Agency
Laser grating setup for atom trapping
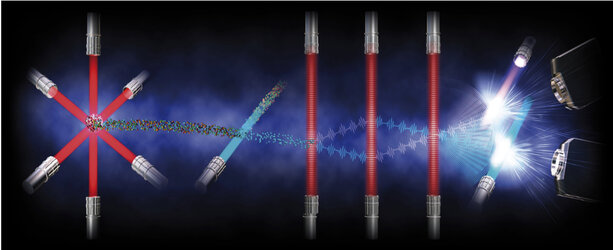
Artist’s impression of the setup. The incoming and diffracted beams (red) overlap in the blue volume. The atoms are cooled and collected in a small dense cloud (small blue dots).
A two-dimensional grating is realised by a regular array of raised circles. The period of this is 1080 nm resulting in a diffraction angle of 46°. A single input beam perpendicular to the surface results in four diffracted beams overlapping in the blue translucent volume. In this region the thermal atoms are slowed to an almost complete halt by the light. With the addition also of a magnetic quadrupole field the atoms collect in a small dense cloud in the centre.