Experiments airborne for 49th ESA Parabolic Flight Campaign
ESA's 49th Parabolic Flight Campaign took to the skies today with the first of three flights over the Bay of Biscay. On board the Airbus A300 Zero-G aircraft is a suite of 14 microgravity experiments.
Microgravity research takes many forms. The most spectacular and high profile experiments take place on board the International Space Station (ISS), but ESA has access to a number of other facilities. One of these is a modified Airbus A-300 aircraft that provides frequent, repeated periods of weightlessness during each three hour flight.
European scientists and engineers have taken advantage of this opportunity for many years, and this week sees the launch of ESA’s 49th Parabolic Flight Campaign. During preparations last week, nine physical sciences experiments, four life sciences experiments and one technology test were loaded into the Airbus in Bordeaux, France.
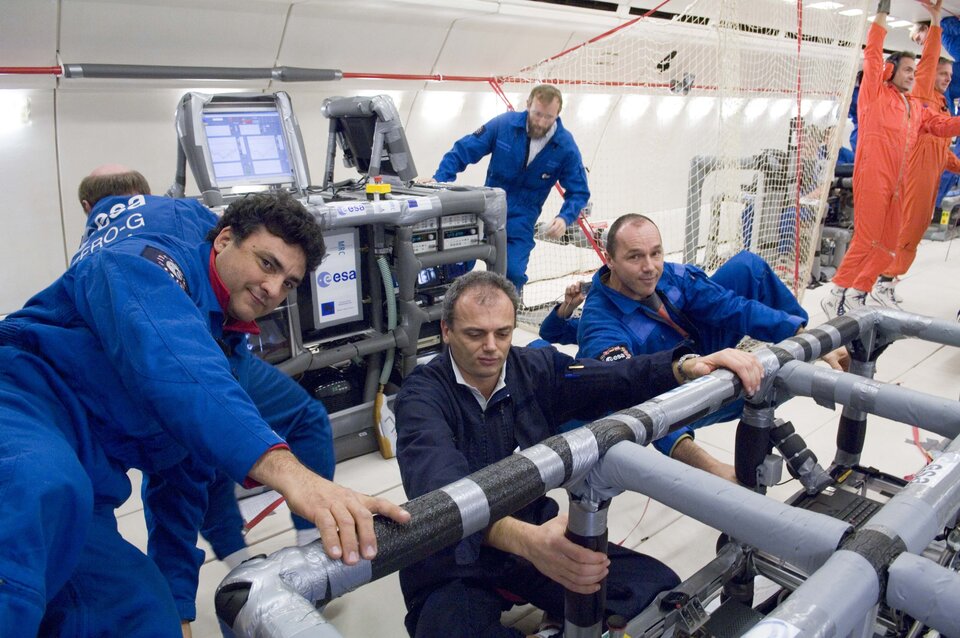

For three consecutive days, the Airbus is scheduled to take off from Bordeaux-Mérignac airport and head out over the Bay of Biscay – weather permitting. Once the first 'warm up' ascent and descent is completed, the experimental programme will begin. Over the next three hours, the aircraft and its occupants will experience 30 parabolas, each providing about 20 seconds of microgravity.
The experiments flying on the 49th campaign include life science research looking at body height as a determinant of blood pressure responses to changes in gravity. This experiment will also test a tool which is set for use on the ISS - the Portable Pulmonary Function System - a miniature portable device for astronauts to perform pulmonary function measurements.
In a further test of equipment destined for the ISS, the PK-4 plasma crystal experiment is also being flown on board the Zero-G aircraft. The continuation of an experiment already on the Space Station, the results of PK-4 will be of fundamental interest for the understanding of complex plasmas, but also for the physics of condensed matter (crystallisation) and fluid dynamics. Further applications might be in the field of semiconductor production and astrophysics (planetary formation).
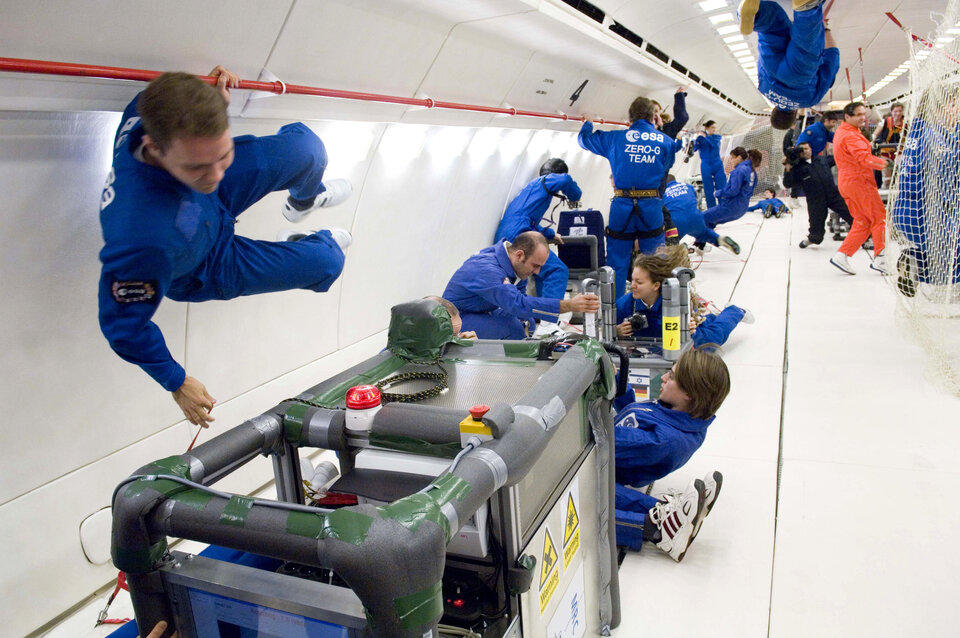

Other experiments include investigations into heat transfer, foam stability, gravity induced neurological changes in the human brain and plant biology, as well as a technology test of a 3-D camera which is also set for flight to the ISS.
French company Novespace owns and operates the A300 Zero-G aircraft, and is in charge of the preparation of the flight campaigns. ESA sponsors the flight opportunity.
ESA has a permanent announcement of opportunity open for researchers wanting to take advantage of the agency’s parabolic flight campaigns. Applications may be put forward at any time. The proposals undergo a peer review by experts from outside ESA and are selected on scientific merit.
The next ESA Parabolic Flight Campaign is scheduled to take place in May 2009.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland




























