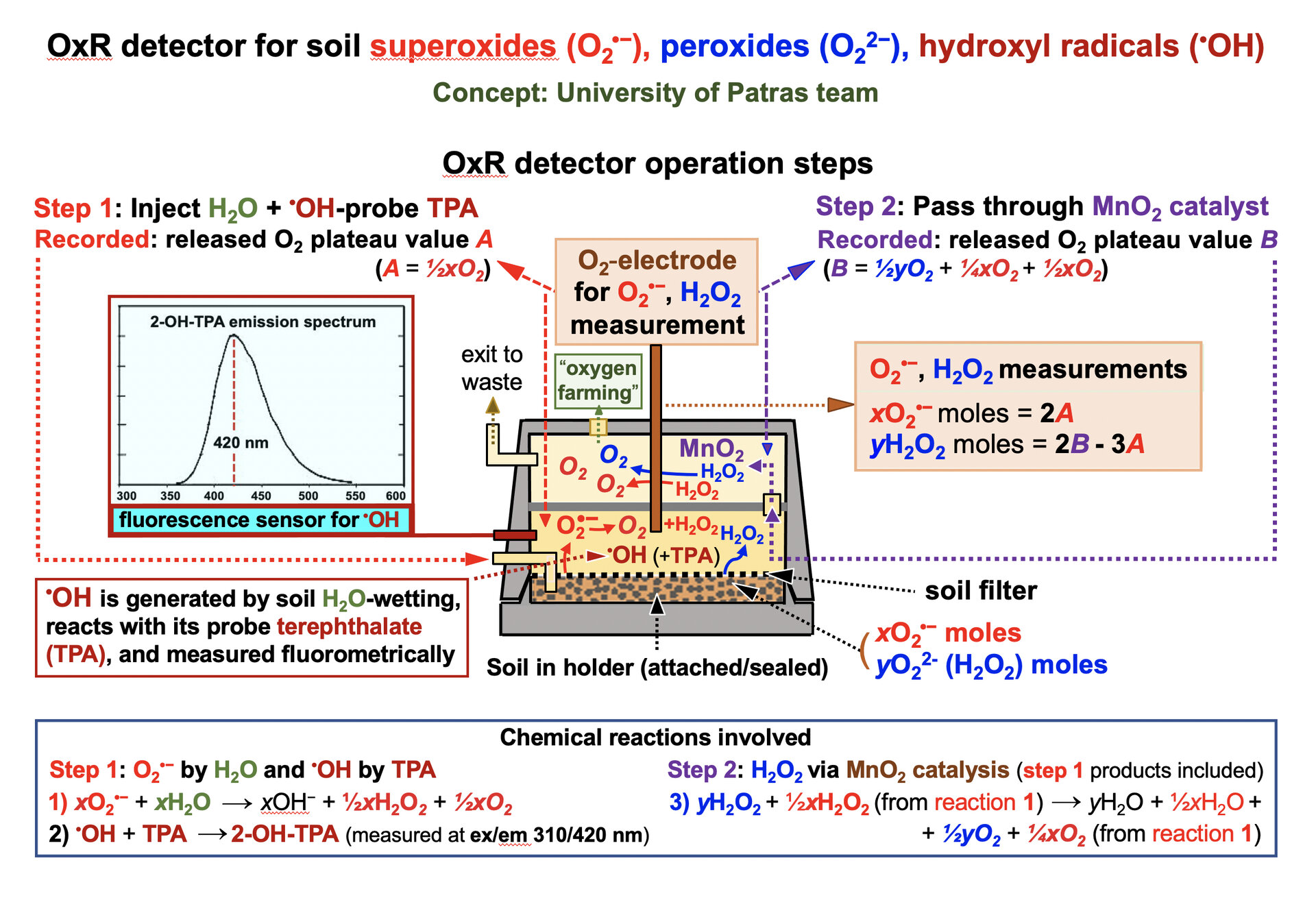
Reactive oxygen species detector concept
H2O-wetting of soil samples by the detector, causes dissolution of metal superoxides (O2•−) and peroxides (O22−, converted toH2O2 after hydrolysis) and release of O2 in sequential steps 1 and 2 (“oxygen farming” concept). OxR detector’s O2-electrode records the respective plateau reaching released O2 values A and B (corresponding to the released O2 moles, shown in red and blue bold italics to designate their origin from respective reactions 1 and 3). Values A and B are converted to yH2O2 and xO2•− moles by insertion to math equations derived from the stoichiometries of reactions 1 and 3. Hydroxyl radicals (•OH), which are generated upon soil H2O-wetting, are measured by the fluorescence of 2-OH-TPA (at ex/em 310/420 nm), the product of •OH specific reaction with its non-fluorescent trap terephthalate (TPA).