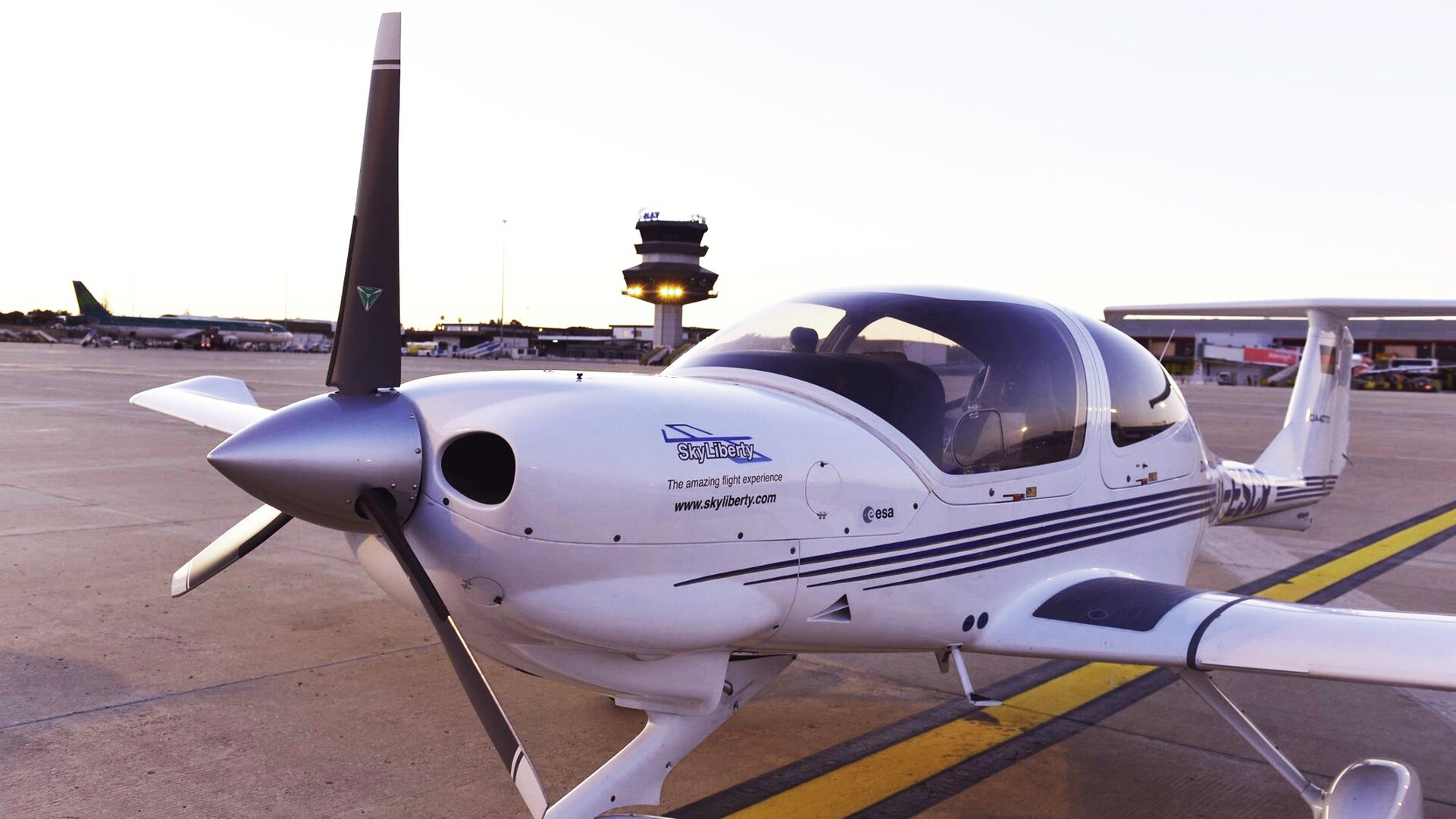
Space-enabled app for pilots takes to the skies
An app that integrates navigational data and weather conditions to improve flight safety for pilots has been launched. Its inventors hope to have a full commercial version on sale by the end of the year.
Preparing a flight plan can be a long and arduous task for pilots, who have to process large quantities of information on weather patterns, ground topology, the flights of other aircraft and fuel consumption.
The SkyLiberty aeronautical navigation support service, developed in partnership between ESA and a Belgian company called ESNAH, aims to overcome these difficulties using a single device.
It integrates aeronautical, geographical and meteorological data with information on airspace regulations.
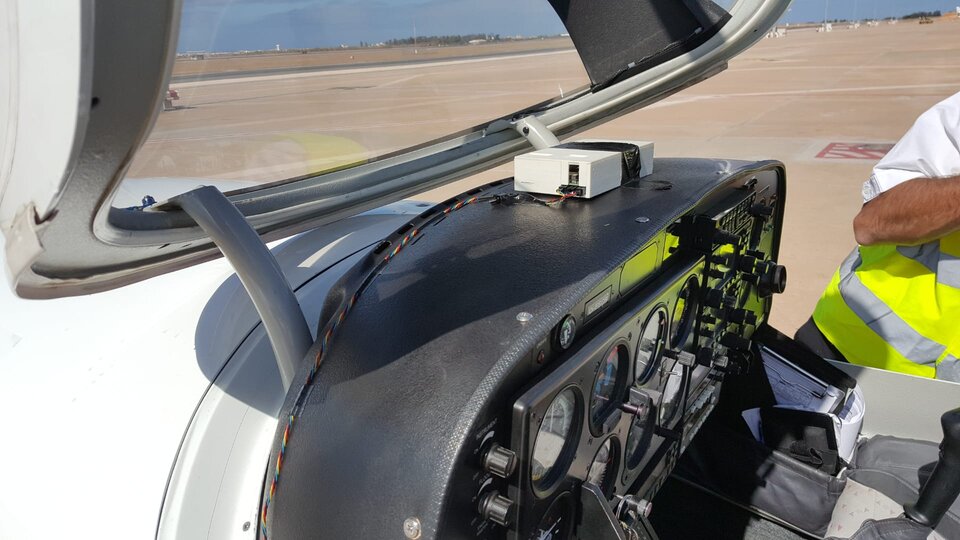

SkyLiberty helps pilots to devise a tailored flight plan. Once airborne, the device informs them of their precise location and the weather conditions ahead.
Because the device is programmed with information on airspace regulations, SkyLiberty can alert pilots and their ground-based support if the aircraft starts to drift towards restricted airspace, such as the areas around commercial airports or buildings such as nuclear reactors.
The device enables two-way communication between the pilots and the ground. Flying schools and air traffic control could use it to track the flight paths of light aircraft and to talk to pilots.
All this is made possible thanks to the combination of satellite communication and data from the global navigation satellite system.
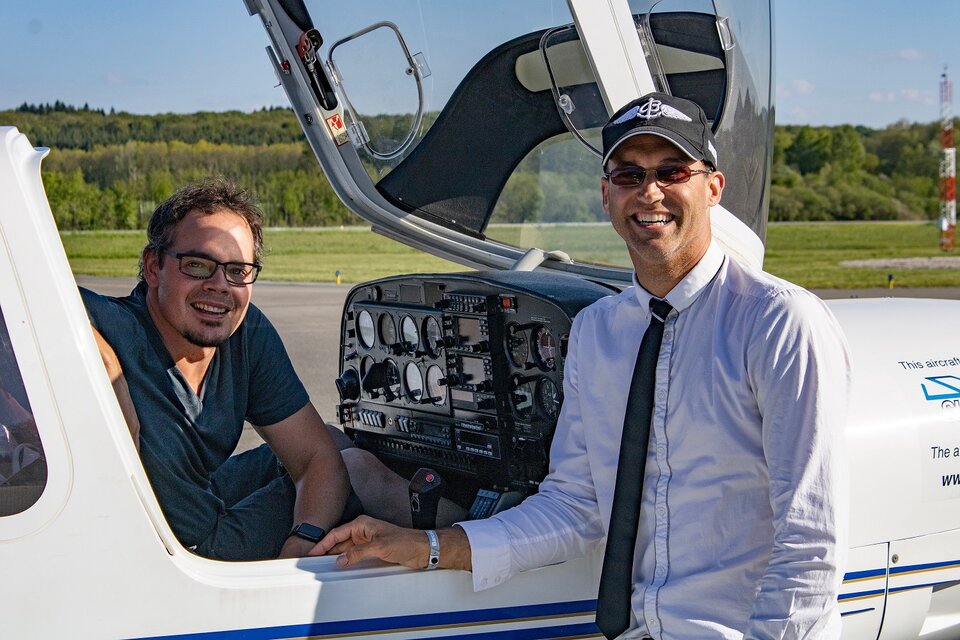

The device was recently extensively tested by two pilots – the inventor of the device and the ESA project manager – who used the prototype technology to fly aboard a four-seater Diamond DA40 on a four-day 7,400-kilometre journey from and to Belgium via France, Spain, Portugal, the Canary Islands and Morocco.
Most of this flight was over water and poorly connected regions – ideal for testing the reliability of the satellite link.
The journey was faster than expected and consumed 15% less fuel than predicted, which was partly because the pilots could use the SkyLiberty device to search for the best wind while airborne.
Arnaud Runge, who is the SkyLiberty project manager at ESA and holds a professional pilot licence, said: “SkyLiberty is offering new opportunities for general aviation and business jets pilots, who often operate without all the enormous logistics support and tools available within large airlines. SkyLiberty shows how space can play a role and make travel by air safer, greener and more effective.”
The Belgian company ESNAH was set up seven years ago at ESA’s business incubation centre in Redu. It joined ESA’s integrated applications promotion, which is an initiative to develop new commercially promising space-based applications or services. The initiative forms part of ESA’s programme of Advanced Research in Telecommunications Systems (ARTES).
Nicolas Hanse, general manager and founder of ESNAH, said: “We started in business in 2012 and, because we were very young company, we needed to build credibility. ESA has helped us to do that. The ESA project manager helped us to get structured and successfully pass each step in our plan. We are now getting a lot of interest from civil aviation and other aeronautical entities.”















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland


























