
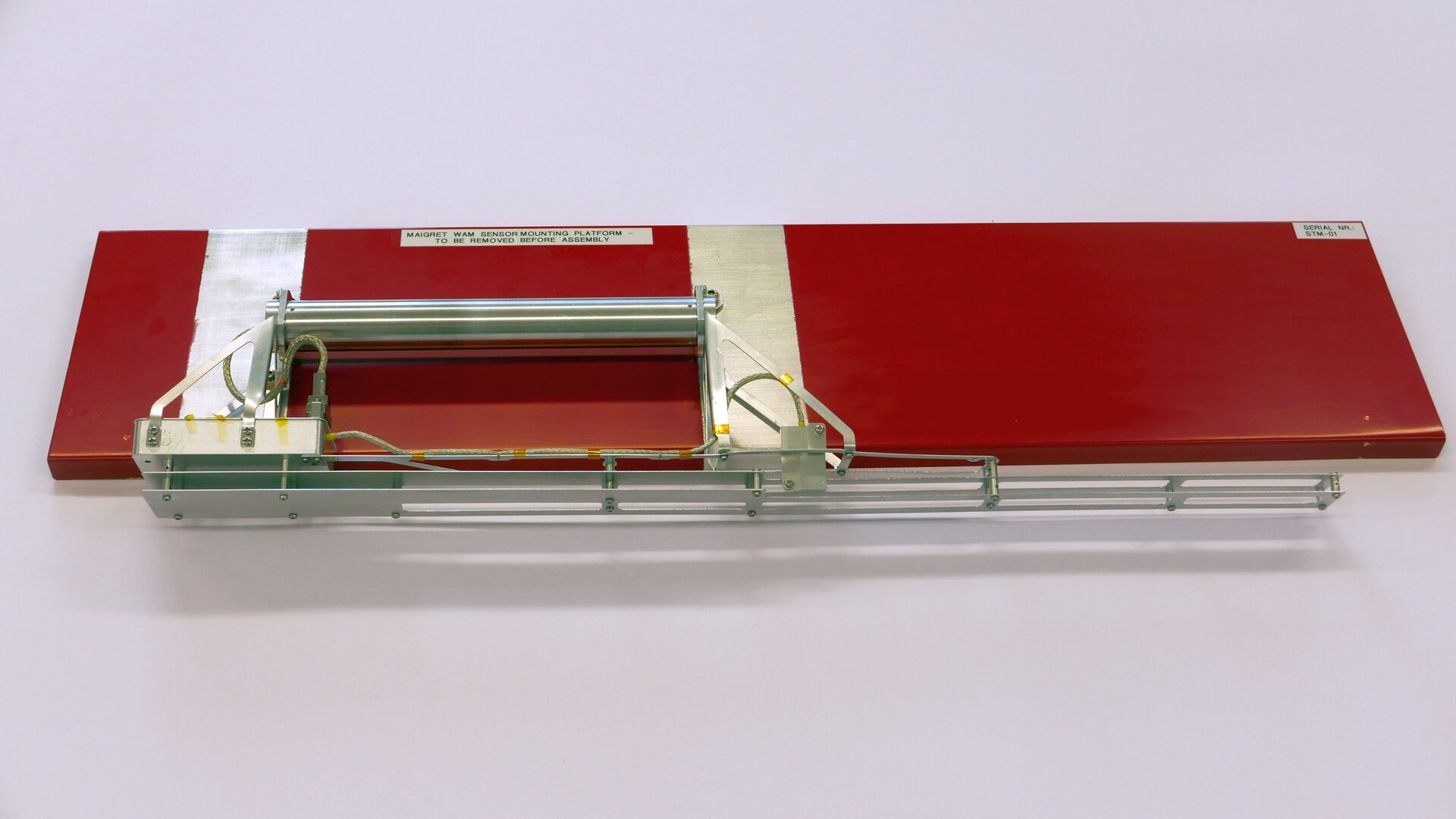
ExoMars electromagnetic sensor (structural model)
A structural and thermal model of the sensor for the electromagnetic wave analyzer that is a scientific instrument on the ExoMars lander platform.
Researchers want to investigate the existence of lightning discharges on Mars by measuring fluctuations in the electromagnetic field within the range of audible frequencies. Other observations have shown that lightning exists on Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, but Mars is still unknown.
The ExoMars rover and platform will launch to the Red Planet in 2020. At its landing site on Mars, Oxia Planum, the Czech-made electromagnetic wave analyser, that is part of the MAIGRET instrument mounted on the Kazachok platform, will scan for electromagnetic frequencies that are typical of lightning discharges. In addition to listening for lightning, the platform will also study the climate, atmosphere, radiation, and the possible presence of subsurface water ice in the landing site and surrounding areas.





