impact crater is located on Vastitas Borealis, a broad plain that covers much of Mars's far northern latitudes, at approximately 70.5° North and 103° East.
The crater is 35 kilometres wide and has a maximum depth of approximately 2 kilometres beneath the crater rim. The circular patch of bright material located at the centre of the crater is residual water ice.
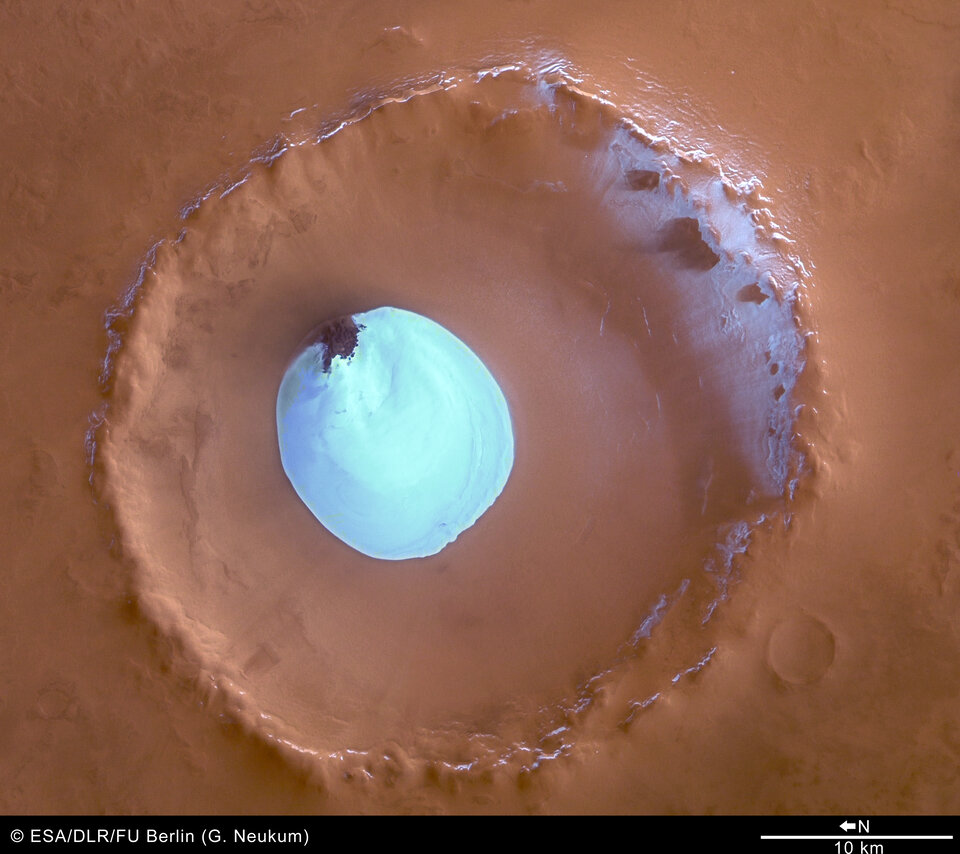

This white patch is present all year round, as the temperature and pressure conditions do not favour the sublimation of water ice.
It cannot be frozen carbon dioxide since carbon dioxide ice had already disappeared from the north polar cap at the time the image was taken (late summer in the Martian northern hemisphere).

There is a height difference of 200 metres between the crater floor and the surface of this bright material, which cannot be attributed solely to water ice.
It is probably mostly due to a large dune field lying beneath this ice layer. Indeed, some of these dunes are exposed at the easternmost edge of the ice.
Faint traces of water ice are also visible along the rim of the crater and on the crater walls. The absence of ice along the north-west rim and walls may occur because this area receives more sunlight due to the Sun’s orientation, as highlighted in the perspective view.
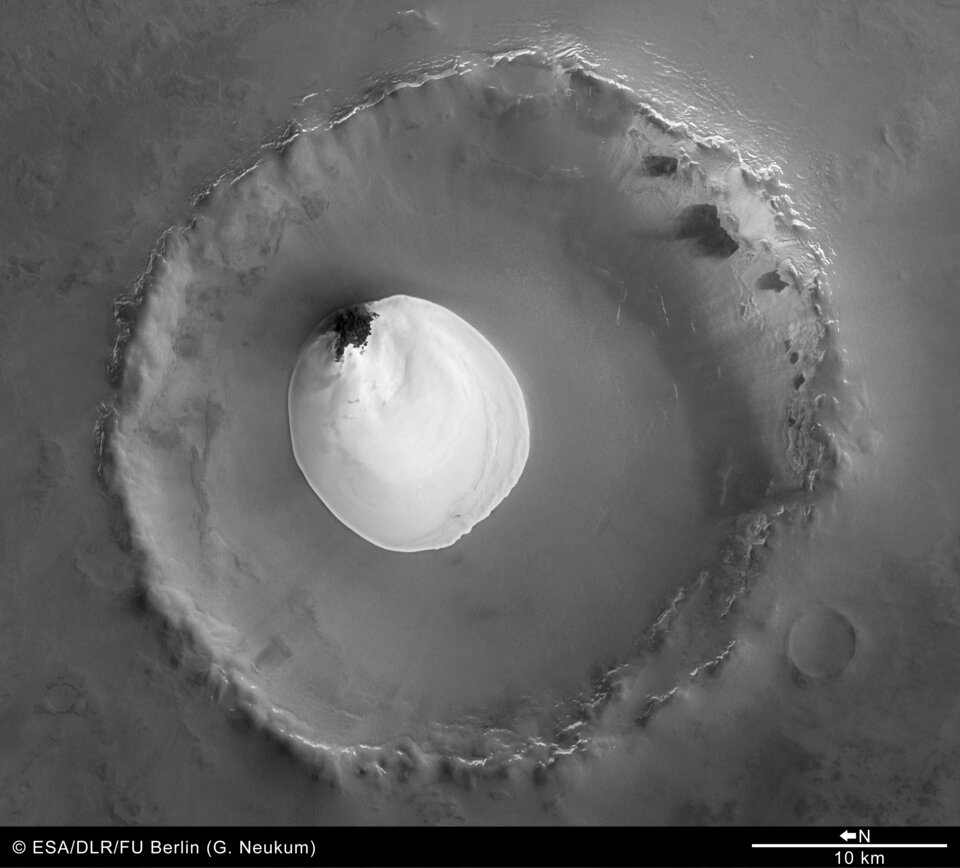
The colour images were processed using the HRSC nadir (vertical view) and three colour channels. The perspective views were calculated from the digital terrain model derived from the stereo channels.
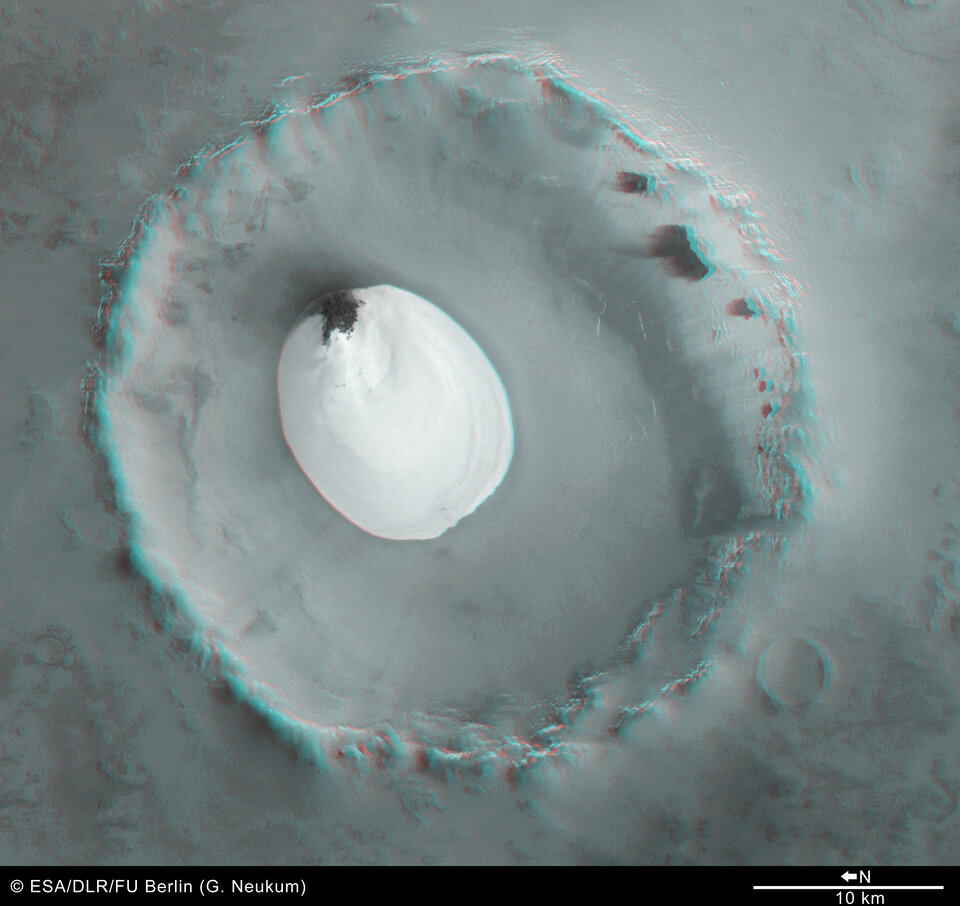
The 3D anaglyph images were created from the nadir channel and one of the stereo channels. Stereoscopic glasses are needed to view the 3D images Image resolution has been decreased for use on the internet.
For more information on Mars Express HRSC images, you might like to read our updated 'Frequently Asked Questions'.