Wet era on early Mars was global
Conditions favourable to life may once have existed all over Mars. Detailed studies of minerals found inside craters show that liquid water was widespread, not only in the southern highlands, but also beneath the northern plains.
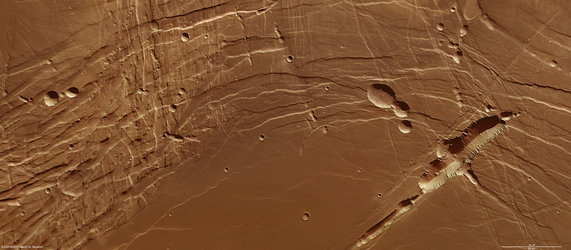
ESA’s Mars Express and NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have discovered hydrated silicate minerals in the northern lowlands of Mars, a clear indication that water once flowed there.

The spacecraft have previously discovered thousands of small outcrops in the southern hemisphere where rock minerals have been altered by water. Many of these exist in the form of hydrated clay minerals known as phyllosilicates, and indicate that the planet’s southern hemisphere was once much warmer and wetter than it is today.
However, until this week, no sites with hydrated silicate minerals had been found in the northern lowlands, where thick blankets of lava and sediments up to several kilometres thick hamper efforts to probe the underlying bedrock.
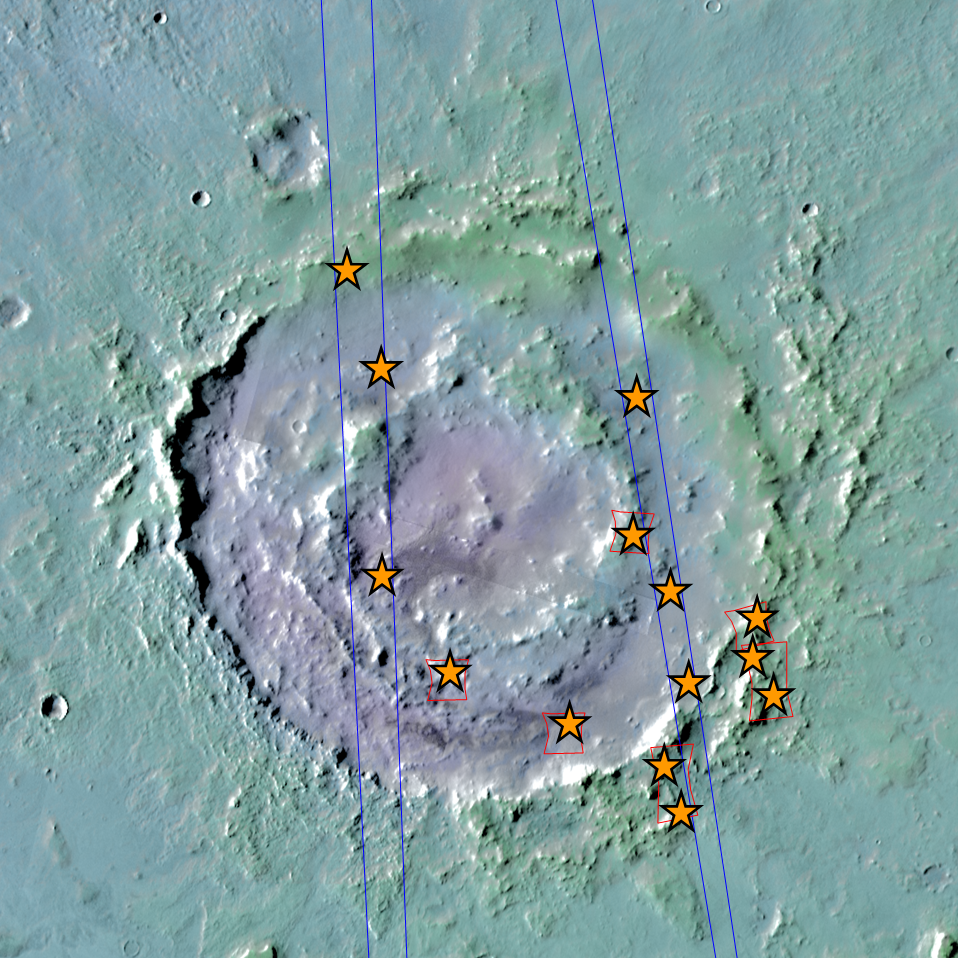
The first hints that there may be hydrated silicates beneath the northern plains were provided by Mars Express’ OMEGA sensor. However, the outcrops were small and more detailed observations were required to confirm their presence. The OMEGA team sifted higher resolution data from a sensor on NASA’s orbiter.

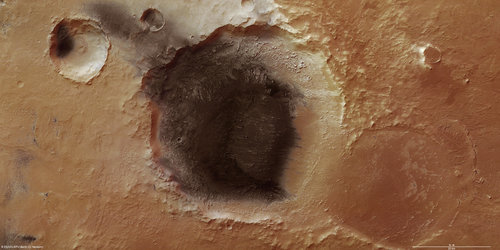
Their search concentrated on 91 sizeable impact craters where incoming asteroids had punched down several kilometres, exposing ancient crustal material. As reported this week in the journal Science, at least nine craters were found to contain phyllosilicates or other hydrated silicates.
These minerals, which formed in wet environments on the surface or underground, were identical to those found in the southern hemisphere.
“We can now say that the planet was altered on a global scale by liquid water more than 4 billion years ago,” says John Carter, University of Paris, the report’s lead author.
With the small sample of widely scattered sites, it is difficult to draw conclusions about the type of environment all that time ago. However, the nature and locations of the minerals provide some clues.
“They are rich in iron and magnesium, but less in aluminium. Together with the close proximity of olivine, which is easily modified by water, this indicates that the exposure to water lasted only tens to hundreds of millions of years,” says Jean-Pierre Bibring, the OMEGA Principal Investigator from the University of Paris.
Although Mars’ potential habitability did not last long, remarkably its record is still preserved in phyllosilicate-rich spots.
A number of scientists have suggested that a shallow ocean subsequently covered the lava-coated northern plains. However, no evidence in support of this is provided by the new results.
“Our studies do not find any signs of the lava plains in the north being altered by water,” says Dr Bibring.
On a positive note, the new results may suggest sites for future landers because evidence for water during the early history of Mars suggests that conditions may have been favourable for the evolution of primitive life.
“These results reveal the history of Mars derived from the planet’s mineralogy,” says Olivier Witasse, ESA Project Scientist for Mars Express. “It is another example of the fruitful cooperation between European and American scientists.”