Fast and Efficient Asteroid Geodesy with MasconCubes
The determination of the internal mass distribution of celestial bodies is essential for understanding their structure, formation history, and potential for resource extraction. Classical methods such as mascon models, spherical harmonics, and polyhedral gravity approaches rely on precise shape models or assume homogeneity, making them less flexible for irregular bodies.
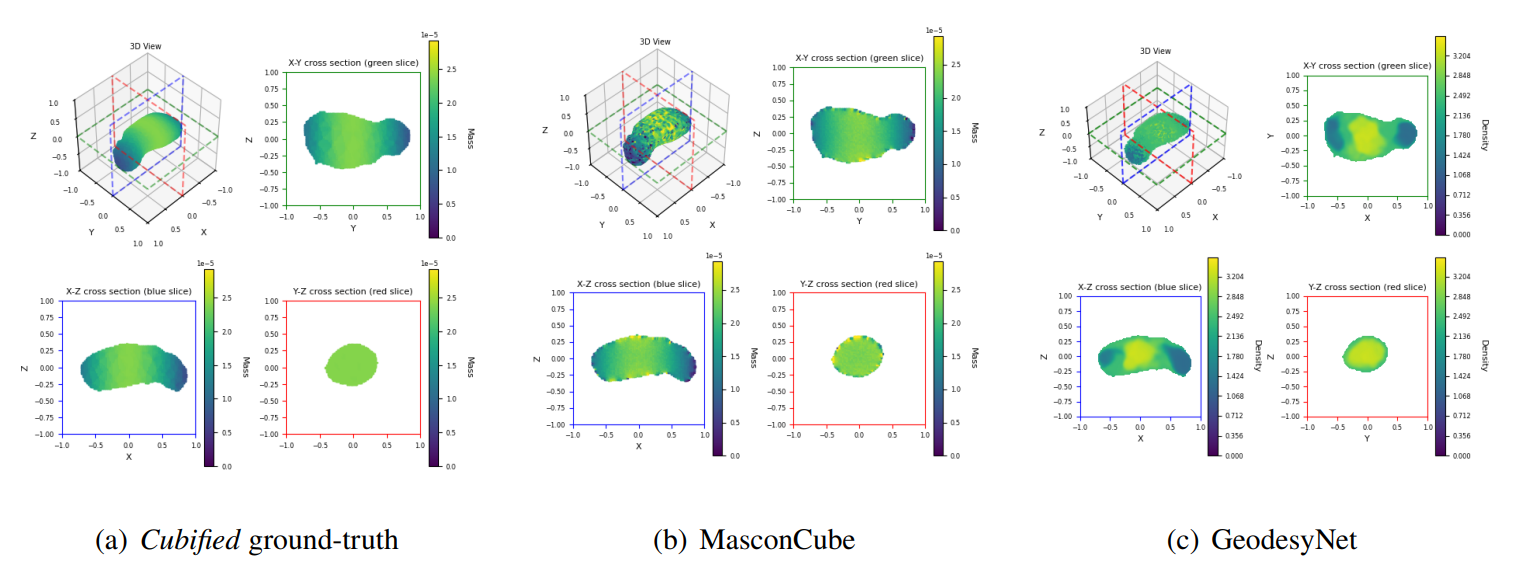
MasconCubes provide a machine-learning-based alternative that directly regresses the mass values of a grid of mascons, bypassing the need for computationally expensive density field integration. This allows for a significant reduction in training time and data requirements compared to previous approaches.
Project Overview
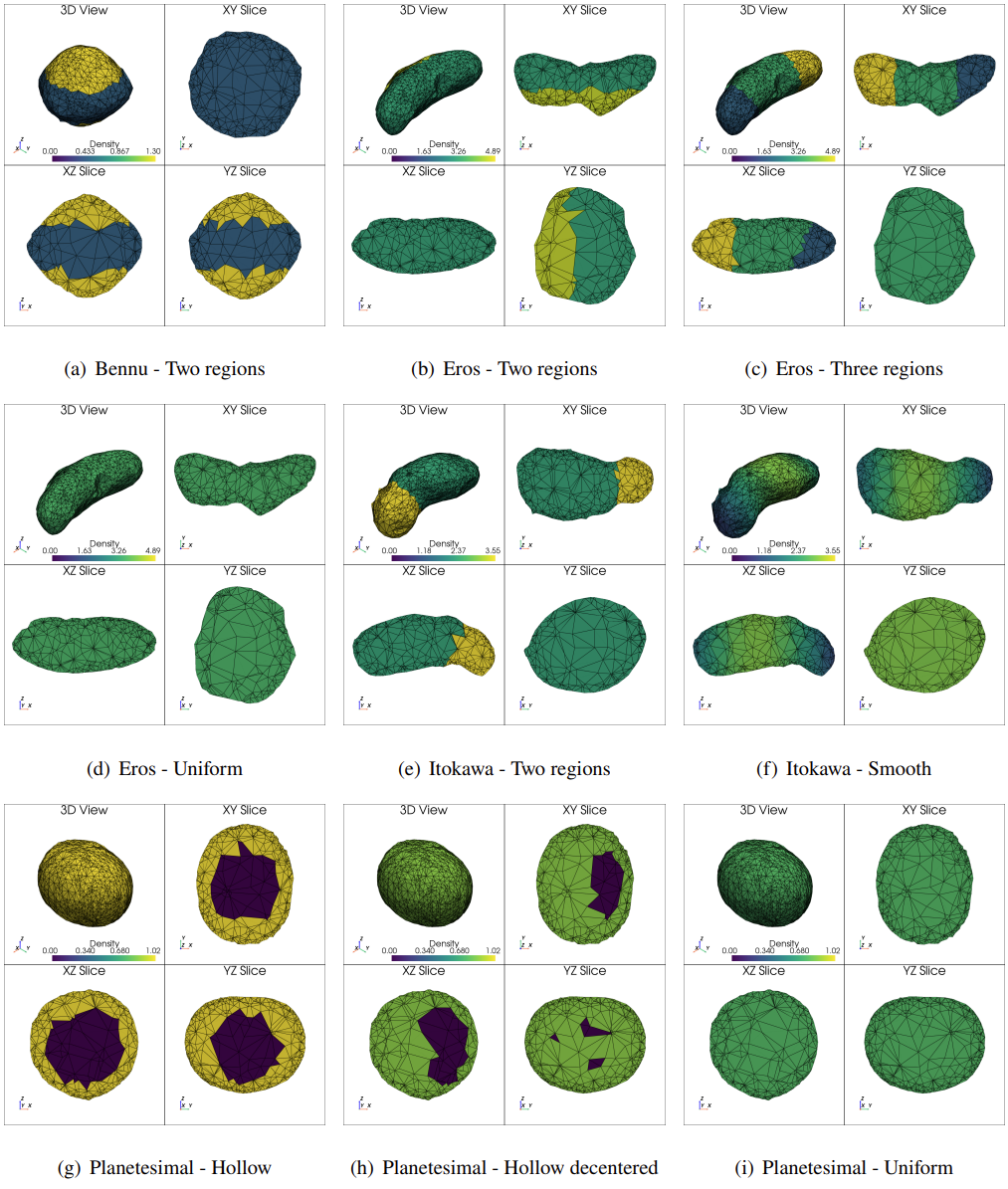
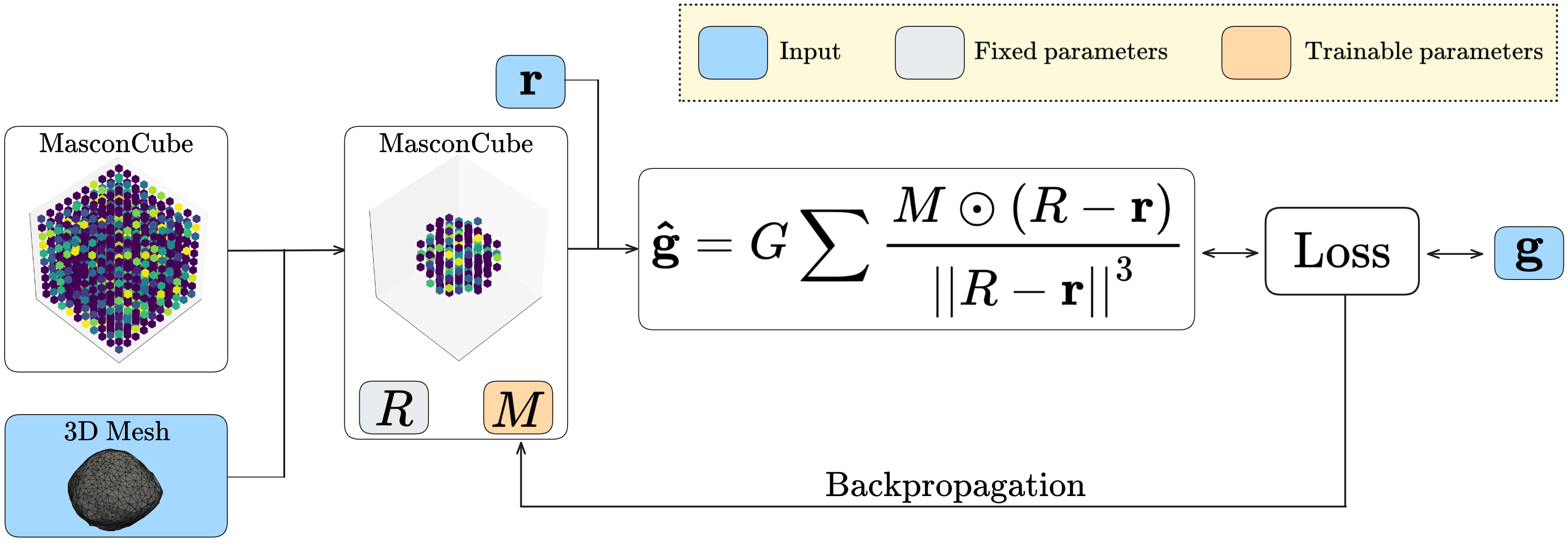
MasconCube builds upon GeodesyNet, which introduced neural density fields to infer asteroid geodesy. Instead of learning an implicit representation of density and integrating it to obtain gravity, MasconCubes directly learns discrete mass values assigned to a grid of mascons. This leads to:
- 40 times faster training since integration is no longer required.
- Better performance across a comprehensive set of metrics, including gravitational acceleration accuracy and internal structure reconstruction.
- More efficient data usage, as fewer observations are needed for accurate reconstructions.
- A direct and interpretable mass distribution, avoiding the implicit density representation of GeodesyNet.
As GeodesyNets, MasconCubes work by minimizing the difference between predicted and observed gravitational accelerations, efficiently adjusting the mascon grid to best match real or simulated measurements.
References
- Izzo, D. and Gómez, P., 2021. Geodesy of irregular small bodies via neural density fields: geodesyNets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.13031. https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13031
- Martin J, Schaub H. Physics-informed neural networks for gravity field modeling of small bodies. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, 2022, 134(5): 46
- Martin J, Schaub H. The Physics-Informed Neural Network Gravity Model Generation III. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2025, 72(2): 1–47
- Tricarico P. Global gravity inversion of bodies with arbitrary shape. Geophysical Journal International, 2013, 195(1): 260–275.