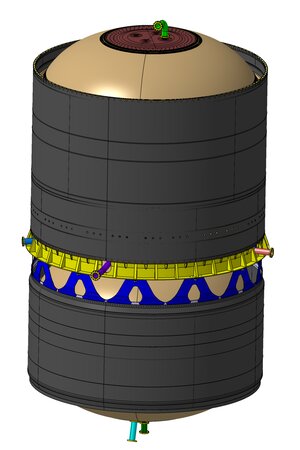
Flint: Phoebus fluid and structural thrust frame
Thank you for liking
You have already liked this page, you can only like it once!
Phoebus fluid and structural thrust frame (known as Flint) hub made using additive manufacturing techniques.
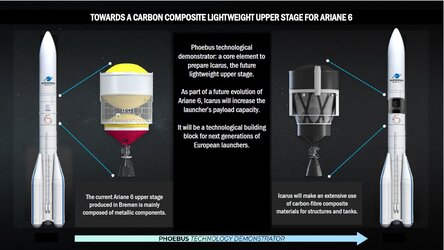
Phoebus is a European Space Agency (ESA) project together with ArianeGroup and MT Aerospace. It aims to assess the feasibility and benefits of replacing the metallic tanks on ESA’s Ariane 6 upper stage with carbon-fibre reinforced-plastic tanks. While this lightweight material offers the possibility of saving several tonnes of mass, such an approach has never been implemented before and presents significant technical challenges.
Project Phoebus is making significant progress in demonstrating that carbon-fibre reinforced-plastic is suitable for rocket tanks. These tanks are integral to the rocket stage, connecting to the engine and adding structural stability to endure powerful launch forces.
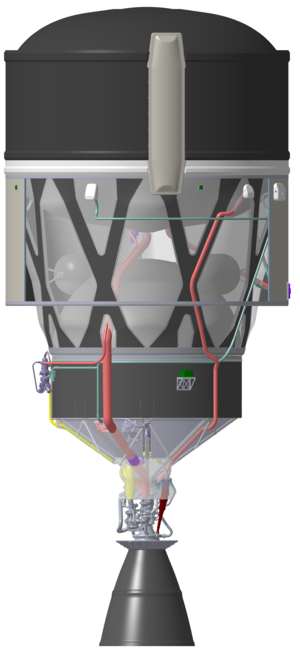
The Ariane 6 rocket upper stage’s engine is attached to the oxygen tank via a “thrust frame” with pipes running down it from the tanks to the engine. ArianeGroup has come up with an innovation that allows the fuel pipes to be a part of the thrust frame structure – two functions in one part equals a lighter launcher. This innovative thrust frame started production in December 2024, at various suppliers in Germany, with the assembly to be performed at ArianeGroup in Bremen, Germany. This innovative thrust frame is now in production, using the best techniques available worldwide such as including additive manufacturing for the central hub. A full-scale demonstrator with integrated pipes will be ready next year for integration onto the Phoebus liquid oxygen tank.
The central core of ESA’s Ariane 6 rocket runs on liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen, two very different molecules, so the Phoebus project is developing and producing two versions of the same carbon fibre tank concept.
Phoebus is part of ESA’s Future Launchers Preparatory Programme (FLPP), that helps develop the technology for future for space transportation systems. By conceiving, designing and investing in technology that doesn’t exist yet, this programme is reducing the risk entailed in developing untried and unproven projects for space.
-
CREDIT
ArianeGroup -
LICENCE
ESA Standard Licence

Phoebus thrust frame
Phoebus concept
Phoebus tank structure concept

Phoebus testing