Implemented OSIP ideas — July 2022
ESA's Open Space Innovation Platform (OSIP) seeks novel ideas for new space research activities. Campaigns and Channels invite solutions to specific problems or ideas on more general topics, with those run by Discovery & Preparation, including the Open Discovery Ideas Channel, specifically looking for ideas that could be implemented as system studies, early technology developments, or PhD or postdoc research co-funded by ESA and a university.
Open Discovery Ideas Channel

In July 2022, the following ideas were implemented through the Open Discovery Ideas Channel.
--------------------------------------------------
Cracking Humboldt's enigma by Earth observation
PRINS Engineering
This study will use data from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 and -2 satellites to uncover how climate, soil and vegetation interact to form forest communities and biodiversity patterns. Through this work, the engineers behind the study hope to crack 'Humboldt's enigma' – what causes global patterns of mountain biodiversity?
--------------------------------------------------
Ground-based space radiation research analogues for beyond-LEO exploration
CERN
Considering the future of human spaceflight as missions explore beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO) to destinations such as the Moon and Mars, this co-funded research project will aim to answer the question: how can we design, construct and commission a ground-based, heavy ion irradiation facility in such a way that it can be used to test electronics, scientific instruments, dosimeters and detectors as if they are exposed to the space radiation environment encountered beyond LEO?
--------------------------------------------------
Development of an in-situ real-time sensor for molecular contamination monitoring based on microwave transduction
CNRS
The aim of this early technology development project is to develop a sensor able to identify and quantify the deposited molecular contaminant on sensitive surfaces. This sensor could be integrated directly into in-flight hardware to monitor in situ and in real time the evolution of the contamination levels during assembly, integration and testing of a spacecraft, with the possibility to be further developed for in-flight use.
--------------------------------------------------
CARLAH, an innovative crystalline silicon solar cell architecture for cost-effective space compliant photovoltaic devices (LEO applications)
French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA)
New solar cell technologies could make generating solar power in space cheaper and more efficient. This early technology development project aims to assess such a new solar cell concept developed by CEA, specifically to assess the performance of the cells before and after ageing tests (irradiation, UV exposure) for space missions in low-Earth orbit.
--------------------------------------------------
Towards high-performance space-grade frequency combs
Menhir Photonics
Read more about this public idea in OSIP
--------------------------------------------------
Commercial use of ESA's inventions
The following ideas were implemented through the Campaign for ideas for the commercial use of ESA's inventions.
--------------------------------------------------
Artificial intelligence for GNSS post-fit residual and position joint analysis – a plugin for Jason, Rokubun cloud GNSS processing service
Robukun
Machine Learning algorithms in the field of GNSS are usually trained using physical models of the different aspects that make up the GNSS signal (the geometric range, ionospheric and tropospheric delay, orbits, clocks, etc.) and positioning filters such as Kalman filter that estimate a state (position, velocity and time) based on a set of observations. However, after the estimation has been obtained, little attention is paid to the ‘post-fit residuals’ – the values that indicate how well the input data ‘agrees’ with the estimated state.
The FITAI project will use these post-fit residuals and positioning errors to develop a processing stage based on an ESA patent for Rokubun's Jason cloud GNSS service. This will improve the accuracy of navigational satellite position estimates, particularly in challenging scenarios such as urban canyons. This technique could be deployed commercially in the form of licensing or pay-per-use to third parties.
--------------------------------------------------
Modular scanning array based on simple antenna manufacturing
CNIT – University of Trento
MOSAIC aims at to improve the technical and commercial maturity of antenna architectures proposed in an ESA patent. The ESA invention describes a design and manufacturing method for large, sparse-phased arrays for satellites in geostationary orbits.
Sparse arrays offer reduced power consumption at the cost of increased complexity. The MOSAIC project will adopt a modular structure to simplify the antenna architecture and the manufacturing.
The targeted demonstration mission is the micro-geostationary satellite that SWISSto12 is developing with the support of ESA. The consortium believes that the original invention, and hence this activity, have the potential to enable a competitive use of phased arrays in platforms whose DC capabilities are limited.
--------------------------------------------------
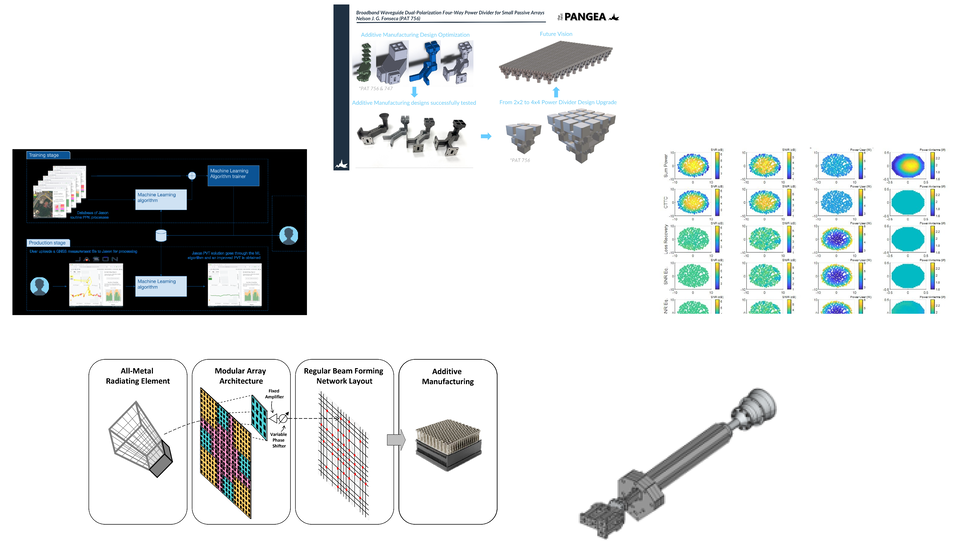
Development of a broadband waveguide dual-polarisation sixteen-way power divider for small passive arrays in a single block optimised for additive manufacturing
Thenextpangea
The next step for extending the ESA patent for a compact dual-polarization four-way power divider is to scale it up to a sixteen-way power divider and produce a small array antenna. This activity will combine four four-way power dividers and a fifth power divider for feeding the four top power dividers. As a result, the design will have a single port for feeding power to a 16-element array antenna.
The project will also involve a second ESA patent for improving the compactness of the system without compromising radio frequency (RF) performance.
The project aims to demonstrate the potential that additive manufacturing has for RF components and space applications as well as the potential for the power divider described above as a key component for the ground segment in the satellite communications sector.
--------------------------------------------------
KAME: A novel KA-band TM01 Mode Extractor for ground applications feeds
EOS Engineering
This project will investigate the feasibility of including an ESA patent enabling a compact TM01 mode extractor design in two product lines currently offered by EOSOL. The first product line is the Ka-band feed for downlinking tracking, telemetry and command (TT&C) and Earth Observation data. This is of great interest for mid-range (3–5 m) antennas for low- to medium-Earth orbit, but could also be applicable for larger antennas. The second is the feeds for SATCOM terminals, where the TM01 could be an innovative element in ground segment antennas (where there is a growing market) due to its simple mechanical design, reduction in mass, volume and manufacturing costs.
The project team will also explore the benefits of additive manufacturing applied to this component.
--------------------------------------------------
Pragmatic design and monitoring of array-fed reflector payloads
Heriot-Watt University
Array Fed Reflector (AFR) antennas provide a favourable trade-off between performance and complexity for new broadband satellites in geostationary orbit. In light of this, satellite integrators and operators are in need of a) efficient optimisation processes to define the antenna configuration (Optics, Focal Array) that is the most flexible and best suited for their users, and b) practical techniques for the dynamic reconfiguration of the payload during operation on a reduced timescale.
Addressing industrial needs, this activity will adapt recent ESA developments on pragmatic techniques for implementing Massive MIMO (multiple-input, multiple output) in satellite systems that were originally conceived in the context of direct radiating arrays to practical AFR scenarios.
--------------------------------------------------
Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components

The following idea was implemented through the Campaign for new ideas for the use of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components.
--------------------------------------------------
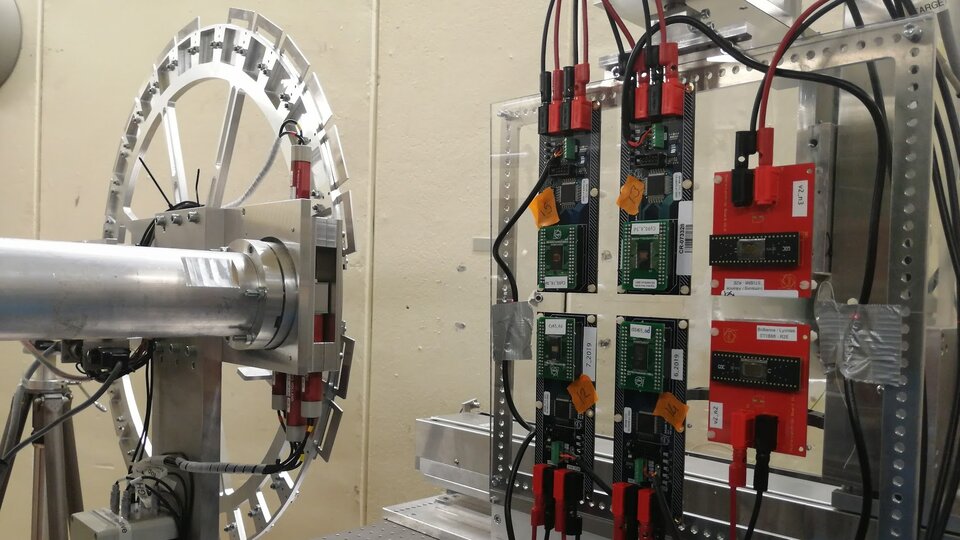
Exploring device radiation variability and related assurance methodologies through large batch procurements
CERN
Testing how well COTS parts fare with radiation is difficult for space applications – partly because different parts in the same batch may respond differently to radiation, and partly because it is expensive to test the few parts that are typically needed. This co-funded research project will explore and implement a scheme through which space system designers could benefit from the availability of COTS lots qualified for CERN applications. It will include an analysis of the related technical requirements and financial/legal aspects, as well as feasibility demonstration on a few selected parts.
--------------------------------------------------

