ESA astronauts help map Europe’s light pollution from space
In brief
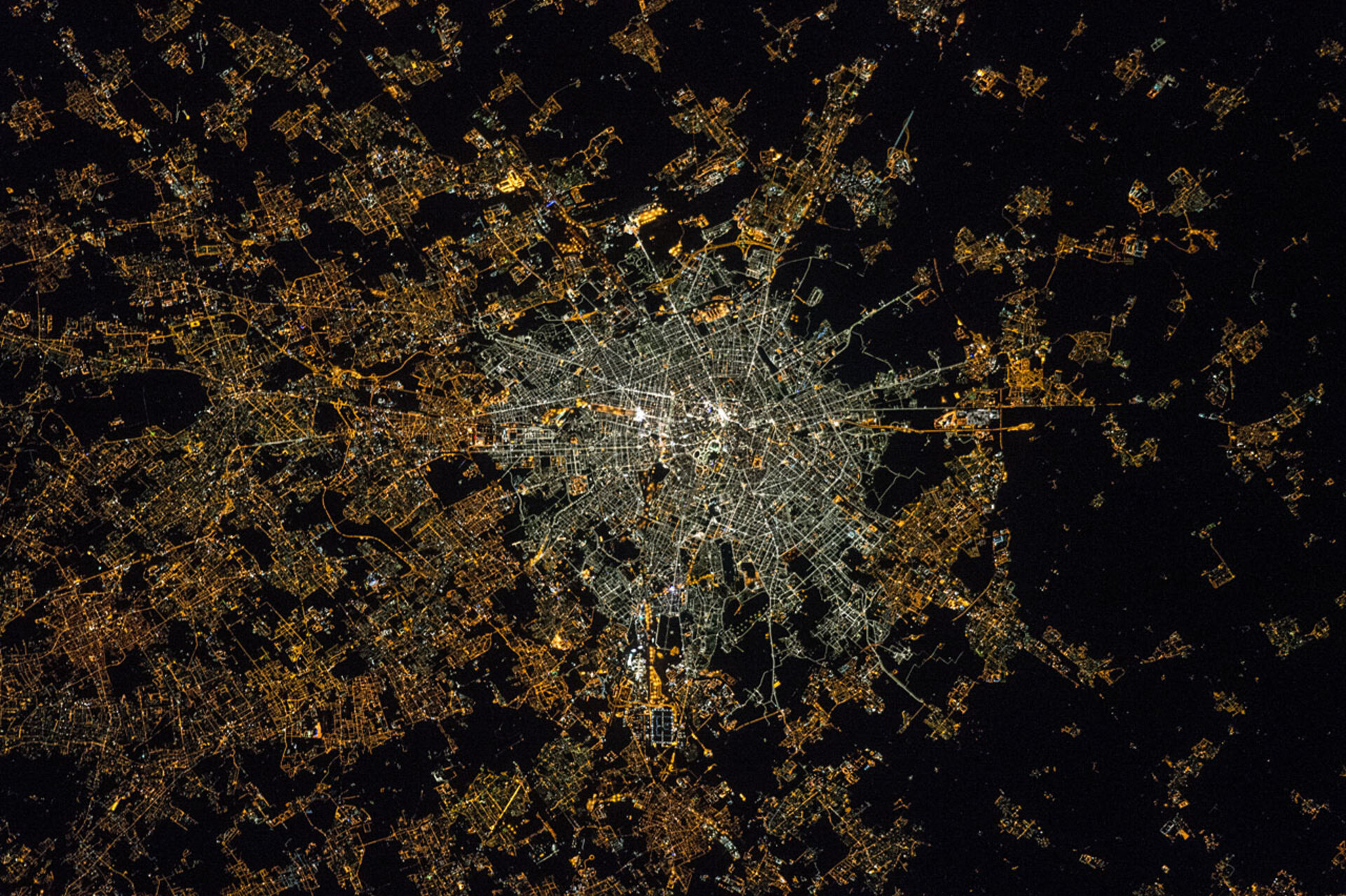
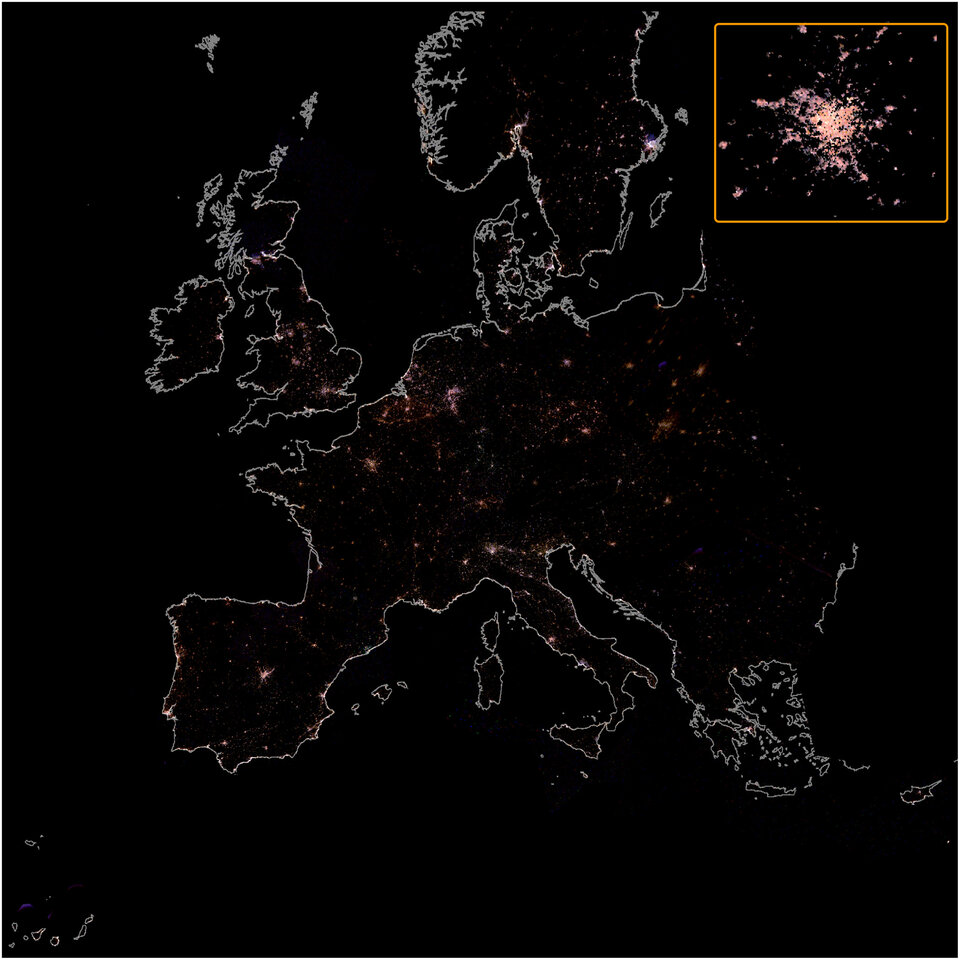
Most Europeans live under light-polluted skies. The first colour map of Europe at night created with images from the International Space Station shows a sharp increase in light pollution, and the resulting picture is not a pretty one for the environment.
In-depth
Over the last two decades, astronauts on the Station have witnessed how cities shine whiter at night as new street lighting technologies were introduced.
When ESA astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti gazed at Earth from orbit during her recent Minerva mission, cities glowed brighter than the stars. Since 2003, Samantha and other European astronauts have taken over a million pictures of Earth at night with digital cameras to demonstrate the true extent of light pollution.
A team of European researchers processed the pictures and compared them over time, showing a clear increase of lighting pollution in urban areas, and a shift towards whiter and bluer emissions. This is due to the widespread introduction of light-emitting diode lamps, or LED technology.
“As seen from space, the resulting image looks like a cancer scan or a fluorescent spider’s web that keeps growing,” says Alejandro Sánchez de Miguel, research fellow at the UK’s University of Exeter. Their recent paper highlights how invasive night lights are and their negative effects for the environment.
As Europe turns lights down in an urge to save energy, scientists warn that it should not only be about reducing bills – brighter nights are disrupting the night cycle for humans, animals and plants.
Astronauts’ contribution
Colour pictures taken from the International Space Station are the best source for scientists to map artificial light at night. Current satellite images are not fit for purpose because their colour sensitivity does not show low wavelength emissions with enough quality.
“Without the images taken by the astronauts, we would be driving blind into the environmental impact of the LED transition,” says Alejandro. “Astronaut photos have always been – and will always be – the baseline for nighttime Earth observations,” he adds.
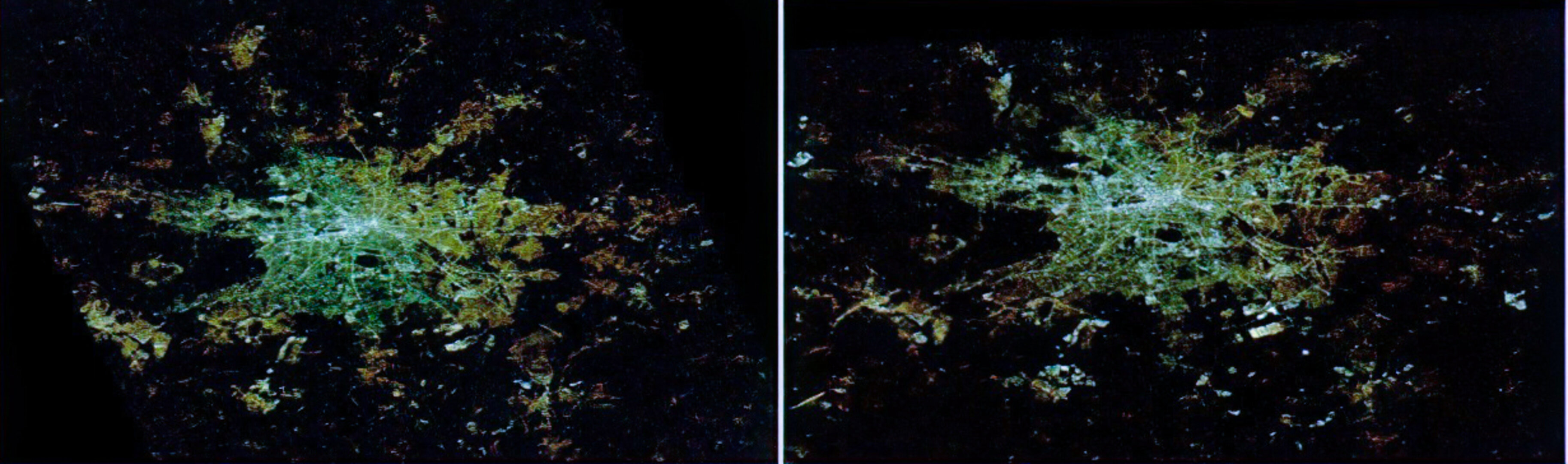
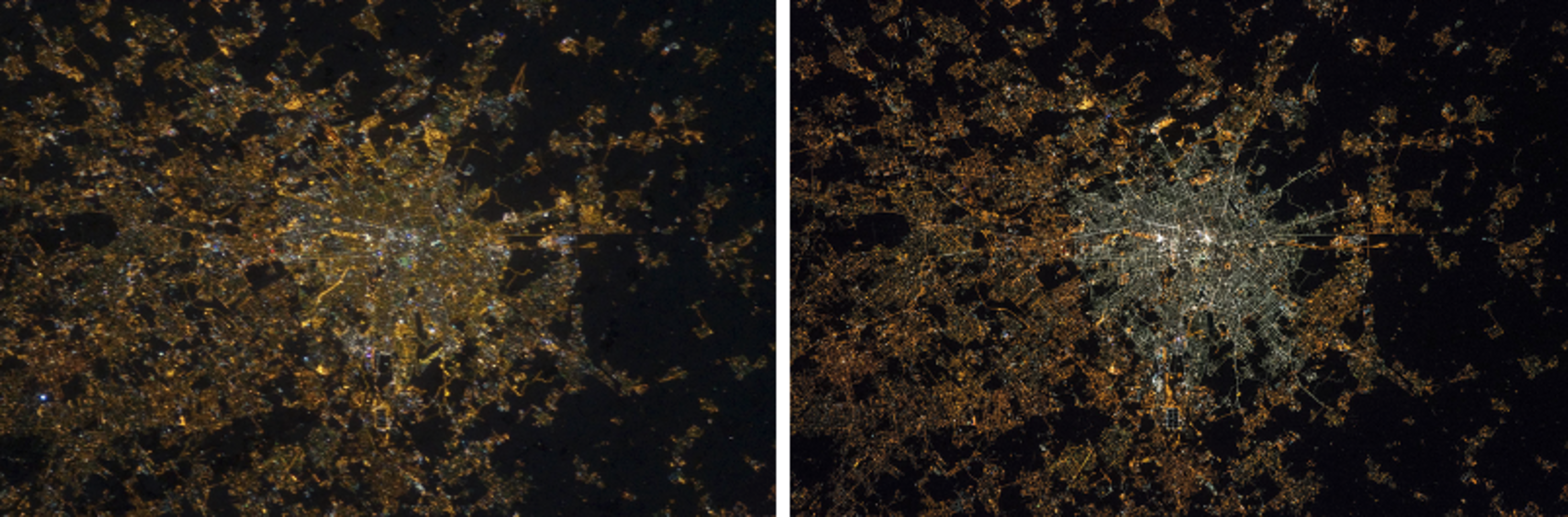
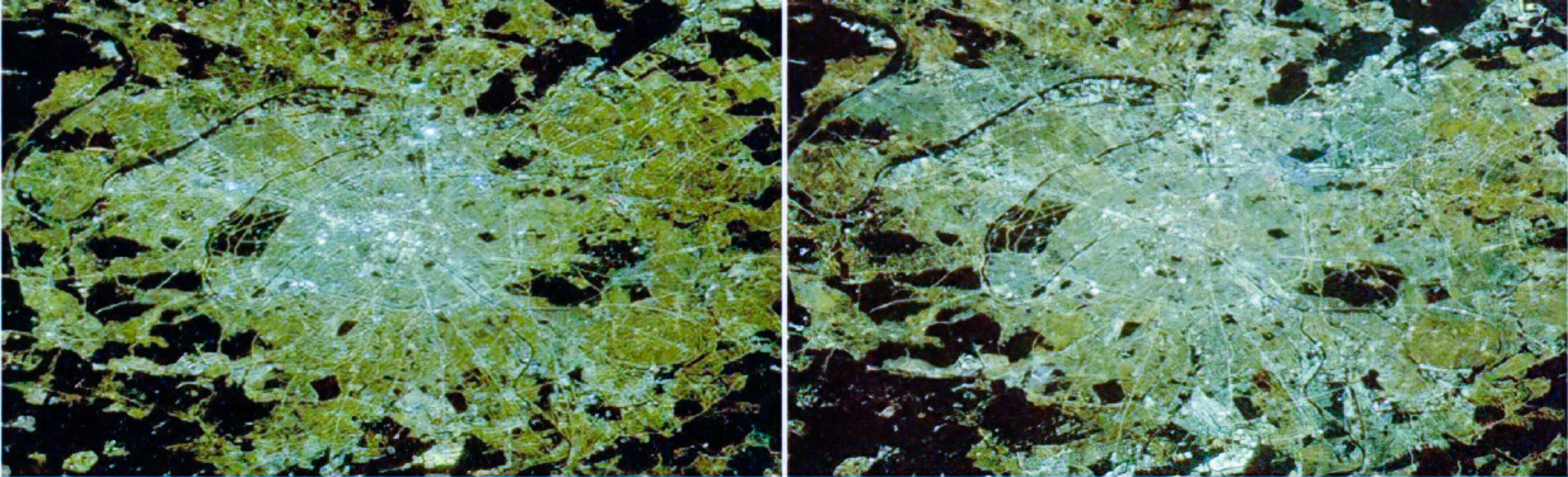
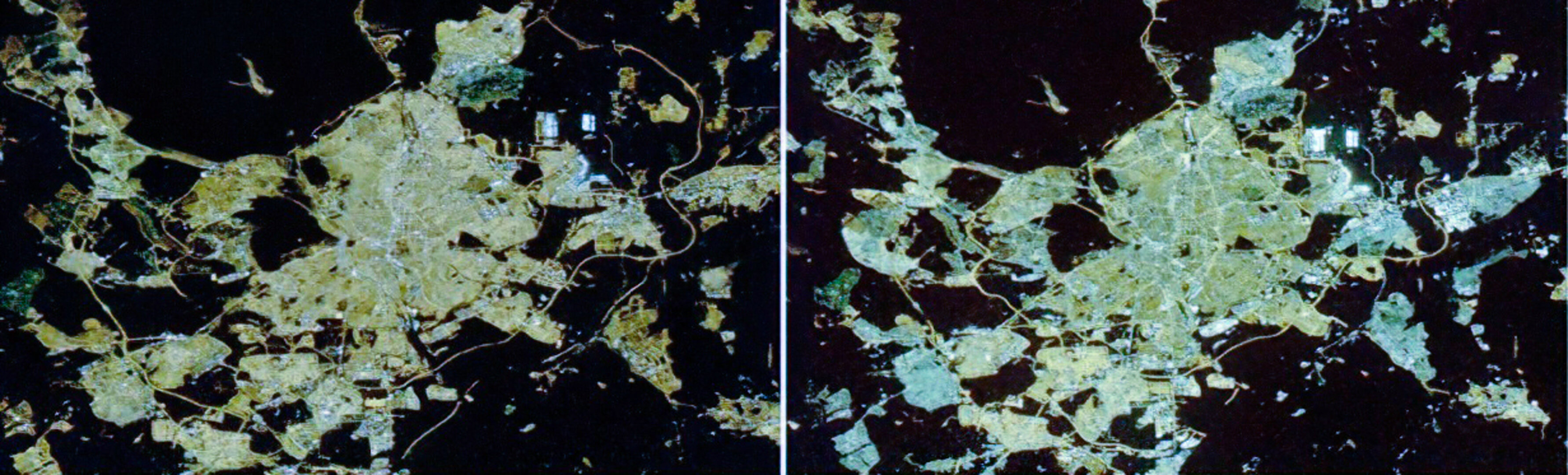
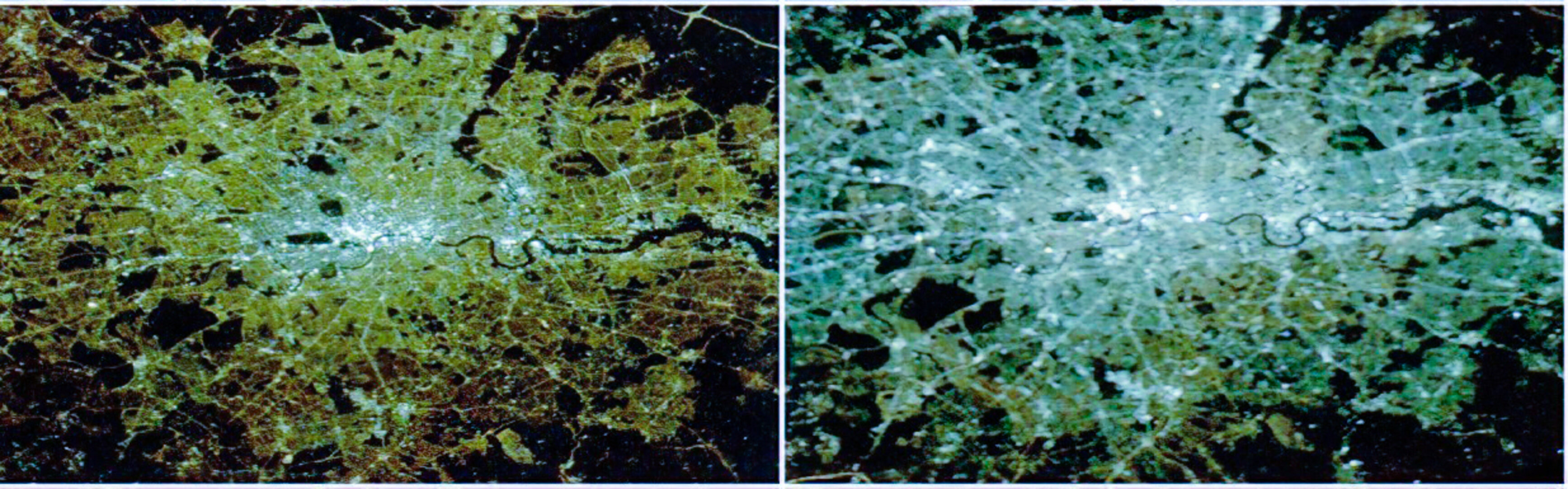
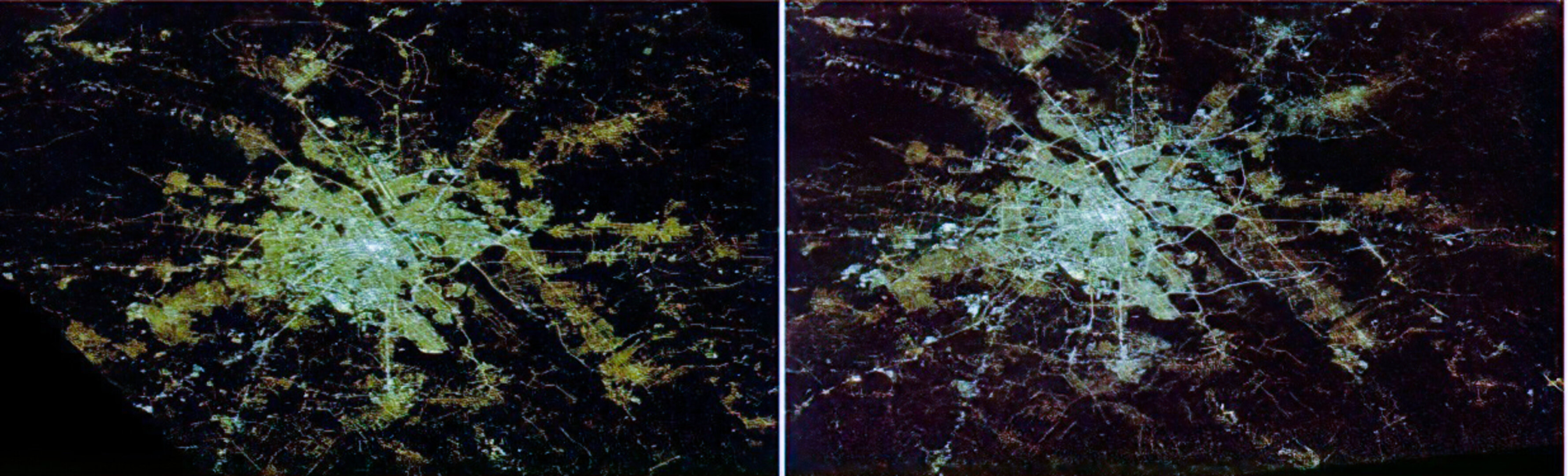
The composite nighttime colour maps created before and after the spread of LED streetlight technology show a pronounced whitening of artificial light.
The changes vary per country, and reflect different systems and policies when it comes to light the streets. Whereas there has been a marked increase in light pollution in Italy and the United Kingdom, countries like Germany and Austria show a less dramatic change in spectral emissions.
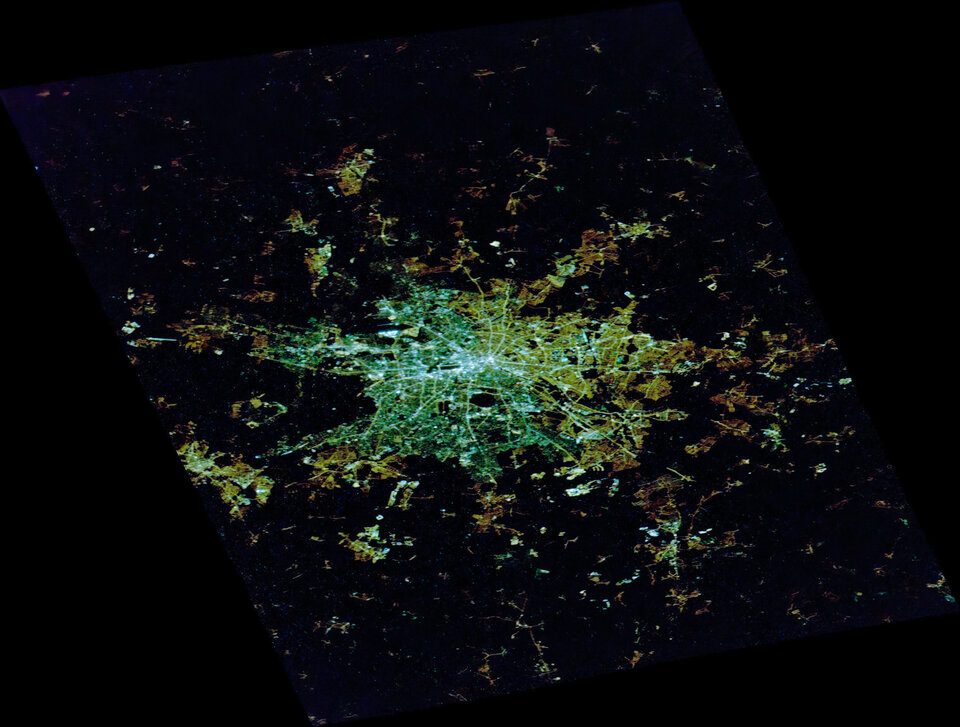

Milan was the first city in Europe to do a total conversion of its street lighting to white LEDs, and more than half of all the public street lighting in the UK was converted by early 2019.
Germany’s glow is whitening, and the country has a lot of fluorescent and mercury vapour lights still in use.
“By the end of this decade, all Europe could look white from space,” says Alejandro.
On the warmer side of the spectrum, Belgium shines in deep orange due to the widespread use of low-pressure sodium lights. High-pressure sodium lights make the Netherlands emit a golden glow.
In a bad light
According to the scientists, the transition towards white and blue-rich light radiation is eroding the natural nighttime cycles across the continent.It disturbs the circadian day-and-night rhythm of living organisms, including humans, with negative health effects on species and whole ecosystems.
The study focuses on three major negative impacts: the suppression of melatonin, the phototaxic response of insects and bats, and the visibility of stars in the night sky.
“When we turn the streetlights on, we deprive our body of the hormone melatonin and disrupt our natural sleep pattern,” explains Alejandro.
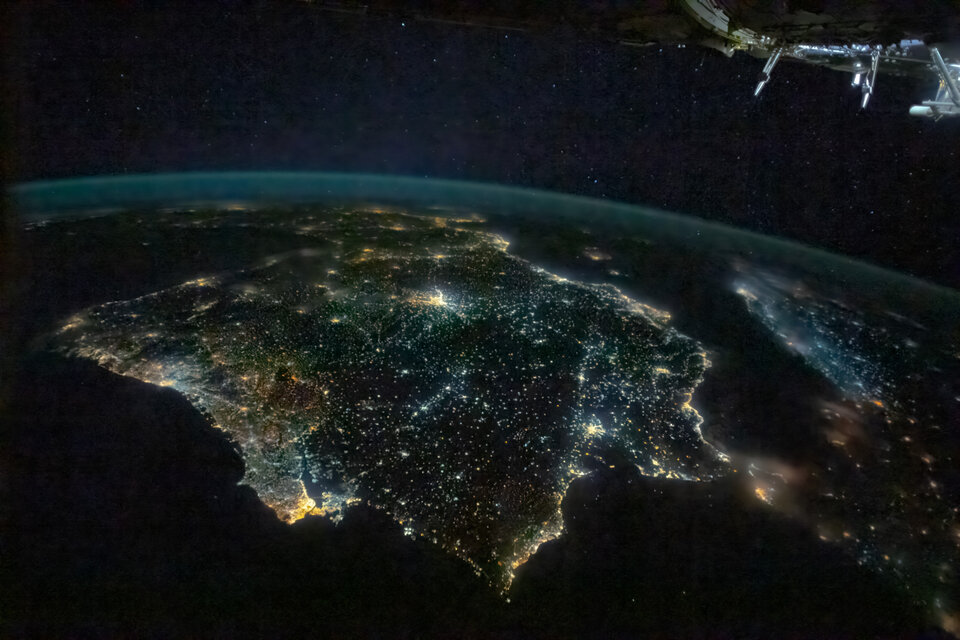

Most insects and nocturnal animals are extremely sensitive to light. Not only moths, but almost all the bat species that bread in Europe live in regions where the spectral composition of nighttime lighting has become whiter. Scientists claim that this has a direct impact in their ability to move and react to a light source, also called phototaxic response.
Along with other animals, humans have long used the stars for navigation. In modern times, a worsening in the visibility of stars goes beyond geolocation and astronomical observations. Scientists are concerned that not seeing the night sky may have negative impacts on people’s sense of ‘nature’ and their place in the universe.
The lighting paradox
While the LED lighting revolution promised to reduce energy consumption and improve human vision at night – and with it, a sense of safety –, the study shows that overall emissions have increased. Paradoxically, the cheaper and better the lighting, the higher is society’s addiction to light.
The paper speculates with the existence of a ‘rebound effect’ in outdoor lighting, where power efficiency and associated cost reduction increases the demand for lighting and diminishes any efficiency gains.
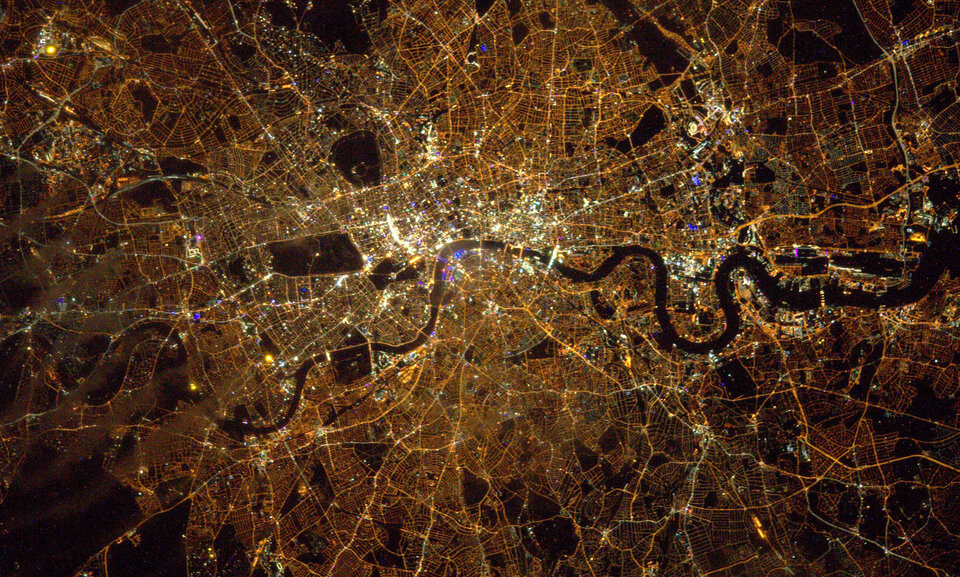

Urban nights in Europe are growing a little darker though. Pushed by a looming energy crisis, wasted light is financially more painful. Several European cities are switching off the lights – from Madrid to Paris and via Berlin, hundreds of monuments and public buildings are no longer illuminated at night.
These initiatives are all part of efforts to reduce energy consumption by 15 percent, following plans laid out by the European Commission last month. The objective is two-fold: to foster a resilient and more autonomous economy ahead of the winter, and to responsibly reduce carbon emissions.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland