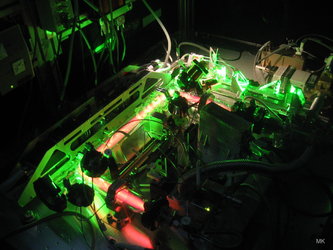
Cold atom interferometry experiment
Emerging cold atom technologies are showing real potential for improving the way measurements are made from space – particularly for measuring non-gravitational accelerations and gravity gradients. This involves using lasers to freeze the atoms within the instrument to near absolute zero, which is −273.15 °C. The lasers are then switched off so that the atoms are free to move in response to the strength of the gravity field. Measuring the phase difference through interferometry as the atoms ‘fall’ according to the pull of gravity will provide an absolute measurement of the variations of the gravity field as the satellite orbits around Earth.
The image shows an experiment where six laser beams cool and trap atoms before sending the cold atom cloud into the atom interferometer. The laser beam then shines the atoms to measure the gravity field they have experimented.
Read full story: Taking climate monitoring into the future with quantum