Craters and channels in Hephaestus Fossae
The High Resolution Stereo Camera on ESA’s Mars Express orbiter has obtained images of Hephaestus Fossae, a region on Mars dotted with craters and channel systems.
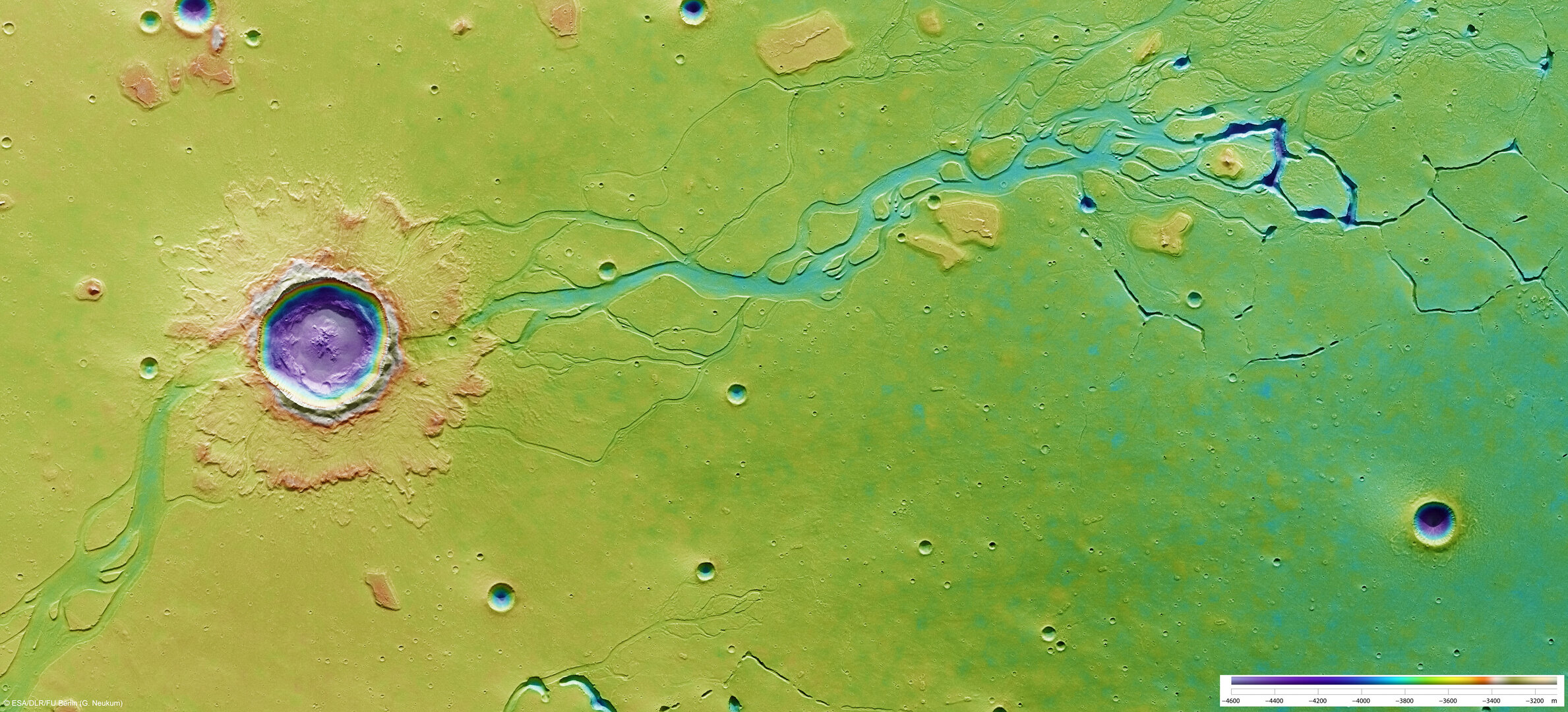
Hephaestus Fossae lies at about 21°N and 126°E on the Red Planet. Named after the Greek god of fire, it extends for more than 600 km on the western flank of Elysium Mons in the Utopia Planitia region.
Obtained on 28 December 2007, the images have a ground resolution of about 16 m/pixel. They show that the region has channel systems of unknown origin.
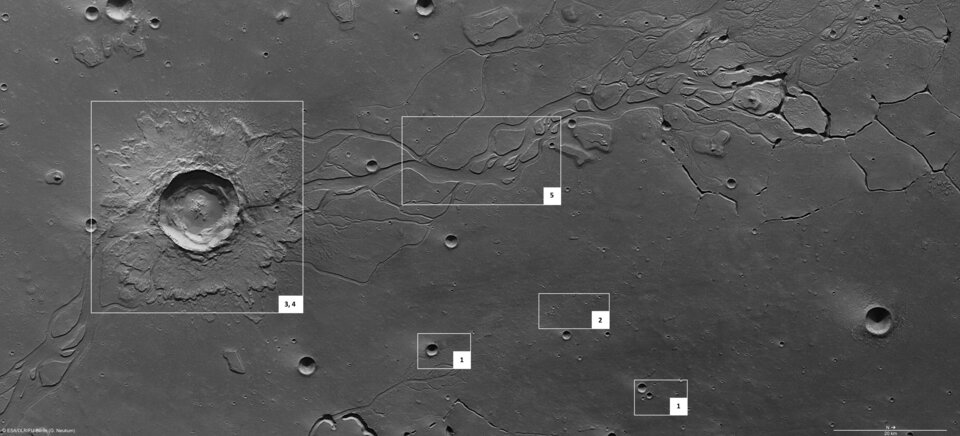
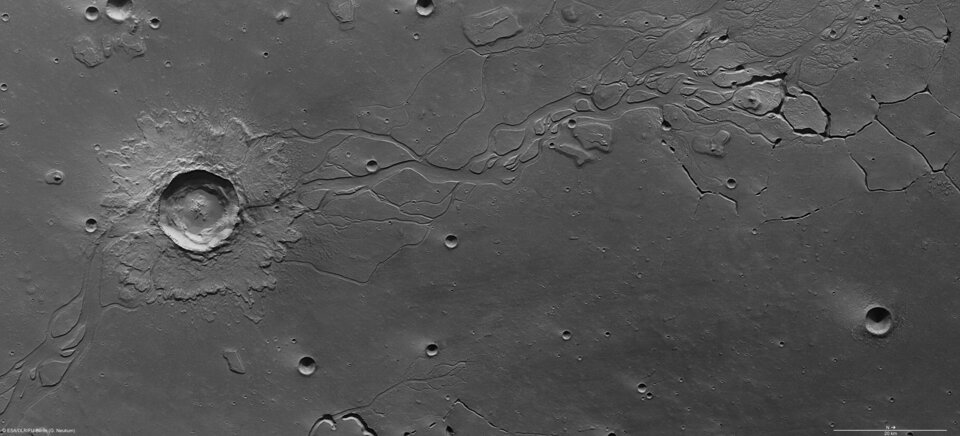
The images cover 170 x 80 km, an area almost as large as Montenegro. The surface is mostly smooth, and is covered by several small impact craters 800-2800 m in diameter. Smaller craters are scattered across the entire region.

The left side of the image shows a large impact crater measuring 20 km in diameter. Covering an area of approximately 150 sq km, a crater of this size on Earth could harbour cities such as Bonn or Kiel. In contrast to the smaller craters, it shows a blanket of ejecta with flow forms surrounding the rim.
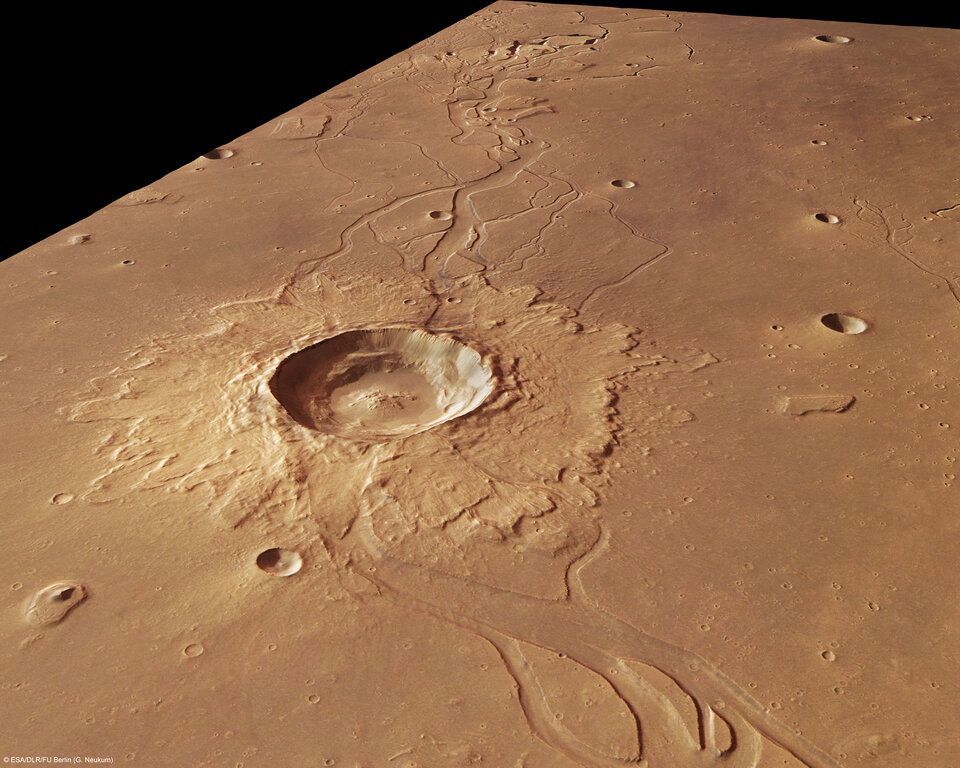

The large craters were formed when loose, soft material was ejected due to impact, and the smaller ones formed due to secondary impacts, when consolidated material was ejected in a ballistic path and impacted the original crater at varying distances.

Most martian water exists in the form of subsurface ice. The presence of a blanket of ejecta and outflow channels around the crater suggest that the primary impact may have penetrated the surface enough to melt a buried frozen water reservoir.

Since the smaller impact craters show neither a blanket of ejecta nor any kind of outflow channel, they did not impact the surface strongly enough to reach the subsurface ice. It is possible to calculate the depth of a possible frozen water reservoir beneath the surface by determining the depth of the impact craters.

The colour scenes have been derived from the three HRSC-colour channels and the nadir channel. The perspective views have been calculated from the digital terrain model derived from the stereo channels. The anaglyph image was calculated from the nadir and one stereo channel. The black and white high resolution images were derived form the nadir channel which provides the highest detail of all channels.

For more information on Mars Express HRSC images, please read our updated FAQ (frequently asked questions).
















