EGNOS navigation system begins serving Europe’s aircraft
Today, the EGNOS Safety-of-Life signal was formally declared available to aviation. For the first time, space-based navigation signals have become officially usable for the critical task of vertically guiding aircraft during landing approaches.
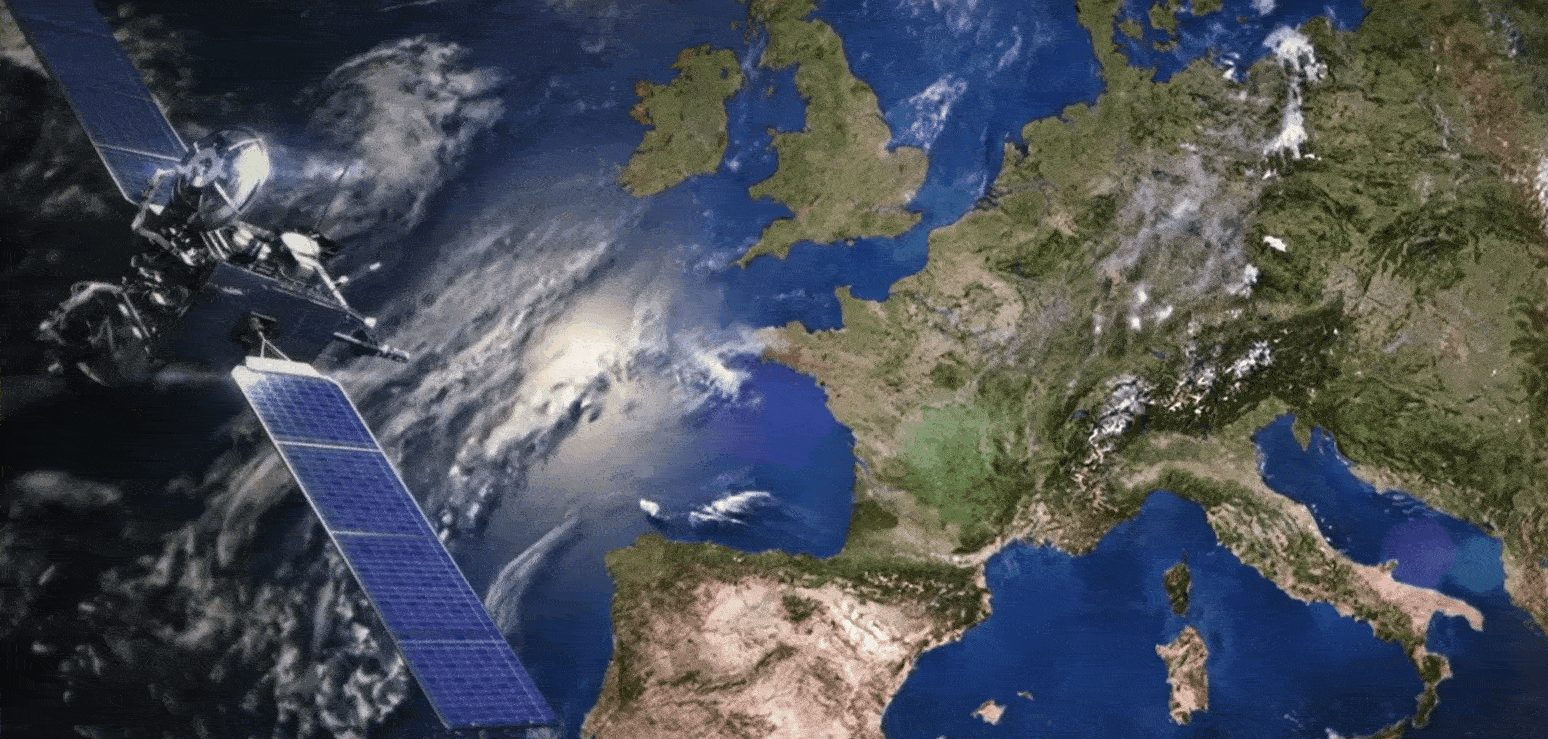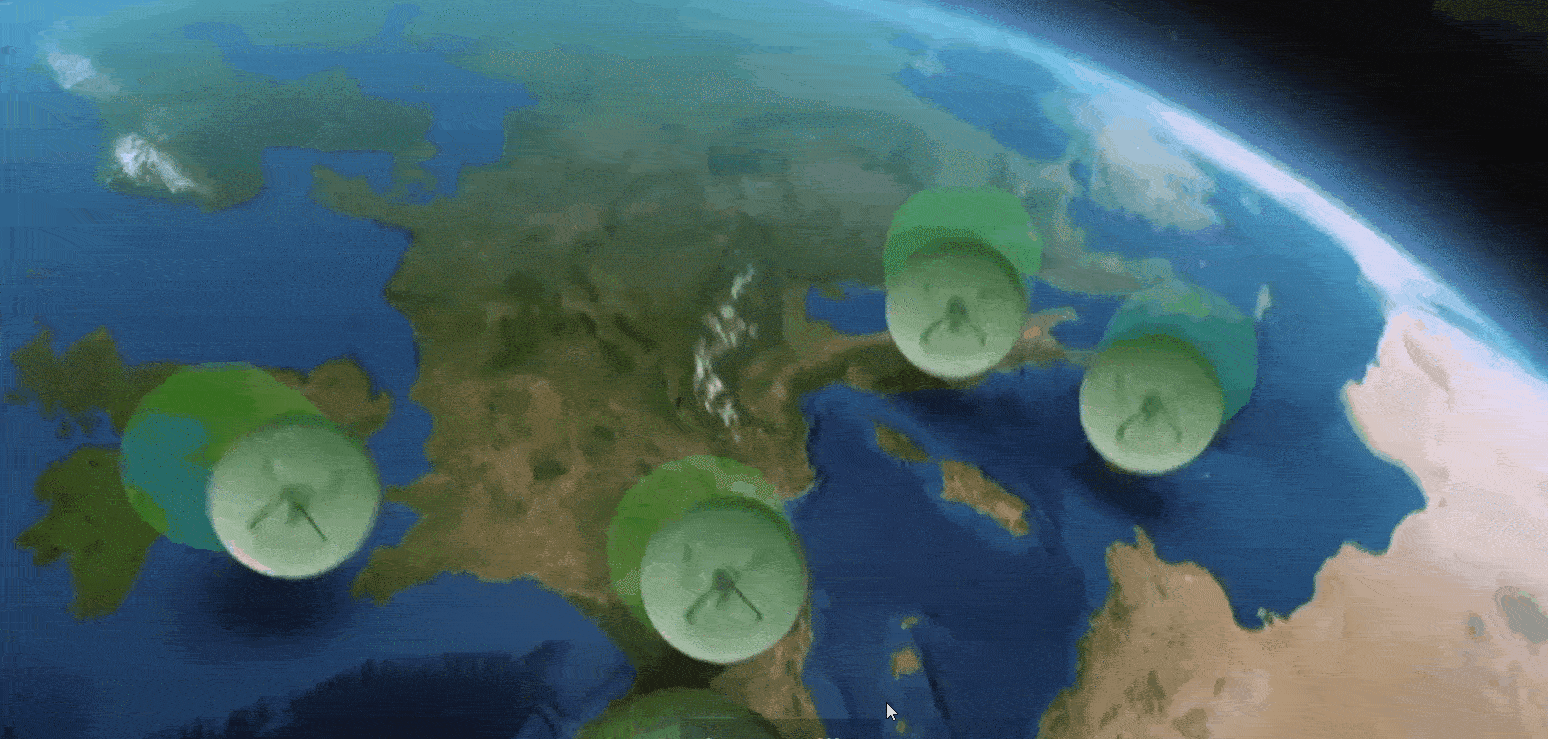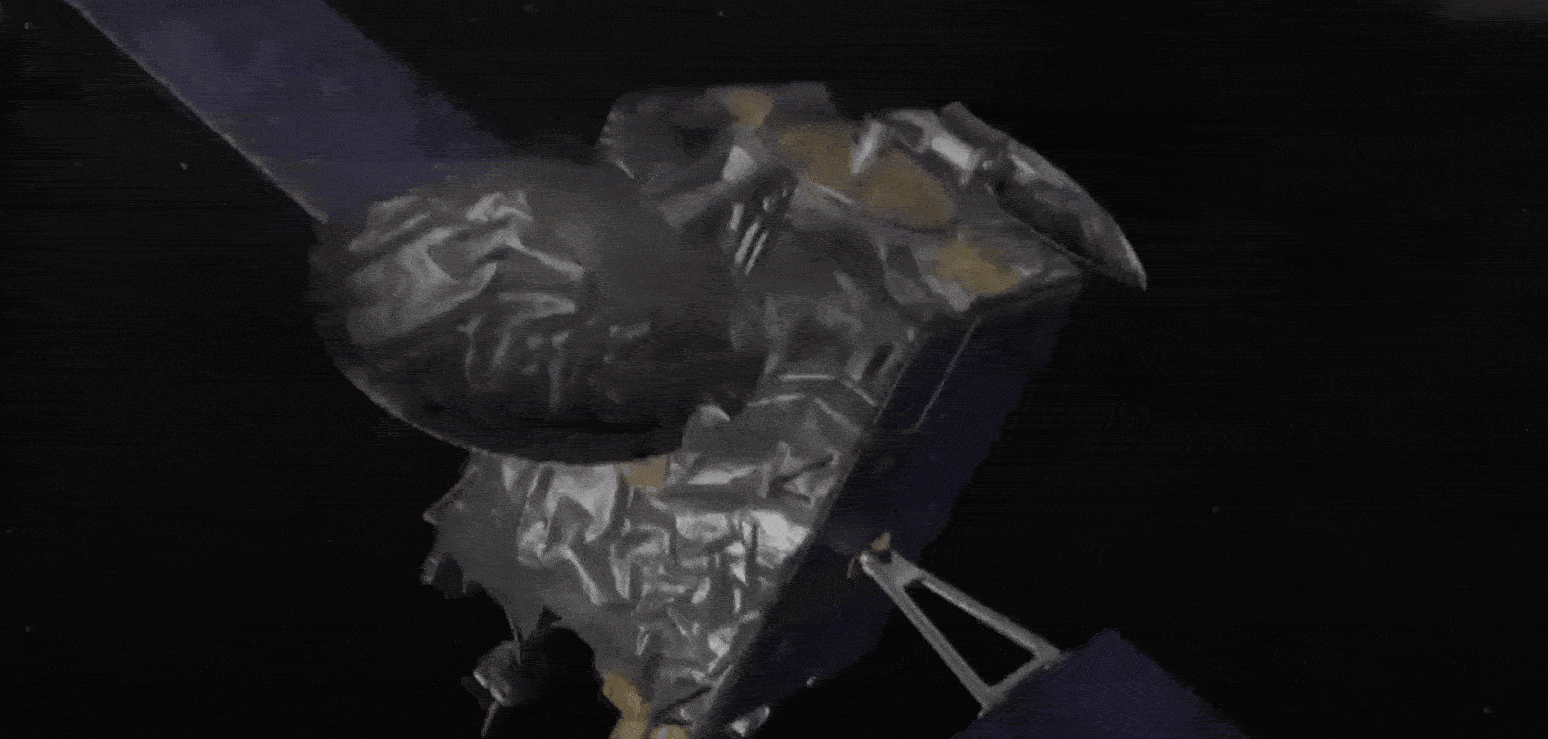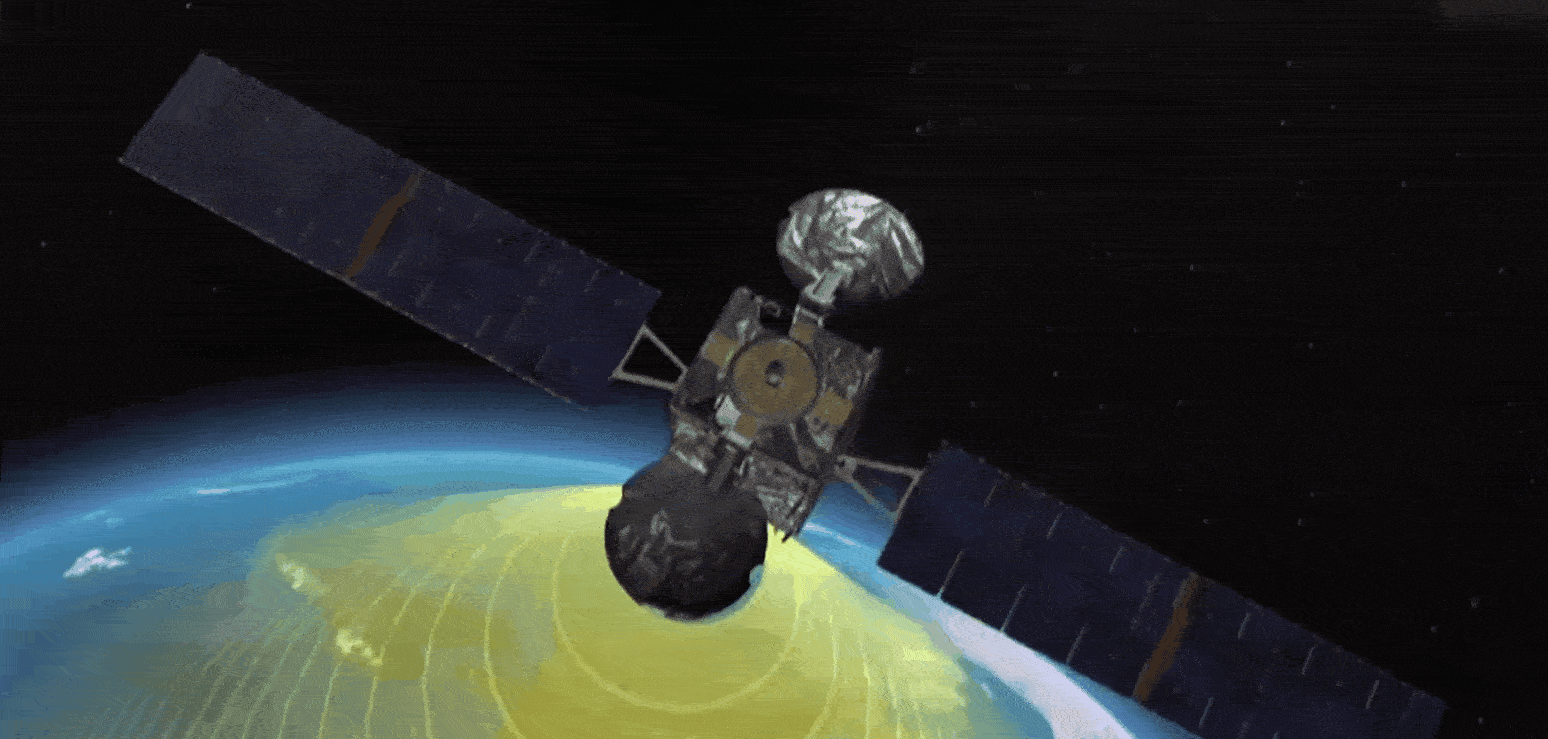
By using three satellites and a 40-strong network of ground stations, the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay System (EGNOS) sharpens the accuracy of GPS satnav signals across Europe.
The signals are guaranteed to the extremely high reliability set out by the International Civil Aviation Organisation standard, adapted for Europe by Eurocontrol, the European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation.
The EGNOS Open Service was launched in October 2009, for navigation applications where the safety of human life is not at stake, such as personal navigation, goods tracking and precision farming.

Today, following an arduous certification and verification process, the EGNOS Safety-of-Life Service has been declared operational, and suitable for use by European aviation.
“We are very proud of the large effort ESA put into EGNOS, and very pleased that it can now be used for the purpose it was initially designed for,” said Philippe Michel, head of ESA’s EGNOS project team.
“Through EGNOS, satellite navigation guidance is being made available for the first time in the vertical as well as horizontal domain,” explained Francisco Salabert of Eurocontrol.
“EGNOS offers the aviation industry the means to provide accurate and safe vertically guided approaches to smaller airports where a conventional precision landing system is not today economically viable.
“Its introduction will reduce delays, diversions and cancellations of flights into and out of these airfields while improving passenger safety.”
In order to use EGNOS for approaches, Air Navigation Service Providers must publish runway procedures and aircraft and operators have to be equipped with certified receivers and be approved for operations.

“Eurocontrol is coordinating EGNOS’s operational introduction across Europe,” Mr Salabert added. “Runway procedures have already been designed for various airports and heliports, with more on the way.
“On the airline side, we are encouraging early adaptors – called EGNOS pioneers.”
After six years in operation, the ‘WAAS’ US equivalent to EGNOS, is being used by more than 40 000 aircraft and more than 2000 procedures have been published.
Some 15 years in the making, EGNOS is the result of a tripartite agreement between ESA, the European Commission (EC) and Eurocontrol.
As initial EGNOS programme manager, ESA designed, qualified and procured the system from a consortium led by Thales Alenia Space France. Overall programme management passed to the EC in 2009. The system's day-to-day running is overseen by the Toulouse-based European Satellite Service Provider (ESSP).
Meeting the aviation industry’s demanding safety requirements, set by Eurocontrol, posed the real challenge for EGNOS’s Safety-of-Life service.
ESA produced much of the technical documentation needed for formal safety certification, while Eurocontrol performed independent monitoring of EGNOS performance.
The final system comes with an extremely high degree of integrity built in. The EGNOS signal is guaranteed to maintain a minimum level of accuracy, with just a one in 10 million chance of error.
If this reliability falls below this level then EGNOS users are alerted within six seconds.
ESA is now acting as the design and procurement agent on behalf of the EC for all major EGNOS system changes throughout its operational lifetime, as well as preparing for the next-generation EGNOS, expected around 2020.