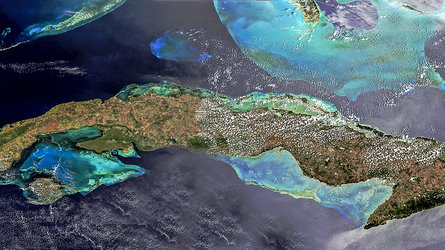
Voyage around the world in 600 metres
UNESCO has unveiled a frieze of satellite images of Earth at its Paris headquarters building to give visitors a view of the planet from a strikingly fresh perspective.
The ‘Belle île en ciel’ exhibition – supported by ESA, Parc Européen du Volcanisme, PlanetObserver, Spot Image, RATP and L’Express – opened on 29 March in the presence of UNESCO Director General Koïchiro Matsuura and ESA Director General Jean-Jacques Dordain.
The exhibition – organised by UNESCO as part of its 60th birthday celebrations – essentially serves to highlight the planet’s fragility. The frieze includes some 60 charts graphically illustrating the main environmental challenges facing humanity in seeking to protect our common heritage: managing the water cycle, biodiversity, pollution, deforestation, global warming, managing natural disasters, plus education, communication, dialogue among civilisations and the preservation of specific cultures.
Humanity’s greatest heritage is the Earth itself, this truly beautiful ‘island’ in the cosmos, home - for better or for worse - to over 6.5 billion inhabitants. But the advent of observation satellites is making us increasingly aware of the limits of our home planet.
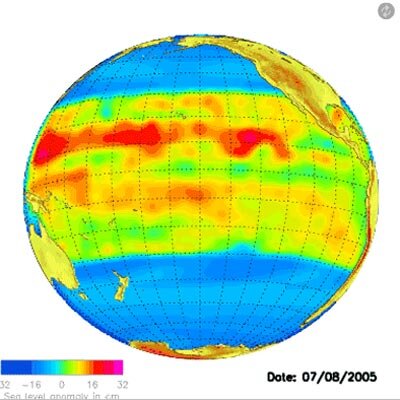
Studying the environment – using ESA satellites such as Meteosat, ERS and Envisat – has significantly contributed to highlighting serious ongoing issues concerning climate change. The data gathered are used today to build up models of the implications of such changes for the world of tomorrow.
To improve and sustain that modelling, ESA has under its Living Planet initiative set up satellite programmes that are designed to enhance our understanding of major green issues such as ocean circulation, ocean salinity, atmospheric dynamics and thinning polar ice.
ESA is also, together with the EU, preparing the way for the Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES) initiative, which aims to coordinate Earth observation from space for the protection of the environment and local populations. The issues highlighted by this exhibition underpin the many joint projects set up since 2000 by UNESCO and ESA.
These projects aim to harness space technologies in order to address humanitarian needs, protect the environment, manage disasters and promote education and culture. The global coverage provided by satellites and their capacity to fly repeatedly over a given region make them a key tool for managing our planet.

With this in mind, in 2001 ESA and UNESCO set up the Build Environment for Gorillas (BEGo) project. This involves using satellite radar and optical imaging to help protect the gorilla habitat in the mountains of Ruanda, Uganda and the Congo. Special tools have been developed from the resulting data in cooperation with the main interested parties, which include the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), the International Gorilla Conservation Programme (PICG) and the WildLife Conservation Society.
Following the 2002 Earth Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg, ESA again partnered with UNESCO in starting up the TIGER initiative, which uses satellite data to manage water resources in Africa. Responding to in-situ demand expressed by various parties, this initiative draws together over 150 organisations throughout the continent – water agencies, remote-sensing centres, universities – under the banner of its various activities, workshops and training programmes. TIGER is thus playing its part in the decision-making process and in improving technical, human and institutional capabilities in a joint effort to place sustainable management of Africa’s water resources on a secure footing.

Under the Data User Element of its Earth Observation programme, ESA will be continuing to provide such support, supplying UNESCO with remote-sensing data on its listed World Heritage sites and on the Biosphere Reserve in Central America. It will shortly be undertaking a feasibility study which could in 2008 become a full-scale project, extended to cover other sites around the world.
Since 2003, ESA has been contributing to the protection of 812 listed sites under UNESCO’s Convention concerning the Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage. Under a cooperation agreement, UNESCO is able to use data gathered by ESA satellites to help monitor and manage listed World Heritage sites.