Implemented OSIP ideas — May 2022
ESA's Open Space Innovation Platform (OSIP) seeks novel ideas for new space research activities. Campaigns and Channels invite solutions to specific problems or ideas on more general topics, with those run by Discovery & Preparation, including the Open Discovery Ideas Channel, specifically looking for ideas that could be implemented as system studies, early technology developments, or PhD or postdoc research co-funded by ESA and a university.
Open Discovery Ideas Channel

In May 2022, the following ideas were implemented through the Open Discovery Ideas Channel.
--------------------------------------------------
Efficient auto-tracking of objects during spaceflight
Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts
Tracking objects in space is a challenge, but is necessary for applications such as removing pieces of space debris. This study aims to develop an autonomous tracking system (auto-tracker or intelligent space camera) using low-profile hardware.
--------------------------------------------------
Quantum receivers for efficient deepspace optical communications
Quantum Optical Technologies
Read more about this public idea in OSIP
--------------------------------------------------
Integrated photonics frequency generation unit for high throughput satellites
Dublin City University
Read more about this public idea in OSIP
--------------------------------------------------
Cognitive cloud computing in space

The following ideas were implemented through the Campaign for new ideas for Cognitive Cloud Computing in Space.
--------------------------------------------------
Dual-camera satellite with onboard AI-based decision-making capabilities
OHB Hellas
Aiming to demonstrate how AI could enable new capabilities in future Earth observation satellite missions. The project will target both high spatial and temporal resolution imaging with minimal use of space and ground resources. AI will be used to fine-point the high-resolution camera towards specific area of interest, after they have been detected in low-resolution images.
--------------------------------------------------
Commercial cloud computing in space
D-Orbit
Kick-starting future economies through a network of data centres in space, connected via intersatellite links. An early step towards this vision is already operating in orbit; this study will take the concept a step further by proposing an open competition for industry in ESA Member States; winners could fly their proposal in space on existing infrastructure.
--------------------------------------------------
LEO-GEO4GHG: LEO-GEO for GreenHouse Gases
SATLANTIS
Detecting and quantifying methane leaks in gas facilities in near real-time with high resolution in space and time. The study will explore combining data from Earth observation and meteorological satellites with cutting-edge AI to detect and quantify leaks.
--------------------------------------------------
Cognition: distributed data processing system for lunar activities
KP Labs
Introducing more autonomy into lunar surface exploration. According to a Euroconsult study, 51 missions to the Moon are planned in 2020–2029, and the lunar exploration market will be worth $2.7 billion by 2029. But the Moon is so far away that transmitting data to Earth is a challenge. This project will investigate processing data on board the rover and lander, to send only the most valuable data to Earth and increase the autonomy of the rover and lander.
--------------------------------------------------
Beyond the Mission Paradigm: Federated Reconfigurable Infrastructure via Edge Devices in Space (FRIENDS)
Mission Control Space Services
Using federated machine learning to repurpose and reconfigure computer assets for sustainable lunar exploration. Federated learning is a decentralised learning strategy that could enable the different nodes in a network, such as lunar rovers or landers, to cooperate to learn to distinguish different lunar terrains.
--------------------------------------------------
Don't try this at home
Planetek Italia
Demonstrating the benefits of a cognitive cloud computing infrastructure in space to provide commercial services to Earth observation sensors and space-based data providers. Based on a use case set in the maritime domain, the study will provide a preliminary design for cognitive computing in space and prepare a technically and commercially viable implementation plan.
--------------------------------------------------
Hybrid edge-cloud AI accelerated astrometric reduction pipeline for agile near real-time in-situ space surveillance and tracking
Vyoma
Accelerating the technologies needed for effective space traffic management from space. In particular, the project aims to investigate hybrid edge and cloud computing to perform near real-time localisation of objects in space.
--------------------------------------------------
NEU4SST: NEUromorphic processing for Space Surveillance and Tracking
University of Strathclyde
Demonstrating the potential of neuromorphic computing (inspired by the human brain) and event-based cameras (inspired by the human visual system), for in-space edge-computing detection and tracking of moving targets.
--------------------------------------------------
Blockchain ecosystem for an autonomous consensus mechanism of federated satellite networks
Parametry UG
Automating cloud infrastructure in space. Bringing a computing system to a higher level of autonomy and awareness comes with the challenge of agreeing on decisions among multiple agents (machines and humans) and detecting needs in resources to plan actions automatically. To achieve this goal, this study investigates some features from blockchain technology and proposes its application for space traffic management and disaster response.
--------------------------------------------------
PERTEO: PErsistent Real-Time Earth Observation for responsive disaster management
Deimos Engineering and Systems SLU
Providing global real-time and persistent disaster monitoring services. This study will define and analyse the theoretical PERTEO mission – a mission that would greatly improve services provided to citizens, enable on-demand disaster services, exploit the satellite-as-a-service concept, and employ on-board processing, intelligence and AI applications.
--------------------------------------------------
D-TACS: On demand data transformations and auto-calibration in orbit
Trillium Technologies
Implementing onboard, on-demand, fast and accurate machine learning emulators (hardware or software that enables one computer system to behave like another computer system) for atmospheric correction. This would expand the range of onboard use cases, in particular, verification and measurement of subtle variables characteristic of vegetation, fire risk or fuel moisture.
--------------------------------------------------
STARCORP: Automated and self-improving follow-up verification of detrimental human-activity from LEO
Trillium Technologies
Enabling the global monitoring of methane emissions using a ‘tip and cue’ system. The project will explore using a non-dedicated satellite that rapidly scans Earth such that it ‘revisits’ the same region of ground often (the tip). When the satellite spots a suspected methane source, it tasks another spacecraft equipped with a high-resolution instrument to look at it in more detail (the cue).
--------------------------------------------------
Making XR a reality

The following ideas were implemented through the Campaign for new ideas to make XR (extended reality) a reality.
--------------------------------------------------
X-aRm
Space Applications Services
Whilst in space, astronauts carry out extravehicular activity. This is often referred to as a 'spacewalk', but it involves risky and difficult work on the outside of the space station. This early technology development project aims to help astronauts train for extravehicular activity by developing an arm exoskeleton with force feedback. Astronauts can wear the exoskeleton arm – or X-aRm – whilst using virtual reality to better perceive the space environment and feel the forces involved in extravehicular activity.
--------------------------------------------------
Audiovisual feedback to augment manual activities during spacewalks
Ilmenau University of Technology
This study will explore the impact of the silence of space on the ability of astronauts to perform manual work on the outside of the International Space Station. It will investigate generating artificial sounds – for example the striking of metal or the humming of a motor – to give astronauts a confirmation during the activity. This may lead to a more natural and precise execution of the task. The sounds will be enriched with visualisations that provide a visual confirmation during the manufacturing, display additional information, and can lead the astronaut through the process step by step.
--------------------------------------------------
Digital Twins of Humans for Space Operations with XR telepresence
Ilmenau University of Technology
A digital version of a human – an avatar – can be created by collecting data such as information on the position of body parts. This study aims to develop an immersive augmented/virtual reality viewer that uses 3D pose estimation to animate realistic avatars of people. This technology would support communications and monitoring – for example in areas like designing missions, assembly, integration, testing & verification of spacecraft, and in mission control.
--------------------------------------------------
Underwater VR for astronaut training
Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg
Astronauts train for extravehicular activity in swimming pools. Currently, very large and deep pools are needed for effective training. This study aims to reduce the need for such large pools by combining diving goggles with a virtual reality headset and to use the university's small pool (40 cubic metres) to simulate a space environment. Besides constructing water-tight VR headsets, the study will develop crucial tracking systems to determine position and orientation in space.
--------------------------------------------------
Europe's green future
The following ideas were implemented through the Campaign for new ideas for how space can boost Europe's green future.
--------------------------------------------------
Extracellular conversion of CO2 into sugars and other functional food ingredients: SweetAir
Wageningen University
Microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast and microalgae can be used as an alternative way to produce food ingredients for humans. But the substances required to grow these microorganisms – sugars, organic acids and proteins – are also currently produced in ways that contribute to biodiversity loss. This early technology development project will build on technologies and lessons learned from human spaceflight to directly convert carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into food ingredients for humans.
--------------------------------------------------
Biodiversity-positive supply chains through satellite remote sensing
Biodiv Watch
Data on biodiversity change for the entire globe are generally lacking and often sensitive, especially at the high resolution needed to record different plant species. The scale of global supply chains also makes it difficult to link them to local biodiversity. This study will address these issues by using recent advances in sensor technology, Earth observation data quality and digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and cloud computing to map patterns in plant biodiversity at regional and continental scales.
--------------------------------------------------
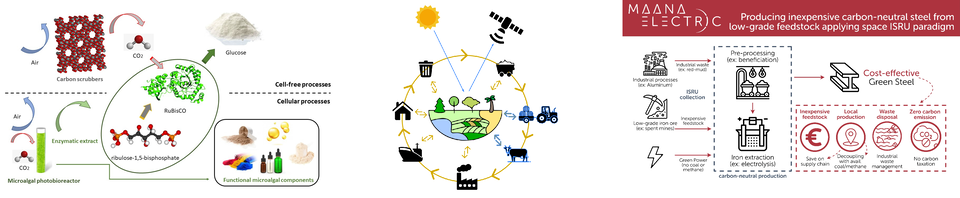
Producing inexpensive carbon-neutral steel from low-grade feedstock applying space in-situ resources utilisation paradigm
Maana Electric SA
Steel production traditionally relies on unsustainable material with a high iron content. An entirely new approach, inspired by the challenges of long-term space missions, could be the answer. In-situ resource utilisation (ISRU) is the practice of collecting, processing, storing and using materials found or manufactured on other planets or moons to replace material that would otherwise have to be transported from Earth. This early technology development project will investigate the possibility of a European prototype system able to use material with relatively low iron content (known as ‘low-grade feedstock’) and electricity to produce carbon-neutral steel. The hope is that such a system would produce green steel at a competitive price compared to steel produced using traditional methods and high-grade iron ore.
--------------------------------------------------
Model-Based System Engineering
The following idea was implemented through the OSIP Model-Based System Engineering Campaign.
--------------------------------------------------
Digitalisation of the ground segment and operations digital integration in early phase 0/A studies
Rhea Systems
Read more about this public idea in OSIP
--------------------------------------------------

