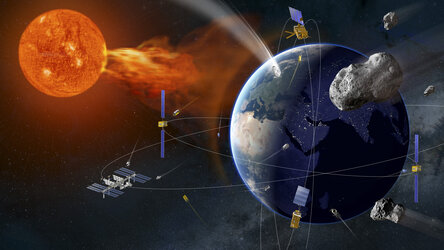
Space Safety Programme at 2022 Ministerial Council
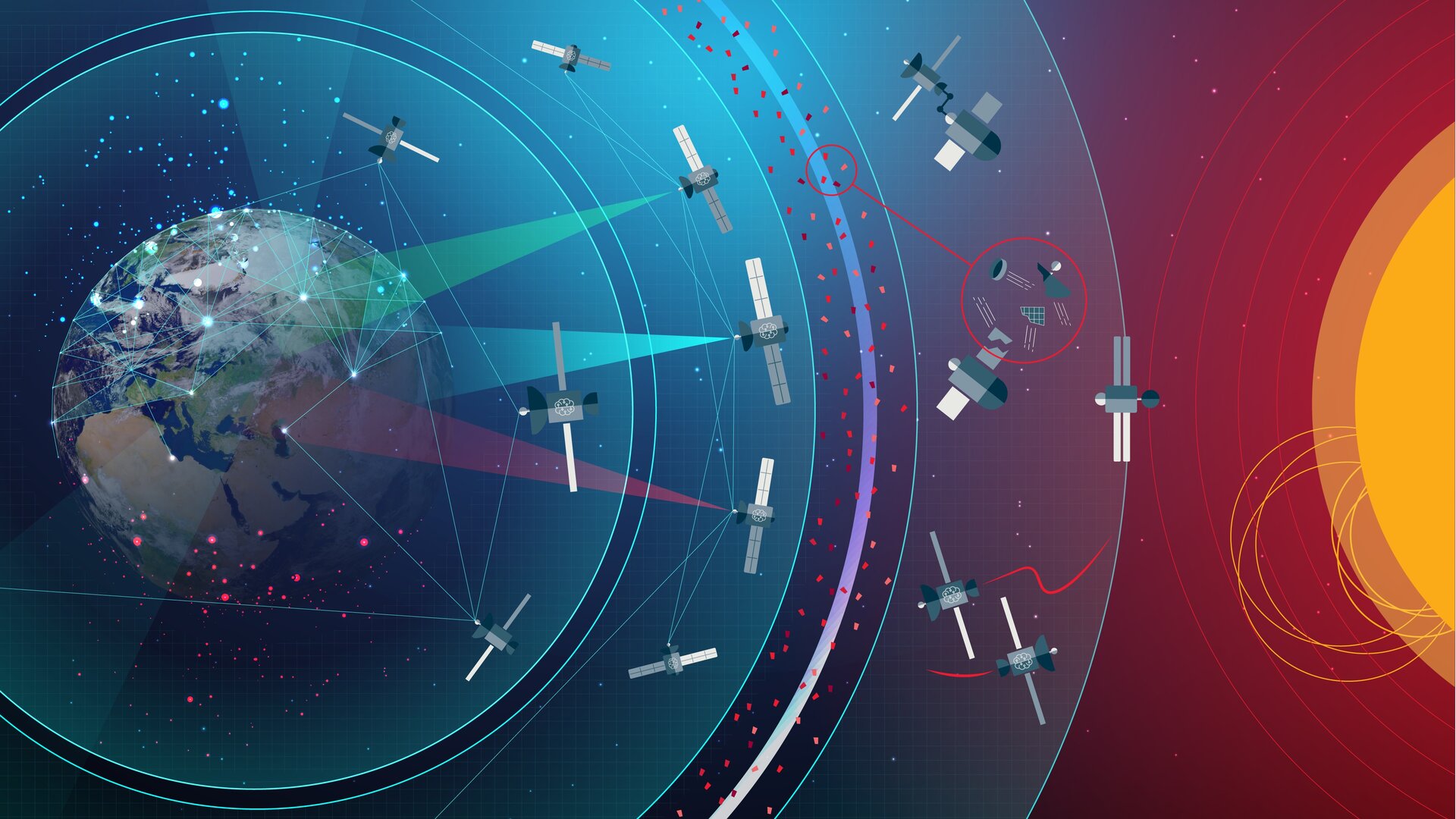
Europe is increasingly reliant on deeply connected infrastructure in space and on the ground. Our growing economy depends on services and data provided by satellites, but space hazards, human-made and natural in origin, are a risk to these vulnerable systems.
ESA’s Space Safety Programme is dedicated to the protection of Europe and its economies from disruption to this critical infrastructure and fostering new commercial opportunities in the European space sector.
Main Goals:
At ESA’s upcoming 2022 Ministerial Conference, the Space Safety Programme is proposing activities to help ensure that, by 2030, Europe is capable of:
- monitoring space weather, assessing risks from solar events and utilising an early warning system that provides services tailored to European users
- obtaining early warnings of asteroids on a collision course with Earth larger than 40 metres at least three weeks in advance
- deflecting asteroids smaller than 500 metres at least ten years in advance of a potential collision with Earth
- becoming a key player in a growing market of space traffic coordination
- introducing a “Zero-Debris Approach” to space technologies and a circular economy in space
- systematically assessing the environmental impacts of space activities and proposing greener technologies
Cornerstone missions:
The Programme’s highest priority is the continuation of the three Cornerstone missions: Vigil, Hera and ClearSpace-1. All three feature large-scale involvement from European industry and will demonstrate a range of innovate new technologies.
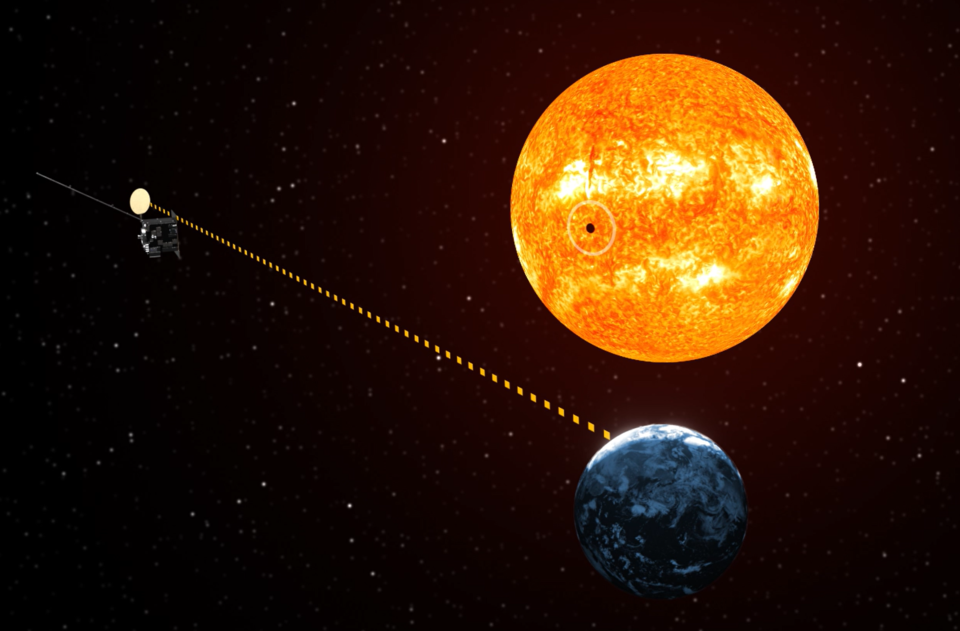
Vigil
From its unique vantage point in space, ESA’s Vigil mission will observe the side of the Sun and send near real-time data on potentially hazardous solar activity before it rotates into view from Earth. This will make it possible to forecast the changing space weather environment and send warnings of oncoming solar storms as much as four to five days in advance of their arrival at Earth.
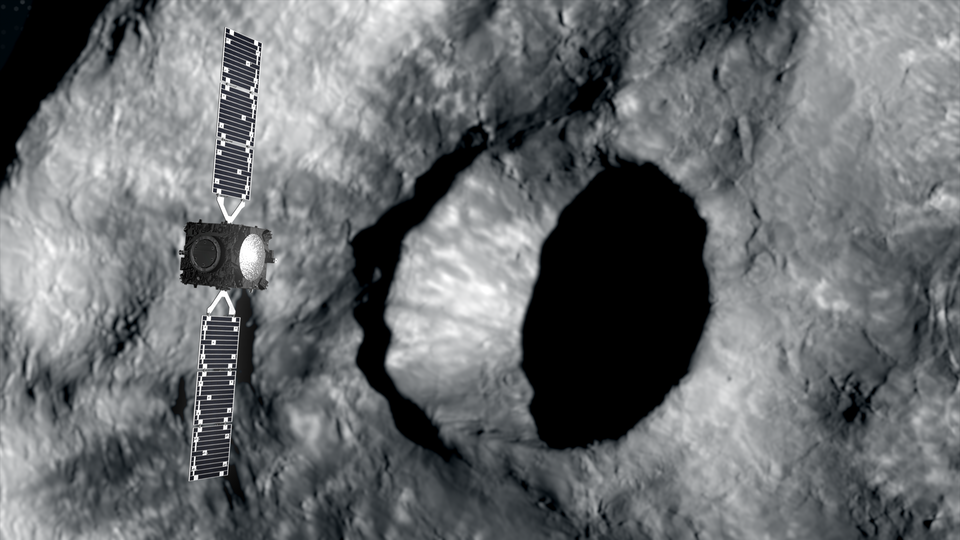
Hera
Hera is the European contribution to the international “AIDA” collaboration with NASA – the world’s first test of asteroid deflection. NASA’s DART mission recently collided with the asteroid Dimorphos. Hera, due for launch in 2024, will perform a detailed post-impact investigation to gather crucial scientific data, validate the deflection technique and demonstrate new technologies such as autonomous, close-proximity CubeSat operations.
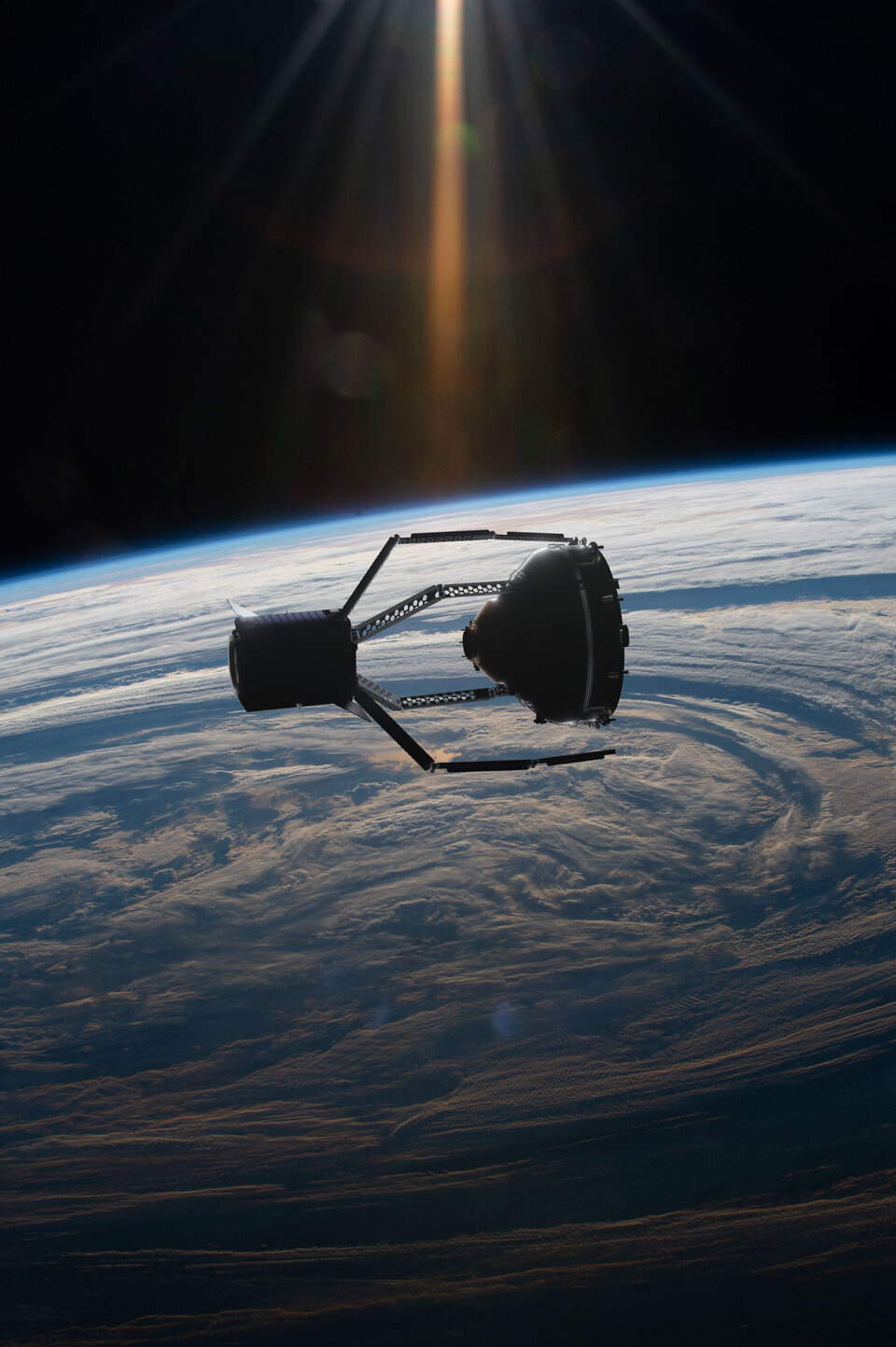

Clearspace-1
ClearSpace-1 is the world’s first mission to remove an existing piece of space debris from orbit – a 112kg defunct rocket part. With its four robotic arms, Clearspace-1 will capture the object and perform a controlled atmospheric re-entry. The mission is being procured as a service contract with the Swiss start-up ClearSpace SA and is supported by an industrial consortium. The mission will help establish a new market for in-orbit servicing and debris removal. Clearspace-1 is in development and planned for launch in 2026.
New Proposals:
Europe’s first commercial In-Orbit Servicing mission
At the upcoming Ministerial Council, ESA is proposing support to boost European competitiveness in the field of “in-orbit servicing” through the implementation of a European industrial servicing mission with a real customer spacecraft by 2028.
Assets in space are crucial for many modern activities. It is sensible and profitable to extend their lifetime as much as possible through in-orbit servicing activities such as repairs, upgrades, refuelling or recycling. The potential market revenue for companies specialised in sustaining the space environment and providing in-orbit services is on the order of trillions of euros and ESA’s Space Safety Programme will kick-start European industrial activity in this area.
COSMIC
COSMIC is the Ministerial Council proposal to expand the Space Safety Programme’s core activities. It will also include new small satellite and nanosat missions that can be implemented quickly by European small and medium enterprises (SMEs), start-ups and academia.
These missions represent an agile way to get innovative space safety sensors into action as quickly as possible and foster the commercialisation of their implementation and operation. The European space safety market will be further boosted by a dedicated Competitiveness Segment.
The following pages contain in-depth information on the individual COSMIC project proposals and the Core Activities of the Space Safety Programme.
The Space Weather new proposals and core activities aim to protect space- and ground-based infrastructure from interference or damage caused by solar activity.
The Planetary Defence new proposals and core activities will improve how we survey the sky for potentially hazardous asteroids and explore technologies for mitigating their risk.
The Space Debris new proposals and core activities will improve our knowledge of the space debris environment and help us better protect active satellites from collisions with fragments of debris.
The Clean Space new proposals and core activities will explore ways to minimise or eliminate the lasting impact of space missions and satellites at the end of their lives.
The Competitiveness Segment is intended to broaden the scope of space safety in commercial markets, by speeding up the process by which innovative ideas go from technologies to products and services.